4361t4_sampleproblems

ACG 4361 Test 4 Practice Problems
Problem 1
The master budget components for Land Company for the quarter ended June 30 appear below. Land’s sells rakes for $10 each. Budgeted sales and cash disbursements for the next five months are:
April
May
June
July
Budgeted sales
20,000 units
50,000 units
30,000 units
25,000 units
Budgeted cash disbursements
$301,000
$362,000
$356,000
$332,000
August 15,000 units $315,000
All sales are on account. The company’s collection pattern is: 70% collected in the month of sale; 25% collected in the month following sale; and the remaining 5% are collected in the next month. The accounts receivable balance on March 31 was $30,000. Lan d’s loan arrangement with its bank requires Land to maintain a minimum cash balance of $30,000. The cash balance at the beginning of June was $40,000.
Land desires to have enough rakes on hand at the end of each month equal to 20 percent of the following month’s budgeted rake sales. On March 31, 4,000 rakes were on hand. Five pounds of aluminum are required to produce each rake. The company desires to have enough aluminum on hand at the end of each month equal to 10 percent of the following month’s production needs. The beginning aluminum inventory was
13,000 pounds. Aluminum costs $0.40 per pound. Each rake produced requires 6 minutes of direct labor.
Employees are paid $12 per hour. In addition, the cost of fringe benefits is $2.50 per hour. MOH is applied at the rate of $0.60 per direct labor cost.
A. Determine the amount of cash collections Land expects to receive during the month ending June 30.
B. In good form, prepare a production budget in units for the month ending June 30.
C. Prepare a materials purchases budget for the month ending June 30.
D. Prepare a direct labor budget and separately, a manufacturing overhead budget for June.
E. Prepare the current assets section of the balance sheet at June 30.
Problem 2
Vince’s Spaghetti is a family-owned restaurant in Southern California. The corporate office provides 2 kinds of services (maintenance and personnel) to Vince’s 3 locations (Ontario, Redlands, and Temecula). In a recent accounting period, the direct cost for maintenance was $25,000 and for personnel was $15,000. Maintenance costs are allocated on the basis of square feet, and personnel costs are allocated based on the basis of number of employees.
Support Departments:
Maintenance
Square Feet # of Employees
Personnel
Operating Departments:
Ontario
Redlands
1,000
1,000
5,000
6,000
15
8
12
18
Temecula 3,000 10 a. If Vince’s uses the direct method, calculate the total support costs allocated to each restaurant location. b. If Vince’s uses the step-down method with personnel allocated first, calculate the total support costs allocated to each restaurant location. c. Assume Vince’s uses the reciprocal method to allocate costs between support departments.
Calculate the total support department costs allocated to each restaurant location.
Problem 3
Allen, Inc. has the following disbursements:
* Variable manufacturing costs are $3 per unit. They are paid 40% in the month of purchase and
60% in the following month. Purchases are made in the month of production.
* Fixed overhead is $2,000, including $500 depreciation. Overhead costs are paid as incurred.
* Selling costs are $1,500 per month plus $1 per unit and are paid 80% in the month incurred and
20% the following month.
* Production for January, February, and March was 3,000, 2,000, and 1,200 units, respectively.
* Sales for the 3 months were 1,000, 2,500, and 1,000 units, respectively.
What is the amount of cash disbursements for February?
Problem 4
Kelita, Inc., projects sales for its first three months of operation as follows:
October November December
Credit sales
Cash sales
$100,000
40,000
$150,000
60,000
$200,000
50,000
Total Sales $140,000 $210,000 $250,000
Inventory on October 1 is $40,000. Subsequent beginning inventories should be 40% of that month’s cost of goods sold. Goods are priced at 140% of their cost. 50% of purchases are paid for in the month of purchase; the balance is paid in the following month. It is expected that 50% of credit sales will be collected in the month following sale, 30% in the second month following the sale, and the balance the third month. A 5% discount is given if payment is received in the month following sale.
A. What is the projected cost of goods sold for October?
B. What is the projected cost of purchases for October?
Problem 5
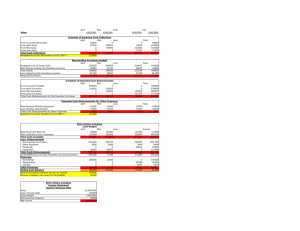
Vegan Wagon is part of a chain of restaurants and has been losing money in past months. Part of the problem has been a decline in sales. However, sales are expected to pick up during the summer months. In March, for example, the loss was $2,250.
Revenue
Static Budget Actual
$80,000 $65,000
Costs:
Cost of ingredients
Serving personnel
Cashier
Administration
Corporate cost allocation
Utilities
Income (Loss)
24,000
20,000
4,000
12,000
8,000
1,500
$10,500
22,750
19,000
4,000
14,000
6,500
1,000
$ (2,250)
The restaurant purchases ingredients directly from the chain and is charged in direct proportion to the number of meals served. Personnel paid by Vegan prepare and serve the food, tend the cash register, bus and clean tables, and wash dishes. The staffing levels in Vegan are rarely changed – the existing crew can handle modest fluctuations in volume. Administrative costs are largely the salaries of the manager and her staff. The chain allocates corporate costs based on revenue, and the usual charge is 10% of Vegan’s revenue. Utilities are the costs of heating and lighting the restaurant during normal operating hours and are relatively unaffected by the amount of food prepared. a. Develop a flexible budget for Vegan Wagon that could be used to evaluate the performance of the manager. b. Calculate the variances for Vegan Wagon. c. Identify the largest variance and list one question that you would ask the manager about that variance.