Annelida
advertisement

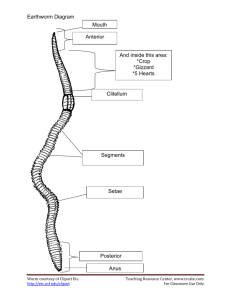
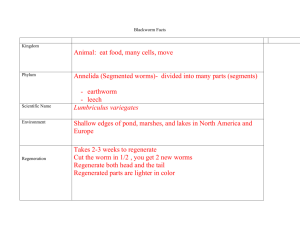
Annelida DISSECTION ANNELIDS Taxonomy Kingdom Animalia Phylum Annelida Class Hirudinea (Leeches) Class Polychaeta (segmented sea worms) Class Oligochaeta (earthworms) Annelida Annelid = ringed Examples: earthworms, leeches, segmented sea worms, feather duster worms, tube worms General Characteristics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Found in all place on Earth Over 15,000 named species Made up of many segments called metameres True coelomates with well-developed internal organs and systems Have hair-like structures called setae made of chiton Body Plan Body Plan: 3 regions: head, metameres and pygidium (tail) Segmented (metameres) and have bristles (setae or chaetae) Segments Segments: Metameres: external segments that contain muscles for movement Septa: internal segments that contain vital organs Clitellum: large segment containing reproductive organs during times of mating Pygidium: the un-segmented tail end of the worm Digestion Digestion: mouth pharynx esophagus crop gizzard intestines anus Some are filter feeders some feed on decaying matter in the soil Circulation Circulation: closed circulatory system with an aortic arch with 5 hearts Blood vessels bring gases and nutrients to all parts of the body Respiration System Respiration: in most annelids, gas exchange occurs through the skin so they have to be kept moist Other marine worms have gills Nervous System Nervous System: consists of a brain and a central nerve cord Sensory organs include eyes, taste buds, tentacles, and equilibrium sensors Movement Movement: movement is made possible by muscles and bristles (setae) Reproduction Sexual: Monoecious or Dioecious but do NOT fertilize their own eggs Asexual: fragmentation, budding, or fission Ecological Importance Feed on decaying matter 2. Recycle nutrients making soil fertile 3. Aerate soil and give it structure 4. Food source to many other organisms 5. Used in medical treatments: leeches leech therapy 1. Class Polychaeta Over 10,000 known species Live in all oceans and at all depths Have many bristles called chaetae Predators, scavengers, parasites or filter feeders Fire Worm Fire Worm Coco Worm Feather Duster Worm Tube Worms Lugworm Sand worm Class Oligochaeta Over 10,000 known species Very few or small bristles called setae Move with peristaltic muscle movement Feed on decaying mater or are predators Live in water or in soil Night crawlers Mekong worm Pot worm Ice worm Black worm Class Hirudinea Most are parasitic, Over 700 species Do not have bristles Have suckers at each end of their bodies Used in medical treatments annelid dissection Leeches