Sound - Strickland Science
advertisement

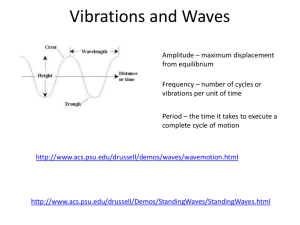
Chapter 13: Sound Camila Enríquez Juliana Borrero Objective: Understand the production of sound waves, compare the speed of sound in different situations, and recognize the Doppler effect. • Relate frequency to pitch, identify intensity, and decibel level. • Approach the perception of loudness, and resonance. • Calculate harmonics and differentiate between the harmonic series of closed and open pipes. • Enduring understandings: Sound waves are longitudinal. (sine curve) • Frequency determines pitch • Sound waves disperse in 3D • Doppler Effect: relative motion creates a change in frequency. • Intensity in decibels • Length of vibrating string and vibrating air column will affect harmonic series frequencies. • The Doppler Effect Australian physicist Christian Doppler When the source that emits the sound (this case the ambulance) is approaching you the wave you receive will be in a higher frecuency (shorter wave lenght). If the source is leaving you, then you will receive a lower frequency wave (longer wavelenght.) The ambulance is moving toward the woman, so the frequency heard by the woman is greater than the ambulance frequency. Remember: the speed of sound waves DOES NOT change. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a3RfUL w7aAY&feature=related Sound Intensity and Resonance Intensity: the rate of energy flow through a unit area of the plane wave. In spherical waves, area = 4πr² Intensity of sound wave decreases as distance from the source increases. ◦ Same amount of energy spread over a larger area. Harmonics In the strings of stringed instruments, the ends are not able to vibrate, but the center has a lot of displacement. ◦ Ends are nodes, and the center is an antinode The distance from one node to the next is always half a wavelength. ◦ Wavelength is twice the string length. The speed of waves is the frequency times the wavelength. Frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength. ◦ fundamental frequency is the lowest possible frequency of a standing wave. The fundamental frequency can be varied by changing the string length. ◦ E.g. If the string is divided in half by another node, the wavelength will be half as the one before and thus the frequency will be doubled. In a harmonic series, the fundamental frequency is the first harmonic (f1), the next one is the second harmonic (f2), and so on. Standing waves in an air column Standing Waves (stationary waves): On a tube/pipe some waves travel down the tube, others are reflected back upward. The combination of the waves traveling up and down the tube are what we call standing waves. If both ends of a pipe are open, all harmonics are present ◦ E.g. trumpet, saxophone, pipes of an organ. Each end of the pipe is an antinode. Fundamental frequency of a stringed instrument can vary by changing the length of the vibrating air column. If one end of a pipe is closed, only odd harmonics are present ◦ One end is a node, the other is an antinode. ◦ The simplest standing wave is ¼ of a wavelength ◦ ¾ of a wavelength are still on the pipe. The frequency of this harmonic is 3 times the fundamental frequency. Harmonics account for sound quality or timbre. ◦ Timbre (sound quality) is the characteristic sound of an instrument, produced by a mixture of harmonics; it’s the spectrum of the sound. In chromatic musical scale: 12 notes, each with different frequencies. The 13th note’s frecuency is exactly twice of the 1st note’s (octaves, n). Sound Barrier The sound barrier refers to the point in which an aircraft moves from a transonic (a point in which air surrounds the aircraft) to a supersonic speed. Approximately velocity is 343 m/s. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wHrwg RsX0BI Bibliography Holt Physics Textbook Chapter 13 Wikipedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sound http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sound_barrie r