Unit 3 Key Terms
advertisement

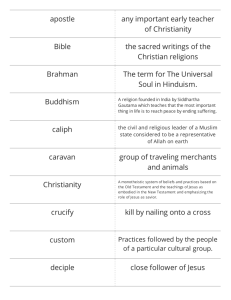
Unit 3 Key Terms 46-90 Religion Regions 46. Hinduism • Most ancient religious tradition in Asia (and possibly the world?). • May be viewed as polytheistic • Central belief is in reincarnation • Ethnic religion = primarily practiced within India • Example/illustration: Characteristics of Hinduism • No clergy or religious requirements • No real splintering or sects – Can be practices in many ways & at many levels so there was no need to “split off.” • Each individual is seeking to comprehend the ultimate reality while living out his/her dharma (duty) with the goal of union with Brahman once the cycle of reincarnation is ended. 4 47. Karma • Definition: the notion that every action a person takes has a consequence at some point in the future. Good or bad, everything we do, according to Hindus, matters. • Example: Abby volunteers at a homeless shelter every week. When she dies, she has accumulated good karma which helps her in her next life. 48. Reincarnation • Definition: the cycle of “rebirth” and “redeath.” • Example: Andy is a human in this life and has accumulated NEGATIVE karma for kicking puppies and babies. As a result, he is reincarnated into a blind puppy with three legs. 49. Caste System • Definition: a social system where status is determined by heredity – – – – Brahman, priestly Kshatriya, warrior/ruler Vaisya, tradesman and farmer Sudra, servant and laborer – Untouchables (5th caste) • Example: Blue Ivy marries Saint West (you only marry people in your social class) 50. Untouchables • Definitions: The lowest group within the caste system. Also called the Harijans or dalits. They perform jobs that Hindus consider to be spiritually and physically unclean • Example: Most Hindus are vegetarians, so any job that requires handling animal carcasses, bodily fluids or waste, or skin is considered very unclean 51. Vedas • Definition: Hindu Holy books. They contain stories of Hindu gods and goddesses • Example/Illustration: 52. Buddhism • One of the major world religions practiced by about 400 million people worldwide • Siddhartha Gautama/Buddha – Enlightened One • Four Noble Truths – Life involves suffering – Cause of suffering is desire – Elimination of desire ends suffering – Right thinking and behavior eliminate desire • Diffused from India 53. Siddhartha • Definition: Another name for Buddha. He was born to a wealthy family and was very sheltered growing up. When he finally left his house as an adult, he was exposed to all the ills of the world (illness, poverty, suffering, etc.). He then left his family and rejected all earthly desires to begin his journey to find a way to end suffering. He is seen as the founder of Buddhism. • Example: 54. Four Noble Truths • Definition: Four aspects of life surrounding suffering that the Buddha taught – Life involves suffering – Cause of suffering is desire – Elimination of desire ends suffering – Right thinking and behavior eliminate desire 55. Pali Cannon • Definition: the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravadan Buddhist tradition • Example: 56. Judaism • Definition: the monotheistic religion of the Jews having its spiritual and ethical principles embodied chiefly in the Torah and in the Talmud • Example: • • • • Judaism 14 million adherents Monotheistic (claims to the oldest one) Based on covenant with Abraham Scriptures: Torah – 5 books of the “Law” – Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy • Sects – Orthodox, Conservative, Reform • Israel – More Jews in New York City than in Israel – Homeland for Jewish people – Created 1948 – Conflict between Israel and Palestine 15 57. Diaspora • Definition: the dispersion of any people from their original homeland. The word is primarily used to describe Jews living outside of Israel • Example: 58. Torah • Definition: Jewish religious text containing 5 books of the “Law” – Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy • Example: 59. Kosher • Definition: A biblical dietary restriction for Jews. • Example: look at the chart on the next slide Kosher Examples 60. Synagogue • Definition: the building where a Jewish assembly or congregation meets for religious worship and instruction • Example: 61. Christianity • Definition: a monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior • Example: Christian Fundamentals • Areas of almost complete agreement – Sacraments of Baptism & Matrimony – Monotheism involving one God in a trinity of persons (referred to as a mystery) – Blessing and sharing bread and wine at least in memory of Jesus sacrifice – Jesus was/is 100% God and 100% human – Salvation comes from belief in and acceptance of Jesus as one’s savior – There will be a second coming at the end of time 22 Christianity • Emerged from Judaism – Jesus was a Jew! • Official religion of Roman Empire – 312 CE – Facilitated geographical spread – Model for its bureaucratic structure • Significant growth in Africa, Asia and Latin America 23 Christian Denominations: Sects • Eastern Orthodox – Greek, Serbian, Russian, Armenian, etc. • Roman Catholic – Latin Rite & Greek Rite – Largest single denomination in the USA • Protestant – hundreds of denominations – Luther, Calvin, Zwingli, etc. • Peripheral – significant differences from the mainstream Christian denominations – Mormon, Jehovah Witnesses, etc. 24 62. Jesus • Definition: A teacher and prophet whose life and teachings form the basis of Christianity. Christians believe Jesus to be Son of God. • Example: 63. Islam • Definition: the monotheistic religion of Muslims founded in Arabia in the 7th century and based on the teachings of Muhammad as laid down in the Koran • Example: Islam • • • • Muhammad, prophet Allah (word for God) Monotheistic Major Sects: Sunni – 85% and Shiite – 15% • Koran (or Qu’ran), the holy book, is sufficient to direct all aspects of life, seen as direct word of god, as told to Muhammad. 27 Five Pillars • Five Pillars of Islam – Belief in one God – Five daily prayers facing Mecca – Generous alms (help to poor) – Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan – Pilgrimage to Mecca (hajj) 28 64. Muhammad • Definition: the founder of the Islam religion; to Muslims, Muhammad is the ultimate and final prophet • Example: 65. Hajj • Definition: annual pilgrimage to Mecca performed by Muslims. It is a mandatory religious duty to be done at least once during each person’s lifetime. It is the fifth pillar of Islam • Example: 66. Qur’an • Definition: the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims believe to be a revelation from God. • Example: 67. Mosque • Definition: a Muslim place of worship • Example: 68. Sharia • Definition: the basic Islamic legal system derived from the religious precepts of Islam, particularly the Qur’an and the Hadith • Example: look at map on next slide for example/illustration 69. Confucianism • Definition: A Chinese folk religion or philosophy that began about 2,500 years ago and that emphasizes proper social relationships and individual morality. It is a system of philosophical and ethicalsociopolitical teachings sometimes described as a religion • Example: Confucianism • Confucius lived from 551-479 BC in China • Importance of loyalty to one’s parents, family and government • Supports an orderly state (strong government) 70. Taoism • Definition: philosophical system developed by of Lao-tzu and Chuang-tzu advocating a simple honest life and noninterference with the course of natural events • Example: 71. Sikhism • Definition: the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam • Example: 72. African Traditional Religion • Definition: A catch all term that refers to many individual religions in Africa that have some things in common. • Most are forms of animism • Focus is on maintaining order in society and life, not on eternal salvation • Failure to respect the gods might bring a bad harvest or infertility • Example: 73. Jainism • Definition: developed about the same time as Buddhism as a reaction to Hinduism (6th Century BC) • Jains believe that the only way to escape the cycle of rebirth is to cease all activity that might accumulate bad karma • Thus, monastic living is the only true way to salvation: monks and nuns renounce all possessions, wandering by foot for much of their lives, begging for food and trying not to harm any living thing. • Example: 74. Shinto • Definition: the ancient indigenous religion of Japan lacking formal dogma; Religion located in Japan and related to Buddhism. Shintoism focuses particularly on nature and ancestor worship. • Believers acknowledge that gods are present in natural objects • Example: 75. Baha’i • Definition: a religion emphasizing the unity of all religions and peoples, teaching that all founders of the world's religions have been God's divine messengers • Main message is that all peoples are the same regardless of background or religion • Seeks to unite all people of the world • Example: on next slide 76. Ethnicity • Definition: a constructed identity that is tied to a place … it is often considered “natural” because it implies ancient relations among people over time. • Ethnicity is NOT the same as race. It is more difficult to define ethnicity than race. It includes shared cultural traits (religion/language) and a common history • Example: Ms. Roti’s ethnicities are Italian, French, German, Czechoslovakian, Austrian, Irish, Austrian, and Polish (where her grandparents are from). Her race is white and her nationality is American because she was born in America. Estimated Percentage of U.S. Population by Race and Ethnicity until 2050 77. Ethnocentrism • Definition: A belief or conviction that one’s own ethnic group is superior • Example: 78. Emergent Ethnicity • Definition: involves the creation of new forms of group identity due to demographic changes or competition and conflict with other groups. • A new ethnic identity based on group solidarity and similarity of experiences might form. • Example: Some argue that the identity of “Asian American” is an example of this 79. Resurgent Identity • Definition: the idea that traditional or ancestral identities can reemerge through historical events and particular circumstances. • Example: Japanese Americans after WWII 80. Assimilation • Definition: process of incorporating new ideas into an existing cultural structure and the loss of your original culture • Example: American Indians experienced forced assimilation in boarding schools when they were forced to follow white culture and lose their traditional cultures 81. Acculturation • Definition: The adoption of the behavior patterns of the surrounding culture but maintaining your original cultural (bicultural) • Example: When the Lost boys ate American food with their hands rather than use utensils. 82. Ethnic Neighborhoods • Definition: An area with a much higher concentration of a particular ethnic or cultural group that doesn’t dominate in the general population • Example: Chinatown in Chicago 83. Segregation • Definition: the practice or policy of keeping people of different races, ethnicities, religions, etc., separate from each other. • Example/illustration: 84. Ghettos • Definition: a poor, densely populated city district populated by a minority ethnic group linked together by economic hardship and social restriction • Note: this word can be a way of perpetuating stereotypes. Please be mindful of your use of the word • Example: Englewood 85. Ethnoburbs • Definition: a suburban residential and business area with a notable cluster of a particular ethnic minority population • Example: Skokie (northwest suburb) where the majority of the residents are Asian Americans 86. Ethnic Islands • Definition: small, usually rural and ethnically homogeneous (similar) enclaves, situated within a larger and more diverse cultural context. • Example: Sardinia, even though it's part of Italy, the people of Sardinia have been formally recognized as a separate "people" than other Italians 87. Sex • Definition: the biological differences between males and females • 52% of the world is female, yet are considered a minority • Example: 88. Sexism • Definition: the subordination of one sex, usually female, based on the assumed superiority of the other sex • Example: 89. Gender • Definition: culturally and socially constructed differences between females and males that are based on meanings, beliefs and practices that a group or society associates with “femininity” or “masculinity” • Example: Boys play with trucks and girls play with dolls 90. Gendered Spaces • Definition: areas in which particular genders of people, and particular types of gender expression, are considered welcome or appropriate, and other types are unwelcome or inappropriate • Example: Illiterate Young Women This map shows the number of young women that would need to be educated to reach the same literacy rates as men in each territory. Girls/Women may be denied an education due to: • Economic factors: Females are needed to work at home so that parents can work or only enough money to educate some children (males picked first) • Social/Cultural factors : A belief that the role of females is to look after children and take care of the home and therefore does not need an education. • Religious/Political: Example: Taliban (banned females from working, therefore eliminating possibility of education for girls)