Nervous System Review Sheet answers
advertisement
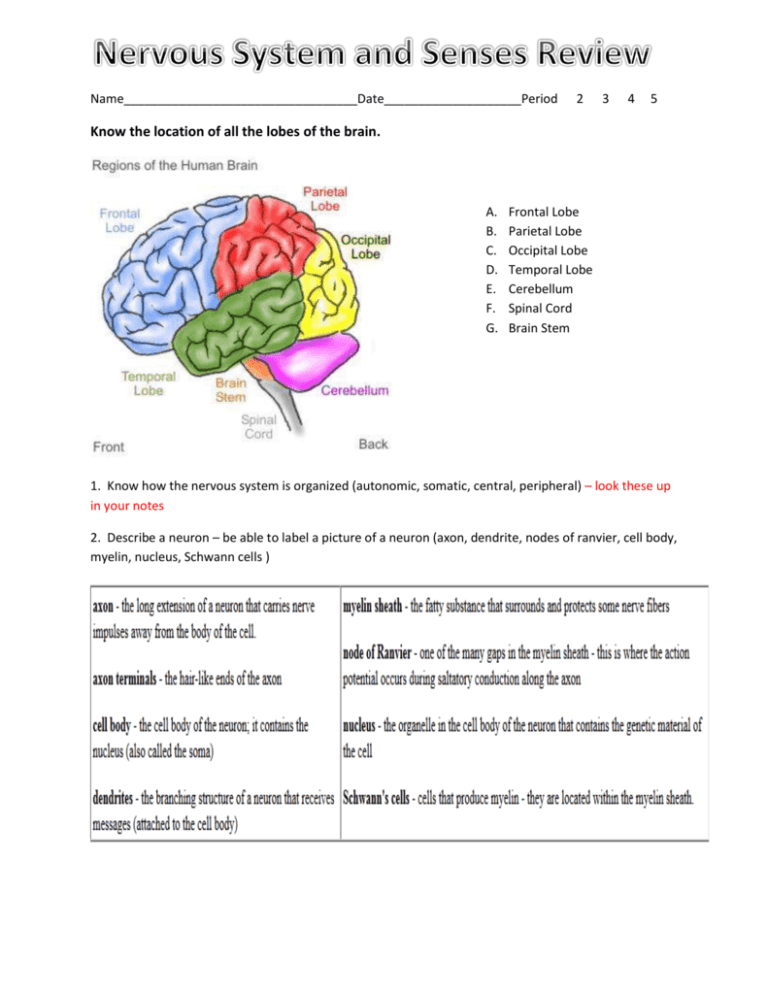
Name__________________________________Date____________________Period 2 3 4 5 Know the location of all the lobes of the brain. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Cerebellum Spinal Cord Brain Stem 1. Know how the nervous system is organized (autonomic, somatic, central, peripheral) – look these up in your notes 2. Describe a neuron – be able to label a picture of a neuron (axon, dendrite, nodes of ranvier, cell body, myelin, nucleus, Schwann cells ) 5. Distinguish between white matter and gray matter in the brain. Gray matter and white matter are components of the brain. One difference between gray and white matter is what they are composed of. Gray matter is made up of nerve cell bodies, while white matter is made up of fibers. Gray matter was given its name because of its appearance. White matter is found between the brain stem and the cerebellum. It allows communication to and from the gray matter areas. Gray matter fills 40% of the brain, while white matter occupies 60%. 6. Describe the events in a nerve impulse. What is an action potential? What ions are necessary? What is a threshold? An action potential can also be called a nerve impulse which is known to be stimulated by an external stimuli or upon internal excitation. This action potential travels through a neuron and involves charged ions (the key ones are sodium ions and potassium ions) that cross the membrane barrier of the neuron. A threshold is the weakest stimulus capable of producing a response; When depolarization at the stimulation site reaches a certain critical level it is called the Threshold. Events of a nerve impulse: (402-406) Resting state, depolarizing phase of the action potential, Repolarizing phase of the action potential and hyperpolarization. 7. What happens at the synapse of neuron? The neurons lie end to end in chains to transmit impulses through the body. Each neuron receives an impulse through its dendrites and passes it on to the next neuron in the chain through its axon. For cell to cell relay of impulse the terminal of the axon of each neuron come very close to the dendrites of the adjacent neuron leaving only a microscopic gap. This end to end position of the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron without actual contact is called the Synapse. At the end of the axon, the impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. These chemicals cross the synapse and start a similar impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. 8. What is a reflex? An automatic involuntary response to a stimulus. Name two reflexes. Moro reflex (in infants only – also known as the startle reflex); gag reflex, startle reflex. 11. What is the difference between a gyri, a sulcus, and a fissure? Gyri- outward fold, sulcusfurrow/inward fold, fissure- a groove or a cleft (longitudinal or transverse) 13. Identify the locations of the large fissures of the brain: lateral, longitudinal, transverse 14. Know the layers of the meninges: Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater Dura mater- outermost layer of the made; made of tough, fibrous CT Arachnoid mater- a fine, delicate membrane, the middle one of the three membranes or meninges that surround the brain and spinal cord, situated between the dura mater and the pia mater. Pia mater – the delicate innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord. 15. What connects the two hemispheres of the brain? Corpus and Colosum 16. Be able to label a brain on an image, also know what each area of the brain is responsible for. 18. Label a picture of the brain/brain stem