Lecture: B-vitamins and metabolism, part 1
advertisement

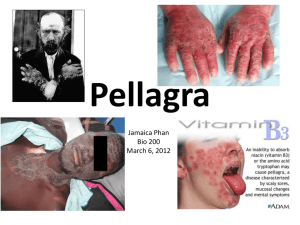
INTRODUCTION TO B-VITAMINS: ROLE OF B-VITAMINS IN METABOLIC PATHWAYS Sept 10, 2014 We get energy on a daily basis from carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. What events must occur, to enable us to employ these dietary components for energy? NIACIN is vitamin needed for a great many events in energy metabolism. Two forms of niacin in the diet are shown: these are precursors for NADH and NADPH NIACIN AS A COMPONENT OF NADH AND NADPH: These participate in >200 biochemical reactions that are essential for health! EACH RED ARROW IS A STEP IN FORMATION OF ATP FROM GLUCOSE, THAT USES NIACIN FADH2 is a riboflavin-dependent component. The FADH2 produced also contributes electrons for ATP synthesis by the ETC ROLE FOR NIACIN GLYCOLYSIS: The molecular steps are easily seen. USEFUL EXERCISE: Draw out the intermediates in the TCA cycle NAD+ Acetyl-CoA NADH CO2 O O H2C H2C O C CO O CO alpha-ketoglutarate H2C CO H2C O C SCoA succinyl-CoA REACTION CATALYZED BY THE ENZYME a-KETOGLUTARATE DEHYDROGENASE (PANTOTHENIC ACID is involved, will be discussed) From TCA NADH (which contains niacin) carries most of the electrons from the TCA to the electron-transport chain. The NAD+ is regenerated, to be used again MANY times. This is VERY simplified, of course. It really just shows the REACTANTS and the PRODUCTS. The niacin functional group as a redox donor/acceptor of electrons H CH3 - C - COOOH NAD+ ? Lactate Reaction catalyzed by LDH NADH CH3 - C - COOO ? Pyruvate Another reaction catalyzed by LDH Glutamate is the main amino acid that donates nitrogen to the urea cycle. NADH is required for this reaction. Niacin (as NAD) is required for the metabolism of ethanol. The metabolic fate of lysine – HOW MANY niacin-dependent steps? Amino acids are degraded for energy in normal metabolism, we will discuss in some detail. Notice the Acetyl-CoA product, which can be used by the TCA cycle to make ATP. OTHER B-VITAMINS HAVE ESSENTIAL ROLES IN ENERGY METABOLISM Pantothenic acid: all steps that use CoA Thiamine Riboflavin Thiamine: as provided in the diet SEPARATE ENZYMES EXIST TO ACTIVATE EACH B-VITAMIN: Thiamine is modified by addition of two PO4 groups The active form of thiamine in metabolism SEVERAL ENZYMES WORK TOGETHER IN THE PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX: WHAT IS THE FATE OF THE 3 CARBONS IN THE INITIAL PYRUVATE MOLECULE? Wet Beriberi: edema is a common feature. What is the diagnostic challenge? Pellagra: dermatitis is typical Pellagra/before and after treatment with high-dose niacin: which biochemical steps are disturbed, that involve niacin? This graphic shows that some dietary tryptophan is converted to NIACIN. The yield is is about 1 mg of niacin, for 60 mg of tryptophan. Corn is a problem because its niacin content is often not bioavailable, and because corn is low in tryptophan. The niacin RDA (20 mg) is based on a lot of our niacin (another 20 mg) coming from tryptophan. People who cannot make niacin are given about 50 mg/day. MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCY: Often very non-specific. How can we be prepared to diagnose these disorders? USEFUL STUDY ASSIGNMENT: -Suppose you ate a VERY limited diet, with foods that are NOT fortified. What nutrients would be deficient? -corn -potatoes -white rice -wheat This can happen during a famine, where there is a sharp reduction in the diversity of the diet.