Assessment for Unit 3
advertisement

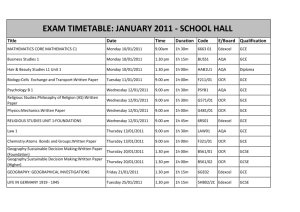
GCE 2008 Geography GCE 2008 Geography Why choose Edexcel? This new GCE Geography specification builds on the strengths of current specifications, namely Edexcel GCE Geography specification A (8214/9214) and Edexcel GCE Geography specification B (8215/9215). • The Specification is brand new and exciting • The content recognizes the need to engage with students and challenge them • The geography is issues and enquiry based and expects students to research and question • Fieldwork is integral, as are skills needed in higher education Slide 2 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Guiding issues • Evidence of assessment overload, especially at AS • Changing global geography, not reflected by old specifications • Declining numbers/competition from newer subjects • A need for renewal, recognised in the Geography Action Plan • Evidence of a repeated curriculum • The ‘stretch and challenge’ agenda Slide 3 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Guiding principles • AS should be stimulating and inspiring • Geography should be current and ‘real’, but set in historical and theoretical contexts • A2 should be challenging and questioning • Choice should be present at AS and A2 • The loss of coursework should not lead to a loss of fieldwork • Quality resources should be available to teachers at an early stage • A balance of local, global and regional geographies Slide 4 GCE 2008 Who was involved? GCE 2008 Geography Student surveys and focus groups Extensive survey of HE views Centre surveys and teacher focus groups The FSC’s Juniper Hall: new spec. birthplace Chief examiners and Principal examiners from both Spec A and B Edexcel Geography support team (revisers, subject officers) Expert input: Dr Rita Gardiner (RGS) David Lambert (GA) Eleanor Rawling Vivien Pointon Slide 5 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography What are the key changes? • 1 new specification; not an amalgam of A and B • 4 units, rather than 6 • No coursework – completely exam tested • Reduction in assessment burden on candidates • Refreshed content Slide 6 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Slide 7 GCE 2008 Geography AS Unit 1 – Global Challenges Global hazards, global hazard trends, global hazard patterns WORLD at RISK Climate change and its causes, global warming impacts and options The challenge of global hazards for the future Globalisation, global groupings, global networks GOING GLOBAL Population and roots, on the move, world cities The challenge of a globalising world Slide 8 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 1 – Global Challenges 1 ½ hour examination including resource booklet Combination of: • data response / short questions • objective items • longer / guided essay questions Slide 9 GCE 2008 Using Figure 4(a): GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 1: data response Figure 4(b) Figure 4(a) Migrations to and from the EU (a) Which EU country was the source of most immigrants to the UK? (1) (i) Suggest reasons for this flow. (2) (b) Which EU country was the destination for most UK emigration? (1) (i) Suggest reasons for this flow. (2) (c) Which of the following population movements is best described as economic migration? Tick the most appropriate box People forced to leave a country to escape from famine Those who arrive claiming to be victims of persecution People travelling abroad to find work elsewhere People entering a country unofficially Those who retire to ‘a place in the sun’ (1) Using Figure 4(b): (d) Explain why the UK is a ‘global hub’ for the movement of people. (4) (11 marks) GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 1: guided essays 10. Study Figure 10. (a) Suggest why the various groups shown hold differing views about this global trade (10) (b) Explain how people can manage the environmental and social costs of globalisation for a better world. (15) UK customers are generally happy but some businesses and workers are less pleased Millions of Chinese people and their government support this venture Maersk shipping lines has offices in 150 countries, and 500 large container ships Critics of this world-wide commercial activity see this as ‘globalisation gone mad’ GCE 2008 Slide 11 GCE 2008 Geography AS Unit 2 – Geographical Investigations PHYSICAL EXTREME WEATHER: extreme weather watch, extreme impacts, increasing risks, management OR CROWDED COASTS: competition for coasts, coping with pressure, increasing risks, management HUMAN UNEQUAL SPACES: Recognising inequality, inequality for whom?, managing urban and rural inequality OR REBRANDING PLACES: time to rebrand, rebranding strategies, managing rural and urban rebranding Slide 12 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 2 – Geographical Investigations 1 hour examination including resource booklet 2 longer response questions Questions in three parts: • data response • investigation skills • impacts/management issues Slide 13 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 2 – data response (a) Suggest some of the physical and economic factors that may have made Florida a crowded coast. (10) (b) Using named examples, examine some of the environmental costs of coastal developments such as those shown in Florida. (10) (c) Describe and explain a programme of fieldwork and research you would use to investigate the impacts of either coastal erosion or coastal flooding, along a stretch of coastline. (15) TOTAL 35 marks Slide 14 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography A2 Unit 3 – Contested Planet Over-arching themes The planet is ‘contested’ in a variety of ways, for example: Increasing demands on a diminishing resource base. Conflicting over the use of resources versus their protection. Questions of economic development and inequality. Should the aim be to make current patterns of consumption more sustainable, or are more radical actions needed? Is technological development the solution to problems of resource depletion and environmental degradation, or it is part of the problem? Slide 15 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Organisation of Unit 3 PLAYERS Providing resources: the costs and problems of consumption; management options and challenges Synoptic Unequal patterns of consumption: poverty – v - wealth The role of technology: In overcoming resource scarcity: inequality and resource management issues. Themes FUTURES ACTIONS Slide 16 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography A2 Unit 3 – Contested Planet Energy Security Energy demand, supply, impacts of energy security, the future of energy supply Water Conflicts Geography of water supply, risks of water insecurity, water conflicts and the future Biodiversity under Threat Defining biodiversity, what threatens biodiversity, management of threats Superpower Geographies Superpowers and geopolitics, impacts and influence of superpower economies, superpower change and futures Bridging the Development Gap Causes, implications at different scales, reducing the development gap The Technological Fix Inequalities in access to technology, technology and development, technology and the planet’s future Slide 17 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 3 – Contested Planet 2½ hour examination including resource booklet Pre-released synoptic materials • Section A – 2 extended essay questions • Section B – 3 synoptic short essay style questions Slide 18 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Paper overview A2 Unit 3 – Contested Planet Q1 Water Q5 Development Q6 a-c Synoptic TECHNOLOGICAL FIX Q4 Superpowers Q2 Energy Q3 Biodiversity Slide 19 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 3: extended essays (a) Explain the pattern of alien species invasions, and suggest the possible impacts of alien species on ecosystems (15) (b) Evaluate the relative importance of global and local threats to one named global ecosystem. (15) Slide 20 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography A2 Unit 4 – Geographical Research Choice for centres and candidates Physical and Human options, but not a physical and human divide Some ‘old favourites’ renewed (tectonic hazards) Some new topics (cultural diversity / glaciation) Research Flexibility in teaching and learning Slide 21 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Tectonic activity and hazards A2 Unit 4 – Geographical Research Hazards and causes, physical impacts, human impacts, hazard response and the future Cold Environments Location, climatic processes and their causes, landforms and landscapes, glaciation, challenges, opportunities and management Life on the margins and food supply Feast or famine, causes of food supply inequalities, desertification and life at the margins, management and security The world of cultural diversity Definition and value of culture, spatial cultural variations, impact of globalization, cultural attitudes and the environment Pollution and Human Health at Risk Health risks, complex causes, pollution and health risk links, managing health risks Consuming the rural landscape Growth of leisure and tourism landscapes, fragility of rural landscapes, impact on rural landscapes, management Slide 22 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography Assessment for Unit 4 – Geographical Research 1½ hour examination Pre-released materials (a research steer) • 1 long report question relating to chosen option study Slide 23 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 Geography A2 Unit 4 – Geographical Research OPTION 1: Tectonic activity and hazards The physical causes of tectonic hazards and responses to them OPTION 1: Tectonic activity and hazards Question 1 Discuss the relationship between the nature of tectonic hazards and human responses to them. (70) OPTION 5: Pollution and Human health at risk The need for international action OPTION 5: Pollution and Human health at risk Question 5 Explain why international initiatives are increasingly needed to cope with the risks of disease and pollution. (70) Slide 24 GCE 2008 GCE 2008 – e-Spec Electronic, interactive version of the specification Content easy to evaluate and discuss Free inside the specification in September 2007 GCE 2008 Slide 25 GCE 2008 – How do I Keep Up to Date? Keep informed – sign up for email alerts on: • www.edexcel.org.uk/gce2008 Regional Office and Team Support Keep in touch : • GCE enquiries – telephone 0844 576 0025 • ‘Ask the Expert’ service www.edexcel.org.uk/about/ask GCE 2008 Slide 26