Creating Amendments - Baltimore County Public Schools
“Tis impossible to be sure of any thing but
Death and Taxes”.
-Christopher Bullock, The Cobbler of Preston, 1716
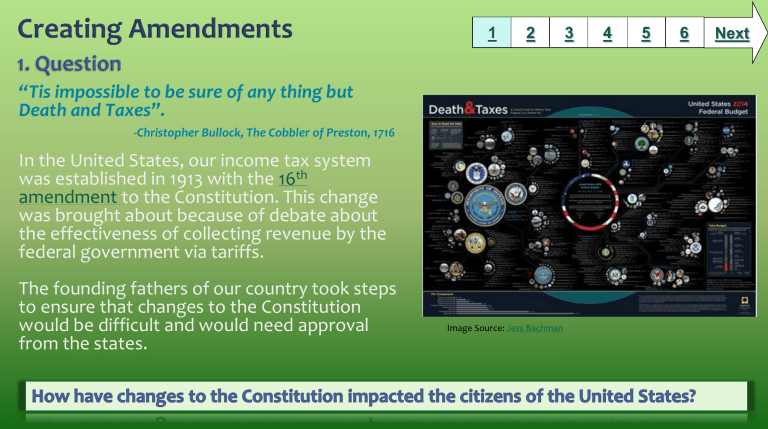
In the United States, our income tax system was established in 1913 with the 16 th amendment to the Constitution. This change was brought about because of debate about the effectiveness of collecting revenue by the federal government via tariffs.
The founding fathers of our country took steps to ensure that changes to the Constitution would be difficult and would need approval from the states.
Image Source: Jess Bachman
The Prohibition movement created the 18 th repealed in 1933 with the 21 st amendment amendment .
in 1919 but was
Using the sources below, describe how Constitutional change impacted
Americans in this case in the early 20 th century.
General Information about the Prohibition Era
Student Resources in Context – Prohibition
People of the Prohibition Era
Unintended Consequences of Prohibition
PBS – Interactive Map and Timeline of Prohibition Nationwide
The Push for National Prohibition
Safari Montage - The Time is Now
The Repeal of the 18 th
Amendment
Safari Montage - The Amber Flood
Clash of Cultures – Prohibition World Book Article – Volstead Act
World Book Article – Prohibition
World Book Article – Eliot Ness
PBS – Roots of Prohibition Image Source: clipart.com
The amendments are
“limited to points which are important in the eyes of many and can be objectionable in those of none. The structure & stamina of Govt. are as little touched as possible.”
Representative James Madison to
Edmund Randolph, June 15, 1789
Using the web 2.0 tool bubbl.us
, create a brainstorming web documenting the
Constitutional actions made by Congress and how those actions impacted Americans.
Click here to get an idea of how to start your brainstorming web.
You can export your web as a picture file in order to submit your notes.
You may also create a brainstorming web using a different technology tool or on paper to document your ideas, as directed by your teacher.
Image Source: clipart.com
Using your prior knowledge about early America, the creation of the government and what you’ve learned about the amendment process, answer ONE of the following essential questions:
1. Was the decision to repeal the 18 th amendment in the best interests of the American people?
OR
2. What if the 18 th amendment had never been repealed? How would this impact Americans today?
Support your argument into the text box below and save this file or use another method as directed by your teacher. Make sure to label which question you answer.
Image Source: clipart.com
Image Source: clipart.com
Just as the 18 th and 21 st Amendments changed Americans’ drinking habits, other amendments have changed how people behave. Many Americans voice opinions on changing laws in our Constitution for many different reasons.
Most recently, the Americans participating in the Occupy Wall Street movement urged to remove big money from politics and change the rights that big corporations have in a court of law. The Move to Amend website is a coalition of organizations that want to influence the government.
Which amendment do YOU think needs to be changed?
Take one of the 27 amendments to the Constitution and identify the parts of the law as well as any groups of people who wish to change the law. Do you agree with the protesters? How would/have people compromised on the issue?
Make your notations on the padlet page created by your teacher.
BCPS Curriculum
Indicator 2: Students will analyze philosophical debates regarding the formation of the Constitution in order to assess the degree to which it reflects compromise. (I-A,B,C)
Objective 6: Describe the methods by which constitutional change may occur.
Maryland State Curriculum
A. The Foundations and Function of Government INDICATOR 1. The student will evaluate how the principles of government assist or impede the functioning of government (1.1.2). E. Describe the formal process for amending the Constitution and why this process is necessary
Common Core State Standards
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.9-10.1
Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, attending to such features as the date and origin of the information.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.9-10.3
Analyze in detail a series of events described in a text; determine whether earlier events caused later ones or simply preceded them.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RH.9-10.9
Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.2
Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.6
Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.7
Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
Standards for the 21 st Century Learner
1.1.6 Read, view, and listen for information presented in any format (e.g. textual, visual, media, digital) in order to make inferences and gather meaning.
2.1.3 Use strategies to draw conclusions from information and apply knowledge to curricular areas, real-world situations, and further investigations.
Maryland Technology Literacy Standards for Students
3.0: Use a variety of technologies for learning and collaboration.
Time Frame: 1 90 minute class period
Differentiation: Each graphic organizer can be created by the
Learning Styles:
AVID Strategies:
Notes to the teacher:
students - does not need to use the provided resources.
Databases have text-to-speech features for some articles.
Field Dependent, Field Independent, Visual, Auditory,
Tactile, Reflective, Global inquiry based learning, Cornell notes
Consult with your School Library Media Specialist to implement this Slam Dunk Lesson.
Students can turn in activities by saving bubbl.us as an image
(export to ‘my documents’) and copying it to your school’s student drive/printing and turning in
Bubbl.us
is a mindmap website that does not require an email for students to create a mindmap – students can save the image as a jpeg.
Students can type their response directly into the white text box on slide 4. Students must save their PP and drop into the drop folder on the student drive.
Teacher needs to create a padlet page for the enrichment activity
Last updated: July 2015
Created by Jamie Higgins Shaull , Department Chair – Social Studies/Library Media Intern
BCPS Slam Dunk Research Model, Copyright 2013, Baltimore County Public Schools, MD, all rights reserved. The models may be used for educational, non-profit school use only.
All other uses, transmissions, and duplications are prohibited unless permission is granted expressly. This lesson is based on Jamie McKenzie’s Slam Dunk Lesson module .