Market Analysis
advertisement

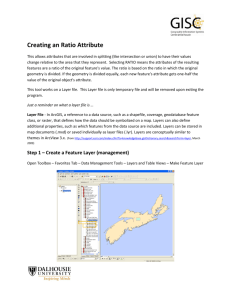
Market Analysis A Six-Step Approach to Understanding the Nature of Competitive Markets Define the Relevant Market Analyze Primary Demand for the Relevant Market Analyze Selective Demand for the Relevant Market Define Market Segments Assess the Competition Identify Potential Target Markets Defining the Relevant Market A set of products and/or services that management considers to be strategically important. • For example, a brand of herbal tea may have a large share of that market but a very small share of the total tea market Defining the Relevant Market Describe the Structure of the Relevant Market Classify competing product market alternatives at three levels. a . Competing brands within a product form b . Competing product forms within a product class c . Competing product classes within a generic need Defining the Relevant Market Define the Boundaries Within the Market. Important for determining “Market Share” Market Structure for Soft Drinks Noncola Cola Diet Regular Diet Regular Caffeine Caffeine Caffeine Caffeine Caffeine Caffeine Caffeine Free Free Free BRANDS Caffeine Free Defining the Relevant Market Describe Product Market Structure •Identify potential competitors •Classify competitors in terms of similarity Define Relevant Market Boundaries Broad Relevant Market Boundary Primary Demand Narrow Relevant Market Boundary Secondary Demand Analyzing Primary and Secondary Demand Define Relevant Market Boundaries Primary Demand Selective Demand •Identity of buyers of product form/class •Factors impacting willingness and ability to buy the product form/class •Type of buyer decision process •Identification of determinant attributes Questions on Buyer Identification Characteristics of Buyers or Users Can buyers of this product category be classified by location, demographics, or lifestyle and psychographic factors? If so, how? Questions on Buyer Identification The Buying Centre Who is involved in the buying process: Reference groups Colleagues Family members? Questions on Buyer Identification Customer Turnover Is there a high degree of customer turnover because of mobility or because purchase is tied to age or other demographic factors? If so, why? Questions on Willingness and Ability to Buy Willingness to Buy Would new or improved related products and services increase utilization? What usage problems exist or are perceived to exist? Is the product or service compatible with the values and experiences of the buyer? What types of perceived risks are significant in the purchase of the product form? Questions on Willingness and Ability to Buy Ability to Buy To what extent do purchase prices and other acquisition and maintenance costs inhibit purchase? Are product size or space problems creating problems for customers? Is the product available at a time and place that meets customer needs? Market Structure for Holiday Travel Need for Holiday Transportation Bus Rail Greyhound Gray Goose Via Automobile Rent Avis Personal Hertz Budget Air Canadian Air Canada Northwest Questions on Selective Demand Decision Processes How extensive is the search for information? Do buyers use personal or impersonal sources of information? Do buyers seek information about brand or supplier characteristics? Sequential Process of Consumer Choice Total Brand Set Awareness Set Consideration Set Tide Trend Cheer Gain Surf Rinso Bold Oxydol Wisk Purex Ultra Fab Tide Cheer Bold Wisk Fab Tide Cheer Fab Types of Decision Processes Consumers COMPLEX Organizations Extensive Problem Solving New Task Limited Problem Solving Modified Rebuy Routinized Response Straight Rebuy SIMPLE Questions on Selective Demand Determinant Characteristics What are the benefits buyers hope to obtain from usage or ownership of the product? What product attributes or characteriatics are viewed as providing these benefits? What is the relative importance of the various benefits desired? How much variation is perceived among the alternatives on each of the important attributes? Attributes of Fast Food Restaurants ATTRIBUTE IMPORTANCE Food Taste 4.30 Quality and Cost 3.79 Food selection 3.58 Menu Alternatives 3.58 1 = unimportant 5 = very important Attribute Ratings for Three Restaurants ATTRIBUTE Food Taste Quality and Cost Food Selection Menu Alternatives 1 = Poor 5 = Excellent A 4 3 3 3 B 3 5 5 4 C 4 4 3 3 Assessing Whether an Attribute is Determinant Perceived Variation Among Alternatives Low Low Perceived Importance High Irrelevant Irrelevant Attribute Attribute Defensive Defensive Attribute Attribute High Optional Optional Attribute Attribute Determinant Attribute Determinant Attribute