Chapter 6
advertisement

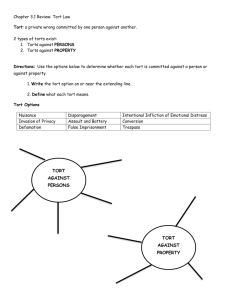
TORT Means “Wrong” 2 TORT A violation of a duty imposed by civil law. 3 CLASSIFICATIONS OF LAW CRIMINAL LAW OUTLAWED BEHAVIOR GOVERNMENT GUILTY OR INNOCENT FINE OR IMPRISONED CIVIL LAW RIGHTS AND DUTIES VICTIMS LIABLE OR NOT COMPENSATE 4 TORT vs. CRIMINAL OR CONTRACT LAW Criminal Law Contract Law Tort Law 5 TORT NORMALLY IS A CIVIL VIOLATION HOWEVER, CAN BE BOTH CIVIL AND CRIMINAL 6 CATEGORIES OF TORT LAW Intentional Torts Negligence Strict Liability 7 INTENTIONAL TORT DEFAMATION Defamation is irresponsible speech to harm another’s reputation. Two Types: libel slander 8 ELEMENTS There are four facts to prove to win a defamation suit: – The defamatory statement was actually made. – The statement is false. – The statement was communicated to someone other than the plaintiff. – Some injury that resulted from the defamation. 9 DEFAMATION (cont’d) Slander per se Some statements are so harsh and potentially damaging that the plaintiff is assumed to be damaged and does not have to prove injury. 10 SOME EXCEPTIONS OPINION TRUTH IS ALWAYS A DEFENSE! 11 OTHER RULES Public Personality Privilege –Absolute –Qualified 12 INTENTIONAL TORT - FALSE IMPRISONMENT False imprisonment is the restraint of someone against their will and without reasonable cause. 13 INTENTIONAL INFLICTION OF EMOTIONAL DISTRESS Historically, no recovery was allowed if the injury was only emotional instead of physical. 14 -ASSAULT AND BATTERY Assault Battery 15 TRESPASS Trespass is intentionally entering land that belongs to someone else or remaining after being asked to leave. 16 CONVERSION Conversion is taking or using someone’s property without consent (civil law version of theft). 17 FRAUD Fraud is injuring another person by deliberate deception. 18 DAMAGES Compensatory Punitive 19 BUSINESS TORTS Intentional torts that occur almost exclusively in a business setting are called business torts. 20 INTERFERENCE WITH BUSINESS RELATIONS Interference with a contract exists if the plaintiff can prove these elements: – Contract between parties and defendant knew – The defendant induced the third party to breach the contract or make performance impossible. – There was injury to the plaintiff. 21 INTERFERENCE WITH BUSINESS RELATIONS Interference with prospective advantage exists: – when there is a relationship which gives the plaintiff a reasonable expectation of economic advantage, even though no contract exists – when the defendant maliciously interferes and prevents the relationship from developing 22 PRIVACY AND PUBLICITY Intrusion Disclosure of Embarrassing Private Facts False Light Commercial Exploitation 23 THE LANHAM ACT This statute prohibits -- and provides punishment for -false statements made by a business intended to hurt another business. 24