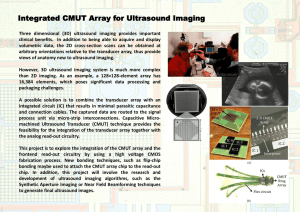
Ultrasound in Medicine1
advertisement

Ultrasound in Medicine عنوان درس :اولتراسوند در پزشکی References: Physical Principles of Medical Ultrasonics C.R.Hill, J.C.Bamber, G. R. ter Haar John Wiley &Sons, 2004 Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging and Blood Flow Measurements K. Kirk Shung Taylor & Francis 2006 Ultrasound in Medicine Edited by: F.A. Duck, A.C. Baker, H.C.Starritt Institute of Physics Publishing 1997 Principles of Medical Imaging K.K.Shung, M.B.Smith, B.M.W. Tsui Academic Press 1992 References: Biomedical Ultrasonics P.N.T. Wells Academic Press 1977 Ultrasonic Instrumentation D.A. Christensen John Wiley 1988 Doppler Ultrasound: Principles and Instruments F.W. Kremkau 1995 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Historical Background 1.2 Physical Nature of Acoustic Wave Motion 1.3 Properties of Isotropic Media 1.4 Equations Governing Wave Propagation in Fluids 1.5 Propagation in Liquid and Solid Media 1.6 Impedance, Energy Density, Intensity and Radiation Pressure 1.7 Reflection and Refraction 1.8 Elements of Diffraction 1.9 Attenuation, Absorption, Scattering and Dispersion CHAPTER 2 Theoretical Basis for Field Calculations 2.1 The Rayleigh-Sommerfeld Diffraction Equations 2.2 The Rayleigh Integral 2.3 Angular Spectrum Method CHAPTER 3 Field Profile Analysis 3.1 Angular Spectrum Method 3.2 Integral Methods 3.3 Impulse Response Method 3.4 Approximate Methods 3.5 Concave and Convex Transducers 3.6 Annular Ring, Annulus and Conical Transducers 3.7 Line, Strip, Triangular and Rectangular Elements 3.8 Transducer Apodization 3.9 Effects of Attenuation CHAPTER 4 Nonlinear Ultrasonics 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Lagrange and Eulerain Coordinate Systems 4.3 High Amplitude 1-D Waves in an Inviscid Medium 4.4 Speed of Sound for Adiabatic Conditions 4.5 Reduced Equations 4.6 Sinusoidal Excitation 4.7 Harmonic Content 4.8 Shock Wave Formation 4.9 Effects of Nonlinearity, Diffraction and Attenuation 4.10 Numerical Methods and Results CHAPTER 5 Scattering of Ultrasound 5.1 Spherical and Cylindrical Representations of a Plane Wave 5.2 Scattering Cross-Sections 5.3 Exact Analysis: Boundary Value Method 5.4 Integral Equation Methods 5.5 Matrix Methods 5.6 Time Domain Scattering Equations 5.7 Pulse-Echo Response 5.8 One-Dimensional Scattering 5.9 Scattering by Distributions CHAPTER 6 Ultrasound Transducers 6.1 The Direct and Inverse Piezoelectric Effect 6.2 Characteristic Piezoelectric Equations 6.3 Ceramic and Polymer Materials 6.4 Methods for Enhancing the Performance 6.5 One-Dimensional Transducer Models 6.6 Application of the KLM Model 6.7 Transient Response 6.8 Protection Circuits 6.9 Noise Considerations CHAPTER 7 Ultrasound Imaging I 7.1 Historical Background 7.2 Properties of Imaging Arrays 7.3 Arrays for 2- and 3-D Imaging 7.4 Summary of Design Factors 7.5 Array Field Synthesis CHAPTER 8 Ultrasound Imaging II 8.1 Theory of B-Mode Imaging 8.2 Image Speckle 8.3 Resolution, Contrast and SNR in Imaging Systems 8.4 Coded Transmission Systems 8.5 Synthetic Aperture Systems 8.6 Nonlinear Imaging 8.7 Ultrasound Computed Tomography 8.8 Ultrasound Elastography 8.9 Ultrasound Microscopy and Biomicroscopy CHAPTER 9 Principles of Doppler Ultrasound 9.1 Historical Background 9.2 Ultrasonic Transit-Time and Phase-Delay Method 9.3 Doppler Equation for Moving Scatterers 9.4 CW Doppler Systems 9.5 CW Doppler Spectrum and its Relation to Flow Profile 9.6 Characteristics of the Doppler Signal 9.7 CW Spectral Broadening CHAPTER 10 Pulsed Methods for Flow Velocity Estimation and Imaging 10.1 Historical Background 10.2 Ultrasonic Transit-Time and Phase-Delay Method 10.3 Simplified Theory 10.4 Cross-Correlation Time-Shift Methods 10.5 Multigate Pulsed Methods 10.6 CW and Pulsed Wave Flow Imaging 10.7 Pulsed Wave Color Flow Imaging 10.8 Volumetric Flow Measurement Methods 10.9 Vector Velocity Methods CHAPTER 11 High Power Ultrasound Some Related Journals: IEEE Transaction on Ultrasound, Ferroelectric and Frequency control Ultrasonics Journal of Acoustic Society of America Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology Ultrasonic Imaging European Journal of Ultrasound ارزشيابي درس %70 %20 %10 امتحان پايان ترم ارائه سمينار تكاليف
![Jiye Jin-2014[1].3.17](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005485437_1-38483f116d2f44a767f9ba4fa894c894-300x300.png)