Truth Propaganda Election_8
advertisement

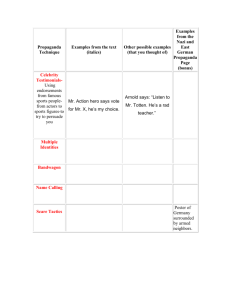
ELA UNIT PLANNING UNIT: Truth, Propaganda, and the Election TIME FRAME: _3 weeks TEACHER/GR:_8th grade Team Unit Summary and Rationale:(Outlines the components of the unit and the reasoning for their inclusion): This unit will focus on the upcoming presidential elections and other topics where the information and sources might be biased. By the end of the unit, students will be able to evaluate sources and make informed decisions. These skills will be invaluable through life since we need to sort through information we come into contact with every day on the news, internet, books, and in conversation UnitConnectionCollege and Career Ready Descriptions: Teachers will select at least one of the following lenses to act as the overlay for the unit. These are the descriptors that must be included to ensure the unit is fully aligned to the CCSS and relevant to the college and career ready student. Students will demonstrate independence. Students will value evidence. Students will build strong content knowledge. Students will respond to the varying demands of audience, task, and discipline. Students will critique as well as comprehend. Students will use technology and digital media strategically and capably. Students will develop an understanding of other perspectives and cultures. Unit Standards: Teachers should list the standards to be addressed within the unit. March 14, 2012 Reading Literature ___ Informational Text___ Writing RI.8.4. Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings; analyze the impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone, including analogies or allusions to other texts. RI.8.7. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using different mediums (e.g., print or digital text, video, multimedia) to present a particular topic or idea. RI.8.8. Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, assessing whether the reasoning is sound and the evidence is relevant and sufficient; recognize when irrelevant evidence is introduced. Rubric & Political ads RI.8.9. Analyze a case in which two or more texts provide conflicting information on the same topic and identify where the texts disagree on matters of fact or March 14, 2012 W.8.1. Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. o ◦ Support claim(s) with logical reasoning and relevant evidence, using accurate, credible sources and demonstrating an understanding of the topic or text. o ◦ Use words, phrases, and clauses to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. o ◦ Establish and maintain a formal style. o ◦ Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented. . Speaking and Listening SL.8.2. Analyze the purpose of information presented in diverse media and formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) and evaluate the motives (e.g., social, commercial, political) behind its presentation. SL.8.3. Delineate a speaker’s argument and specific claims, evaluating the soundness of the reasoning and relevance and sufficiency of the evidence and identifying when irrelevant evidence is introduced. Language L.8.5. Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings. o Interpret figures of speech (e.g. verbal irony, puns) in context. o Use the relationship between particular words to better understand each of the words. o Distinguish among the connotations (associations) of words with similar denotations (definitions) (e.g., bullheaded, willful, firm, persistent, resolute). interpretationPolitical ads March 14, 2012 W.8.2. Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. o ◦ Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information into broader categories; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. o ◦ Develop the topic with relevant, wellchosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples. o ◦ Use appropriate and varied transitions to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. o ◦ Use precise language and domainspecific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic. o ◦ Establish and maintain a formal style. o ◦ Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented. o ⁃ Introduce claim(s), acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence March 14, 2012 logically. W.8.6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and present the relationships between information and ideas efficiently as well as to interact and collaborate with others Essential Questions: Essential questions center around major issues, problems, concerns, interests, or themes relevant to the classroom. Essential questions should lead students to discover the big ideas. They need to go beyond who, what and where. They need to lead to the how and why. Why is it important to know who wrote or created the source? How do we determine whether a source is trustworthy or not? How can the truth be distorted or skewed? What are the reasons truth is skewed? Is it ethical to skew the truth? Is it inevitable to skew the truth? Where and when do we need to consider the author or creator of a work? Big Ideas: These are what students will discover as a result of instruction and learning activities. They are the main ideas of the learning, the conclusions, or the generalizations. Big Ideas should be open-ended and apply to more than one area of study. •Students will learn to evaluate sources and biases in various media sources. Learning Targets: What should students be able to do by the end of the lesson? Students should be able to correctly produce a piece of propaganda using the studied propaganda techniques. Students should be able to evaluate propaganda techniques that they come across in various media forms. March 14, 2012 Learning Tasks: Teachers list the various tasks students will engage in throughout the unit, include use of media/other forms of information. Reading Tasks “How Propaganda Works” “Propaganda Techniques” “War Propaganda” Writing Tasks Create propaganda script to sell a business or product Propaganda techniques used in literature graphic organizer Discussion Tasks Analyze and discuss examples of media propaganda. Identify types of propaganda techniques used . Language/Vocabulary Tasks Frayer Model Turn and talk Assessments: List types of assessments that will be used throughout the course of the unit. *If you do not have assessments for this unit, they should be created before moving on to the lesson design* DIAGNOSTIC FORMATIVE SUMMATIVE Students will watch a short Mac commercial. Answering questions that require students to Group script and commercial using They will be asked to analyze how the Mac dig into the text. propaganda techniques and tier-2, 3 character and the PC character were portrayed Frayer model vocabulary. and why. Turn and talk Followed by a peer assessment with rubric for Discussions of propaganda in the media the group commercials. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v8UxyJewd Propaganda techniques used in a graphic 3Q&feature=related&safety_mode=true organizer &persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active March 14, 2012 Text(s) Selections/Resources(generated by both teacher and student) Teachers will list the genres/titles/resources for study and indicate text complexity: Sampling of commercials using propaganda (Caution: The lexile average is around 1320L. Teachers will need to adjust accordingly): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=llZ6k4gfrCw&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Include presidential campaign ads in order to identify the techniques in a meaningful and relevant way. Notes ( include accommodations/grouping/modifications): For the commercial project: EC/ESL students could create poster scripts AIG students could use more vocabulary words or incorporate more techniques Team size could be changed A review of techniques with examples on Youtube: Testimonial : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Od3Y8_A1qpk&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Glittering Generalities: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Od3Y8_A1qpk&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Plain Folk: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kpu2nnjGYYU&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Band Wagon: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MEnJiOrWiUg&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Name Calling: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W5lsyeJOPr0&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Transfer: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCayrGzv75Y&feature=relmfu&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active Card Stacking: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCayrGzv75Y&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1&safe=active March 14, 2012