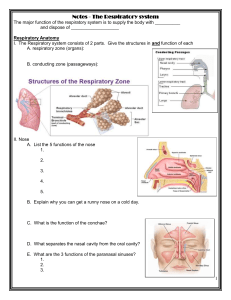
lecture 4 - INAYA Medical College
advertisement

Foundation year OBJECTIVES Are to: 1. Explain the functions of the respiratory system. 2. Label a diagram of the respiratory system. 3. Identify and use the roots pertaining to the respiratory system. 4. Describe the major disorders of the respiratory system. 5. Interpret abbreviations used in referring to the respiratory system. 6. Define medical terms used in reference to the respiratory system. 7. Analyze case studies pertaining to diseases that affect respiration. 1. Lung (n) one of two organs of respiration in the body into which air is sucked when a person breathes. The combining form pneumon/o means the lungs and air. Pulm/o and pulmon/o are additional combining forms which means lung. Pulmonary – adj. 2. Pneumonia (n) (new-moh-nia) lung inflammation caused by bacterial or viral infection, in which the air sacs fill with pus and may become solid. Inflammation may affect both lungs 3. Pneumothorax (n) the presence of air or gas in the cavity between the lungs and the chest wall, causing collapse of the lung. 4. Bronchus (n) air passage leading from the trachea into the lungs. Bronchial – adj. bronchi – plural. 5. Bronchitis (n) (brong-ky-tis) inflammation of the mucous membrane in the bronchial tubes. It typically causes bronchospasm and coughing. .The combining form bronch/o means bronchus. 6. Bronchiectasis (n) (bronk-i-ekta-sis) abnormal widening of the bronchi or their branches, causing a risk of infection. . The suffix –ectasis means dilatation or stretching. 7. Bronchodilator (n) a drug which expands the opening of the passage into the lung. The opposite is bronchoconstrictor. 8. Trachea (n) (tray-kia) means the main air passage which runs from the larynx to the bronchi, also known as the wind pipe. Tracheal – adj. trache/o – combining form. 9. Tracheostomy (n): a surgical operation to make a hole through the throat into the wind pipe to allow the patient to breath. 10. Larynx (n) the hollow muscular organ forming an air passage to the lungs and holding the vocal cords in humans and other mammals; the voice box Laryngeal – adj. laryngitis – noun (inflammation of the larynx). 11. Laryngoscopy (n) means visual examination of the larynx. 12. Nose (n) an organ through which a person breathes and smells. The combining forms rhin/o and nas/o both mean nose. Nasal- adj. 13. Rhinoplasty (n) means surgical repair of the nose. 14. rhinitis: (n)inflammation of the mucus membrane in the nose. 15.rhinorrhea (n): watery discharge from the nose. The suffix -rrhea means flow or discharge. 16. Diaphragm (n) ( dy-a-fram) means the muscle separating the chest and abdomen. The combining form phren/o means diaphragm Diaphragmatic – adj. 17. Sinus (n) (sy-nus) means a cavity inside the body including cavities inside the head behind cheekbone, forehead and nose. The combining form sinus/o means sinus or cavity. 18. sinusitis (n) (sy-nus-I-tis) inflammation of the sinuses. 19. Thoracic (adj) means pertaining to the thorax. The combining forms thorac/o , steth/o and pect/o all mean chest 20. Thoracocentesis is a procedure to remove excess fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This space is called the pleural space.. 21. Costal (adj) (kost’l) referring to the ribs. 22. Stethoscope(n): means an instrument with two earpieces used for listening to the chest sounds. 23. Anoxia (n) (an-oks-ia) lack of oxygen in body tissue. The combining forms ox/o, ox/i and ox/y all mean oxygen. 24. Hypopnea (n) (hy-poh-nee-a) means abnormal decrease in the rate of breathing. 25. Apnea (n) (ap-nee-a) means the absence of spontaneous breathing or respiration. The prefix ameans without. The suffix –pnoea means breathing. 26. Asthma (n) (ass-ma) means narrowing of the bronchial tubes, where the muscle go to spasm and the patient has difficulty in breathing. Asthmatic – adj. 27. Cyanosis (n) (sy-a-noh-sis) means bluish discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes. Caused by a lack of a adequate oxygen. Cyan/o means blue. Cyanosed – verb. Cyanotic – adj. 28. Dysphonia (n) (dis-foh-nia) means any voice impairment. The combining form phon /o means voice or sound. 29. Emphysema (n) means air in the tissues. 30. Haemothorax (n) means accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity. The combining form haem/o means blood. The root word thorax means chest. 31. to respire (v) means breath deeply. respiration – noun respiratory – adj 32. to intubate (v)means to insert a tube into any organ or part of the body. Intubation – noun. 33. Aspiration (n) (ass-per-ay-shon) means: (i) Removing fluids from a cavity in the body. (ii) inhaling foreign materials e.g. vomited stomach contents into the lung. Aspirate – verb. Aspirator – noun ( the instrument that suck fluid out of a cavity) 34. Oedema (n) (ee-de-ma) an excessive accumulation of liquid in body tissues. 35. Spirometer (n) an instrument for measuring the volume of air taken in and out of the lungs. • 36. sputum (n) (spew-tum) mucus found in an inflamed nose, throat or lung and coughed up by the patient, also known as phlegm • 37. septum (n) means a wall between two parts of an organ. The combining form is sept/o. Septal – adj.