Ancient China
advertisement

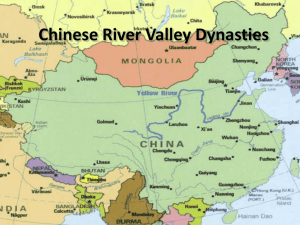
Ancient China World History Core Geography/Interaction with Environment Location: Asia Natural Barriers EAST: Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and Pacific Ocean WEST: Taklimakan Desert and Plateau of Tibet SOUTHWEST: Himalayas NORTH: Gobi Desert and Mongolian Plateau Geography/Interaction with Environment Isolation by Distance Yangtze River Central China to Yellow Sea Huang He (Yellow River) Northern China to Yellow Sea LOESS: deposits of yellow silt (fertile soil) “China’s Sorrow”: dangerous floods of the Huang He Yangtze River Yellow River Geography/Interaction with Environment Challenges Dangerous Floods Solution: Yu’s irrigation and flood control methods Isolation Solution: Had to supply all goods, could NOT rely on trade! Geography/Interaction with Environment China’s Heartland 10% of land in China is ARABLE North China Plain Farm land between the two rivers Power and Authority Dynastic Civilization Ruled by families Xia Dynasty and Yu the Great: First Dynasty Mathematician and Engineer Developed way to control flooding which allowed a civilization to develop Power and Authority Shang Dynasty: 1st family to leave written records Warrior Kings: rulers who were constantly at war Middle Kingdom: China’s name for itself, believed they were the center Barbarians: outsiders to China Class Division: Between peasant and nobles NOBLES: owned all the land that the peasants worked on Power and Authority Zhou Dynasty: overthrew Shang 1027 BC Mandate of Heaven: divine approval to rule comes from heaven Developed by the Zhou to get rid of Shang Dynasty Dynastic Cycle: pattern of rise, decline, and replacement of dynasties (see p. 54 and next slide) Feudalism: political system in which nobles are granted land that legally belongs to the King In RETURN: Nobles must (1) Give loyalty and military service to the King and (2) Must protect the people living on the land Religious and Ethical Systems Loyalty to Family: Center of Chinese society #1 virtue: Honor and respect PARENTS Elder men were in charge of family Women were inferior 13-16 arranged into marriage Must bear a son to improve your social worth Religious and Ethical Systems Ancestor Worship: Power to bring good or disaster to a family Must give sacrifices to ancestors Polytheistic: Belief in many GODS Shang Di Oracle Bones: used to communicate with the Gods How they worked: Wrote question on animal bone Priest pokes bone with a hot rod Bone cracks Priest interprets the cracks to answer the question on the bone Cultural Interaction/Economics/Empire Building Agrarian Society: depend on farming Expansion Limited by Distance Warring Nomads: Sacked Zhou capital, killing the monarchs Leads to quarrels among NOBLES, thus the end of the Zhou Dynasty Revolution Shang are overthrown by the Zhou Due to the idea of Divine Mandate Zhou believed the Shang were no longer doing a good job Developed idea that Gods no longer wanted the Shang to rule Thus giving ruling power to the Zhou Science and Technology Written Language: united large, diverse area because you didn’t have to be able to speak the same language to be able to read Chinese Symbols NOT letters: each character = one syllable Calligraphy: writing of characters, each character made up of single brushstrokes Difficult to LEARN: 1500 = barely literate 10,000 = scholar Science and Technology Silk Production: religious beginnings, discovered by a Goddess Silk worms produce the fabric Worn by rulers Silk Road: Chinese silk trade route Science and Technology Coined Money: To improve trade Iron Weapons and Tools: Blast furnaces to cast iron Weapons: daggers and swords Agriculture: knives and spades Made farming more efficient!