Human Reproduction
advertisement
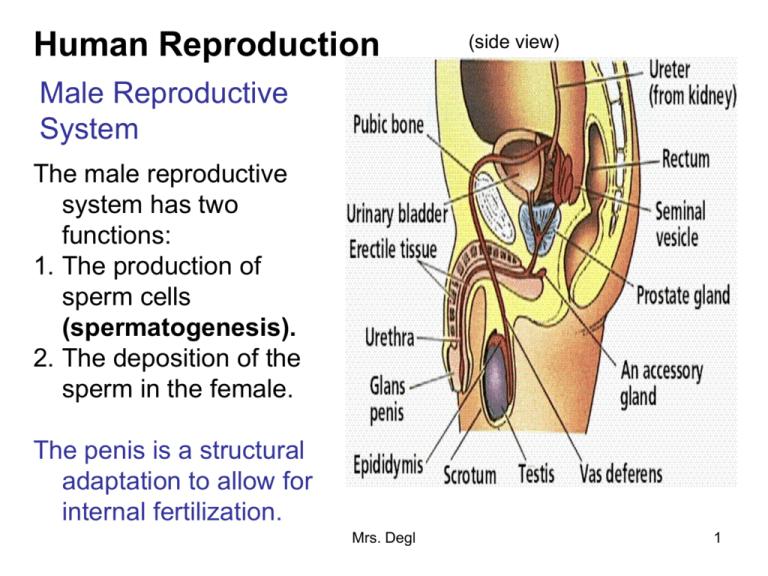
Human Reproduction (side view) Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system has two functions: 1. The production of sperm cells (spermatogenesis). 2. The deposition of the sperm in the female. The penis is a structural adaptation to allow for internal fertilization. Mrs. Degl 1 •Testes – Sperm production occurs here. The testes are located in the scrotum, where the temperature is 1-2 degrees cooler than the rest of the body. The testes also produce the male sex hormone “testosterone”. Testosterone is responsible for sperm development and the development of physical features. (front view) •Urethra – The sperm move from the testes, through the sperm duct (vas deferens) and the urethra until they exit the body (ejaculation). The urethra is a long tube inside the penis that either sperm or urine flows through before it is released. They cannot flow at the same time. It is either one or the other. •Semen is the combination of sperm and liquid. The liquid is a transport medium for the sperm to travel in. Mrs. Degl A Hermaphrodite is an organism that has both testes and ovaries. 2 Female Reproductive System Ovaries – Ovaries produce eggs (ova) in the cavities called follicles. The process is called oogenesis Ovulation is the release of the egg from the ovary. After ovulation, the egg cell is transported through the oviduct (fallopian tube) to the uterus. The bottom of the uterus is the cervix. The cervix is the opening to the muscular tube called the vagina. The vagina receives sperm from the male and is also called the birth canal during child birth. Mrs. Degl 3 Menstrual Cycle A woman is born with all of her eggs, in the immature form. No more eggs will develop. Usually, only one egg is released at a time, during each ovulation period. In addition to eggs, the ovaries also produce the female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone. These hormones regulate the development of the secondary sex characteristics of a female, as well as play a role in the menstrual cycle. Mrs. Degl 4 The Menstrual Cycle begins at puberty and ends at menopause. Menopause is the permanent cessation of the menstrual cycle. The Menstrual Cycle lasts an average of 28 days, but many women have shorter or longer cycles. Pregnancy, medications, illness, and other factors can interrupt the menstrual cycle. There are 4 stages to the Menstrual Cycle: 1. Follicle Stage – This involves the maturation of an egg in the ovary and the secretion of estrogen. The estrogen causes the thickening of the uterine lining (the blood volume builds up). 2. Ovulation – One egg is released from the follicle in the ovary. 3. Corpus Luteum – The follicle breaks down and forms a yellow mass of cells which secrete progesterone and enhance the thickening of the uterine lining. 4. Menstruation - This is when the uterine lining (blood) is shed and released through the vagina. This lasts for up to a week and happens when egg fertilization does not take place. Mrs. Degl 5 The role of hormones in the Menstrual Cycle During the menstrual cycle, under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland releases certain hormones. FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone – Stimulates follicle growth and the ovary to produce estrogen. LH – Luteinizing Hormone – Stimulates the growth of the corpus luteum (in the ovary) to secrete progesterone, which stops estrogen production. Mrs. Degl 6 Human Fertilization and Development Fertilization usually occurs in the upper part of the oviduct (fallopian tube). If the egg is not fertilized within approximately 24 hours after ovulation (when the egg is released), it deteriorates. If the egg is fertilized it is called a zygote, and Cleavage (the first stage of development) begins in the oviduct. Six to ten days later the egg will be implanted into the lining of the uterus. The Gastrulation stage occurs next, after the egg is implanted in the uterus. The Differentiation and Growth stages result in tissues and organs developing and specializing into an embryo, from the gastrula. At 8 weeks, the embryo becomes a fetus. Mrs. Degl 7 In rare occasions, more than one egg can be released and fertilized. from the ovary. There are also times when one egg was released, but split after fertilization. Identical Twins develop from one egg splits after fertilization in the cleavage stage. Fraternal Twins develop from two eggs that were released at the same time and each fertilized by a different sperm cell. There can also be multiple births of 3 (triplets) to 7 (septuplets) babies at once. Reproductive Technology has increased the amounts of multiple births across the world. There is in-vitro fertilization, artificial insemination, and many prescribed medicines that help with the process of conceiving a baby. Mrs. Degl 8 Artificial Insemination Mrs. Degl 9 An average human pregnancy lasts 40 weeks. This is 9 entire months. The pregnancy is broken up into trimesters, each trimester lasts 3 full months. Mrs. Degl 10 (Refer back to your Fertilization and Development notes for details on this.) Mrs. Degl 11 Prenatal Care Pregnant women must take excellent care of themselves. Most of the fetus’s organs develop before a women is 10 weeks pregnant. Unfortunately, this is before some women even know that they are pregnant. Pregnant women must eat very healthy and avoid the following risks because everything that the mother ingests or breathes, goes to the baby. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (Effects of FAS on children) Tobacco (causes low birth weight) Drugs (causes many deformities) Alcohol (causes Fetal Alcohol Syndrome) Regular household chemicals Radiation Infections Many birth defects are caused by a mothers exposure to harmful environments, but many also occur for no known reason at all. We will discuss birth defects in more detail in the Genetics topic. Mrs. Degl 12 Birth As stated earlier, birth occurs about 40 weeks after conception. Because of modern medicine, some babies can live with assisted technology, after 26 weeks. A pregnancy is said to be full term after 38 weeks. Most babies are very healthy at that point. The birth process involves strong contractions in the women’s uterus. Each contraction pushes the baby down further. This is called labor. The baby will exit the cervix into the vagina (birth canal) until it is outside the mother’s body. After the baby is delivered the placenta must exit as well. In some cases, a baby cannot be delivered vaginally. This could be because of a medical emergency on the part of the baby or the mother. If this is the case, the baby will be born by a cesarean section (c-section). This is a cut through the uterus of the mother which allows for the baby to be pulled out. Mrs. Degl 13 Sexually Transmitted Diseases There are many sexually transmitted diseases that both males and females can get and also transmit. •Some of these diseases may cause infertility •Some can cause death •Some can be treated with medications and will not return •Some can never go away and will reoccur many times throughout a persons life Some examples are: •Chlamydia •Genital Herpes •Gonorrhea •Hepatitis B •HIV/AIDS •Human Papillomavirus (HPV) •Pubic Lice •Syphilis •Trichomoniasis Mrs. Degl 14 What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. How many people have STDs? The United States has the highest rates of STDs in the industrialized world. In the United States alone, an estimated 15.3 million new cases of STDs are reported each year. Women suffer more frequent and more serious complications from STDs than men. How do you get an STD? You can get and pass STDs through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Some STDs cause no symptoms. But STDs can still be passed from person to person even if there are no symptoms. Mrs. Degl 15







