File - Study Guides
advertisement

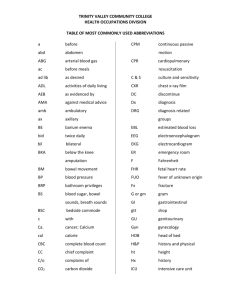
BTEC 222 UNIT 5 STUDY GUIDE HUC & ORDER TRANSCRIPTION BE ABLE TO: 1. Briefly describe the responsibilities of a health unit coordinator. Clerical, Reception/Communication, and Coordination/Organization 2. State where a health unit coordinator works in a hospital. The nursing station 3. State the seven steps of physician order transcription. A. Recognize (that there is a doctor’s order) B. Rip (paper) C. Prioritize (important task) STATS, this AM, Discontinued (ASAP) D. Kardex (to be carried out by the nurse) E. Requisition (what the doctor has ordered) F. Symbols (documenting completion of tasks) G. Nurse check 4. State and be able to recognize the four categories of physician orders. 1. Computer notice 2. Location of chart 3. Flagged physician order divider 4. Color coded chart 5. Describe a “kardex” form and its purpose. NOT IN PATIENT RECORD Kardex is a nursing tool to consolidate record of all patient treatments, medications and tests of each patient. 6. State the purpose of health unit coordinator symbols on the physician orders. To indicate to the nurse that the work (transcription) has been completed. 7. Describe a Medication Administration Record and its purpose. MAR is where medications orders are written onto after a physician orders them to be given. It is used to keep a record of all medications that are given to the patient. 8. Describe a telephone order and a verbal order and how they are documented in the physician orders. T.O. – The nurse writes a T.O. order on the physician’s order sheet. The physician then needs to sign the order when they come into the hospital V.O. – Physician’s order written by the nurse with V.O. after it (means that the doc told them verbally what to do.) 9. Describe a routine order. Physician orders preapproved by the medical staff, which are preprinted and placed on a patient’s record. Include standard admitting orders for a surgical patient discharge orders following surgery. 10. Provide the meaning of the following abbreviations: T.O – telephone order BM – bowel movement c - with I&O – intake & output IV - intravenous Neg. - negative Tx - treatment WC – wheel chair V.O. – verbal order BR or br – bed rest s - without +Hs – before sleep or half strength OT – occupational therapy ROM – range of motion W/A – while awake RECORDING TPRs 1. State the meaning of the abbreviation TPR. Temperature, pulse, respiration 2. Describe what is meant by “daily TPRs”. Take TPR daily according to hospital schedule 3. Describe what measurements are included in a Vital Sign order. Body temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure 4. Describe the TPR sheet and state why it cannot be copied and placed in a patient’s medical record. It cannot be copied onto the patient’s medical record because the nurses use them as worksheets with all the patient’s information on them 5. Describe a graphic record. It is a record of vital signs on a graph. 6. Describe a flow sheet. Columns with flow of daily information on patient – goes into record 7. Describe the proper method(s) to make a correction on a graphic record. Put a squiggle line through the error and then initial and date it. 8. Provide the meaning of the following abbreviations: ASAP – as soon as possible @ - at ht. - height q - daily qh – every hour Temp - temperature BM – bowel movement DC - discontinue Noc – night qAM – every a.m. q2h – every two hours VS – vital signs BP – blood pressure Hs – at bedtime post op – post operative qd – every day q4h – every four hours wt. - weight MEDICATION ORDERS BE ABLE TO: 1. Define antimicrobial drugs. Drugs used to treat a microbial infection. They include antibiotics, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antivirals. 2. Define pharmacodynamic drugs. Drugs that affect the body physically 3. Define chemotherapeutic drugs. Drugs used with specific and toxic effects upon disease-producing organisms. 4. Name the components of a medication order and be able to identify the components. Name of the drug Dosage of the drug Route Frequency Qualifying phrase – used for “headache” and “ad lib” 5. State the three different names given to drugs and state which name is usually capitalized. 1. Chemical name 2. Generic name (lower case) 3. Brand name (capitalized) 6. State the use (or affect) of the following drug categories: Analgesic: used for pain narcotic – drug that has a controlled substance in it non-narcotic – without narcotic incredients Nonsteriodal anti-inflammatories – NSAIDS – reduce inflammation and fever Anesthetic: general – produces loss of sensation & muscle relaxation accompanied by loss of conscienciousness local – loss of sensation or “deadening” in a localized area of the body Antianxieties – used to treat patients with anxiety problems Anticonvulsants – used to suppress convulsions or seizures Antidepressants - medication used to treat patients with various types of depression Antipsychotic – major tranquilizers used to relieve symptoms of psychoses or severe neuroses Hyponotics - used to promote sleep sedatives – used to relax Stimulants – used to stimulate the CNS Insulin – used to aid in the metabolism of sugars in diabetics Corticosteroids – used for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant properties Hormones – used for the replacement of hormones for the prevention of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women Antihistamines – helps to relieve allergic symptoms by countering histamines in the body Antitussives – relieves coughing Bronchodilators – dilates the bronchioles in the lungs, used in the treatment of asthma Expectorants – used to help break up the mucus in the lungs Antacids – used to reduce acidity of gastric secretions Anticholinergics – drug that blocks the action of the parasympathetic nervous system Antidiarrheals – used to reduce the number of loose stools Antiemetics – used to prevent or treat nausea, vomiting, or motion sickness Cathartics – used to promote bowel movements Emetics – used to produce vomiting; syrup of ipecac Antianginals – used to relieve the symptoms of angina pectoris (severe chest pains) Anticoagulants – used to prevent formation of clots or decrease the extension of existing clots Antidysrythmics – misnomer of anti-arrhythmias – used to prevent or alleviate arrhythmias Antihyperlipidemics – used to treat hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol) Antihpertensives – used to treat high blood pressure Cardiotonics – an agent that has a tonic effect on the heart – strengthens the heart Diuretics – increase urine output Thrombolytics – used to dissolve clots after they have formed Vasodilators – used to expands the wall of the blood vessels resulting in increased blood pressure Antiarthritics – used to treat the symptoms of arthritis & other related diseases Muscle relaxants – used to relax muscles from spasms of skeletal muscles 7. Describe the affect of the antimicrobial drug categories. They are drugs that fight fungi, parasites, virus and bacteria 8. Describe what is meant by therapeutic drug monitor. The measurement of specific drugs at intervals in order to maintain a relatively constant concentration of the medication in the bloodstream. 9. Define the abbreviation for the following pharmaceutical preparations: Ampules – amp Spansules - spans Capsules - cap Suppository - supp Elixir – elix Tablets - tab Enteric coating - EC Troches, lozenges – troche Extract - ext Others: drops - gtt Liniment - lin milliequivalent - mEq Liquid - liq teaspoon - tsp Lotion – lot tablespoon - tbsp Ointment - ung unit - U Powder - pul 10. Define metric measures and interpret basic apothecary measures. Metric measure - Based on multiples of 10. This makes it easier to calculate dosages. Apothecary – Current usages but being phased out – more complicated with use of grains, drams & oz 11. Define the routes of administration: Oral – by mouth Sublingual – under the tongue Inhalation - inhaled Topical – applied on the skin Parenteral: intramuscular – given within the muscle subcutaneous – given under the skin intradermal – given into the skin intravenous – given into the vein intravenous piggyback (IVPB) – 2 lines with 2 different solutions @ same time into one IV 12. Describe an intravenous push (IVP or IV-P). Medication that is given by syringe directly into an IV line 13. Define the following routes of administration abbreviations: AD – right ear AS – left ear AU – both ears H - hypodermic IM - intramuscular IV - intravenous IVP – intravenous push OD – left eye OS – right eye OU – both eyes p.o. – by mouth subling - sublingual subqu - subcutaneous 14. Describe a heparin lock. Small tubes attached to a catheter, inserted into the arm and held in place with tape in order to administer drugs and fluids without injecting patients multiple times unnecessarily. 15. Describe a PCA device. Patient controlled analgesic device. Pain medication that is administered by the patient as they feel they need it (only a set amount is allowed per hour) 16. Be able to convert from clock time to European or military time and back. 17. Define the following times of administration abbreviations: qod – every other day qd – every day bid – Two times daily tid – Three times daily qh – every hour q_h – every (however many) hours hs – at bedtime ac – before meals pc – after meals stat – at once, without delay prn – as needed sos – if there is a need, may be repeated once if necessary 18. Describe an “automatic stop” related to a stop order. Some drugs have an automatic stop date (controlled substances, potent drugs) that stop automatically and need to be written again to start again 19. Describe the transcription of a “change order” and a “discontinue order”. Change order – Changing a previous orders frequency, route, or dosage. It is considered a “NEW” order. Discontinue order – Order that discontinues the use of an order 20. State what the numbers assigned to analgesics containing Codeine indicate. #1 – 7.5mg, #2 – 15mg, #3 – 30mg, #4 – 60mg 21. Read and understand medication orders. NURSING PROCEDURE ORDERS BE ABLE TO: 1. Briefly define the following: Catheter – used to remove urine from the bladder Intake and Output – food or fluid taken in and food or fluid that comes out Normal saline solution – saline solution that has not other properties but saline Traction – leg in a sling with pressure – for fractures 2. Describe a nasogastric tube/Levin tube (NG tube). It is a tube that is placed up the nose, down the throat, and into the stomach. It is used for feeding and irrigation (washing out) of the stomach 3. Identify the abbreviations related to the following bowel orders: TWE – tap water enema SSE – soapsuds enema NSE – normal saline enema OR enema – oil retention enema Fleet or Travad enema – disposable enema 4. Describe a colostomy and colostomy irrigation. Colostomy – Creating an opening into the colon Colostomy irrigation – flushing of fluids to clean out the opening to the colon 5. Discuss moist and dry application and types: Moist - soak – warm or cold, compress – warm or cold, tub, sitz bath Dry - ice pack and ice collar, heat lamp, aquamatic K-pad, thermal blanket 6. Describe the purpose of urinary catheterization. Used on patients who are unable to urinate due to surgery or other reasons 7. Describe a retention (indwelling or Foley catheter) and non-retention catheters. Retention – It is inserted into the bladder and kept in place with an inflated balloon Non-retention – It is a “straight” catheter used for taking a sterile urine sample (goes in and comes out) LAB AND DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING BE ABLE TO: 1. Identify the major laboratory departments and describe their functions. Hematology – The study of the blood itself Chemistry – The study of the components in the blood 2. Give a short description of the following hematology tests and know the abbreviations. Complete blood count (CBC) - all component blood test – WHOLE #s Hematocrit (hct)/ Packed Cell Volume (PCV) – red blood cells as a % in a volume of blood (for anemia) Hemoglobin (hgb) – hemoglobin test for protein in the blood White Blood Count (WBC) – total white blood cell count Differential (Diff) - % of the total WBC made up by different types of leukocytes Red Blood Count (RBC) - whole number count of red blood cells Reticulocytes (Retics) – measure of immature red blood cell count in blood Sedimentation Rate (sed rate) (ESR) - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Red Blood Cell Indices (RBC indices) – tests to measure the bloods ability to carry oxygen to the cells 3. Name the three methods of obtaining a urine specimen and give short description of each. 1. Voided 2. Clean Catch 3. Catheterized (cath UA) 4. State the purpose of the following chemistry tests and know abbreviations: Electrolytes (Lytes) - used to screen for an electrolyte or acid-base imbalance & to monitor the effect of treatment on a known imbalance that is affecting bodily organ function Bilirubin (Bili) – used to detect if bilirubin is adequately being removed from the body – increased bilirubin causes jaundice Fasting blood sugar (FBS) – measures blood glucose after you have not eaten for at least 8hours Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) – test to check how fast the level of glucose is cleared in the blood Iron (Fe) – level of iron in the blood Blood Uria Nitrogen (BUN) – used to evaluate kidney function and to help diagnose kidney dysfunction or failure SGOT (APT) – used to test for liver damage SGPT (ALT) – used to test for hepatitis LDH – Lactate dehydrogenase levels in the blood - used for MI infarction CPK – high creatine phosphokinase levels in the blood can indicate injury or stress to the heart, brain, or muscle tissue - used for MI infarction Alk Phos – high levels of alkaline phosphatase can indicate liver damage Uric acid – used to determine if the body is breaking down cells too quickly or not getting rid of uric acid quickly enough – used to determine if you have gout 5. List the four divisions of microbiology. 1. Bacteriology 2. Mycology 3. Parasitology 4. Virology 6. Describe the following abbreviations: C&S – Culture and Sensitivity T&C – type and cross match O&P – ova and parasite CC – cubic centimeter AP – anterior/posterior PA –posterior/anterior BE – barium enema CT Scan – computerized tomography scan GI - gastrointestinal IVP – intravenous push KUB – kidney, ureter, bladder MRI – magnetic resonance imaging UGI – upper gastrointestinal US – ultrasound QUESTIONS JOHN ASKED IN THE MORNING, BUT NOT ALL ARE ON HERE THAT HE ASKED!!