Matter and Atoms
advertisement

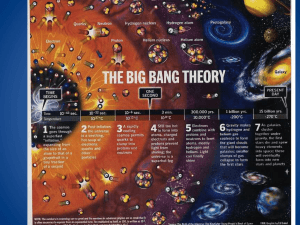
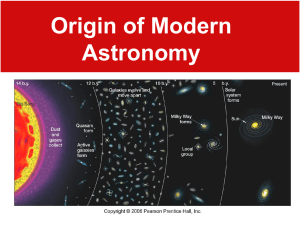
1. What is a system? A group of related parts that work together to accomplish a common goal 2. List the 5 parts of a system and their duty. Goal – objective Input – ingredients Process – directions Output – what you get Feedback – a way to change the input and process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Define Matter and Atoms. Matter – Anything that has mass and volume Atoms – “building blocks” of matter What are the two parts of the atom and what subatomic particles are housed there? Nucleus – Protons(+) and Neutrons (0) Electron Shell – Electrons (-) What is an Ion? Charged atom from gaining or losing electrons What is an element? Matter with all identical atoms How are the atomic number and mass number different? atomic number is the number of protons in an atom (different for each element) atomic mass number of protons and neutrons (could determine if the element is an isotope) What are Isotopes? atoms of the same element but different mass numbers (neutrons) 1. 2. How is a chemical property different from a physical property? Chemical properties are observed with chemical changes; during a chemical change, the original matter changes its identity. When changing a physical property, you still have the same type of matter. How is the state of matter determined? Depends on the kinetic energy or how fast the atoms are moving. State of Matter Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Attraction Volume Shape State of Matter Attraction Solid Strong Liquid Medium Gas Weak Plasma Weak Volume Shape State of Matter Attraction Volume Solid Strong Fixed Liquid Medium Fixed Gas Weak Will fill the container Plasma Weak Will fill the container Shape State of Matter Attraction Volume Shape Solid Strong Fixed Fixed Liquid Medium Fixed Of the container Gas Weak Will fill the container Of the container Plasma Weak Will fill the container Of the container 1. 2. Is changing the state of matter a physical or chemical change? Think about water. PHYSICAL – no matter if I boil or freeze water, the chemical composition is still H2O What are two ways to change a state of matter? Adding or removing heat energy Changing the pressure 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is energy? The ability to cause change or do work What are the two categories for types of energy and how do they differ? Kinetic Energy – motion and movement Potential Energy – stored energy What transfers energy? Matter What is the Conservation of Matter and Energy? Matter and energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only transfer into different forms What is the Unifying Principle? All matter is influence by GRAVITY 1. 2. What is a natural resource? Matter on Earth, living and non-living, that has value to humans in some way. What is the difference between a renewable and nonrenewable resource? Give an example of each. Renewable – replaced within a human life time EX – wildlife, water, soil, wind Nonrenewable – cannot be replaced fast enough naturally, exists in only small fixed quantities EX – fossil fuel, minerals 1. What is Einstein’s famous equation and what does it mean? E =mc2 All matter posses energy 2. 3. 4. Define electromagnetic radiation. Do we give off radiation? If so, what type? kinetic energy given off by all atoms YES, infarred What form does radiation travel in and how fast? waves speed of light What is a wavelength? How does it relate to energy? wavelength – distance from crest to crest longer wavelength – less energy shorter wavelength – more energy 5. 6. 7. 8. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? A graph of all types of radiation based on their wavelength What’s visible light? What happens when white light passes through a prism? Radiation that we can detect with our eyes. White light is separated into all visible colors What type of radiation has the longest wavelength? The shortest? longest – Radio – least amount of energy shortest – gamma – most amount of energy What are five ways that radiation can interact with the environment? Give a quick description. a. b. c. d. e. Refraction – bends or changes direction Reflection – bounce off Scattering – energy is split into multiple paths in all directions Absorb – when matter takes in energy Transmission – pass through without interaction 1. List three ways heat is different than temperature. Heat Temperature Measures how fast the kinetic energy TRANSFERS Measures the average kinetic energy During change of state heat energy is absorbed or released Marks the number where the state changes Units: calories Units: celcius 2. 3. How does heat flow? From high to low What is latent heat? hidden or absorbed heat 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is cosmology? The study of our universe – past, present, and future What are theories and how are they different than laws? theories describe a complex series of events laws explain a simple universal action True or False: The best way to describe the universe or unknown is to observe what happens on Earth and apply that knowledge elsewhere. TRUE The Universe formed from the __________ __________, and occurred ____________________ years ago in an explosion. Big Bang 13.7 billion True or False: The Big Bang is a series of events that led to the formation of our solar system. FALSE!!! 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. What are two pieces of background information that we can apply to help describe the Big Bang? How do they support the theory? The Electromagnetic Spectrum – determines all galaxies are red shift and moving AWAY from us Doppler Effect – the change is only apparent b/c we are in constant motion The Universe is constantly expanding. How do we know? All galaxies are red shifted or moving away Finish what Hubble started, if the Universe is constantly expanding, rewind it, at one point the Universe must have … began at one point What are two ways that we can test the Big Bang Theory? Measure the Cosmic Background Radiation (Temperature) Apply the Unifying Principle What were the first two elements in our universe? Think simple. H (Hydrogen) He (Helium) 11. 12. 13. 11. 12. What is Nuclear Fusion? The nuclei of two hydrogen fuse (glue) together from colliding at high speeds. This fusing makes one helium atom and releases large amounts of heat and light. What is a supernova? the implosion that marks the death of a very large star; stars die when they run out of hydrogen to burn How did we get an element rich universe? the process of nebula to fusion to supernova and back to nebula repeats for almost 9 billion years. After the Big Bang, describe what occurred to create our Solar System? How long after the big bang was it? a huge cloud of gas and dust (nebula) begins to clump together due to gravity and form galaxies the nebula will continue to move inward until enough matter and energy are located centrally to start the fusion process – a star is born the rest of the dust cloud revolves around the central star and begins to combine and form planetesimals Planetesimals collide forming larger planets with well defined orbits What was the iron catastrophe? the early Earth was liquid rock that separated into layers based on the liquid’s density. 16. 17. 18. 18. What are the four layers of Earth and how are they sorted? Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Liquid Core the most dense material is toward the center of the Earth During the solar stew lab you compared the densities of items to the density of the planets, how does this apply to our solar system? the rocky inner planets are the most dense and the gaseous outer planets are the least dense Describe baby Earth. How did we develop oceans? The atmosphere? Very hot, incredibly acidic, and poisonous to humans Oceans 1: condensation from volcanic gases Oceans 2: Earth was hit by ice comets ATM: from volcanic gases (carbon dioxide and ammonia) What are stromatilites and what role did they play in the development of modern Earth? Photosynthetic bacteria – very simple life form that changed the carbon dioxide into oxygen