Publishing for impact : Elements for a pubication
advertisement

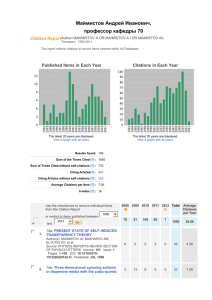
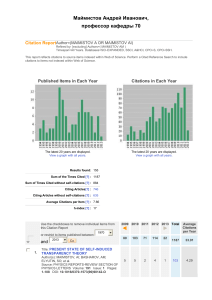
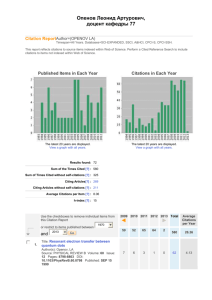
Publishing for impact Elements for a publication strategy Wouter Gerritsma, Wageningen UR Library Social science publications at Wageningen UR Full screen image with title How are we able to compare numbers? Scientist Z. Math has a publication from 2001 with 17 citations Scientist M. Biology has a publication from 2007 with 32 citations Baselines for Mathematics Baselines for Molecular Biology A quantitative example Bouma, J, Bulte, EH, & DP van Soest (2008) Trust, Trustworthiness and Cooperation: Social Capital and Community Resource Management. J. Env. Ec. & Mngmt 56(2)155-166. ● Cited 12 times Journal of Environmental Economics and Management from journals menu in ESI: ● Economics & Business Baseline data for Economics & Business (from ESI) ● Article from 2008: Average: 3.62 Citations; Top 10%: 9 citations; Top 1% 27 citations RI = 12 / 3.62 = 3.31 Baseline data to normalize citation data? Citations data source Baselines Web of Science ESI or InCites Scopus SciVal Strata Google Scholar none Propriatary A&I database none H-index Balance between productivity and citedness To rule out the effect of one or two highly cited papers Applicable to authors, journals, research groups, compounds, subjects etc… But there are some serious doubts about robustness Waltman, L. & N. J. van Eck (2011). The inconsistency of the h-index. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 63(2):406-415 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/asi.21678 In practice After excellent research, where should you publish? Where to publish? A valued journal? ● Quality ● Editorial board ● Acceptance rate ● Time to publication ● Journal circulation ● Visibility 50% of articles generate 90% of all cites Seglen, P. O. (1997). Why the impact factor of journals should not be used for evaluating research. BMJ 314(7079): 497-502. http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/314/7079/497 Look at the IF in a different way Journal quality and impact global universities Highlighting Dutch Universities But where is Tilburg? Journal quality and article impact 20032009, for Wageningen UR Journal Quartile Pubs RI T10(%T10) T1(%T1) Q1 7170 2.26 2444(34%) 505(7%) Q2 2919 1.26 578 (20%) 61 (2%) Q3 1303 0.93 143 (11%) 10 (1%) Q4 587 0.66 Aggregate 11917 1.79 30 (5%) 3195(27%) 6 (1%) 582(5%) Source: Wageningen Yield, Feb. 2012 Document type and article impact 20032009, for Wageningen UR Document type Pubs RI T10(%T10) T1(%T1) Article 11212 1.62 2777(25%) 437( 4%) Review 705 4.45 418 (59%) 145(21%) 11917 1.79 3195(27%) 582(5%) Aggregate Source: Wageningen Yield, Feb. 2012 The impact factor Matthew effect The journal in which papers are published have a strong influence on their citation rates, as duplicate papers published in high-impact journals obtain, on average, twice as many citations as their identical counterparts published in journals with lower impact factors.. Larivière, V. and Y. Gingras (2010). The impact factor's Matthew Effect: A natural experiment in bibliometrics. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 61(2): 424-427. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/asi.21232 Final word on journal quality It is better to publish one paper in a quality journal than multiple papers in lesser journals. [...]. Try to publish in journals that have high impact factors; chances are your paper will have high impact, too, if accepted. Bourne, P. E. (2005). Ten Simple Rules for Getting Published. PLoS Computational Biology 1(5): e57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010057 Networking International cooperation University EUR RUG RUN TUD TUE UL UM UT UU UvA No Cooperation % output Impact 16 1.13 23 1.07 20 0.94 33 1.24 29 1.50 20 0.90 16 0.90 33 1.33 21 1.54 20 1.15 International Cooperation % output Impact 40 2.00 39 1.43 39 1.46 43 1.52 41 1.52 46 1.38 42 1.48 37 1.36 39 1.61 43 1.64 UvT 25 1.15 42 1.21 VUA WUR 18 21 1.15 1.12 43 49 1.68 1.27 Aggregate 25 1.15 44 1.53 NOWT (2008). Wetenschaps- en Technologie- Indicatoren 2008. Maastricht, Nederlands Observatorium van Wetenschap en Technologie (NOWT). Cooperation is effective WTI2 report 2011 Cooperation... Teams increasingly dominate solo authors in the production of knowledge. Research is increasingly done in teams across nearly all fields. Teams typically produce more frequently cited research than individuals do, and this advantage has been increasing over time. Teams now also produce the exceptionally high-impact research, even where that distinction was once the domain of solo authors. Wuchty, S., B. F. Jones, et al. (2007). The increasing dominance of teams in production of knowledge. Science 316(5827): 1036-1039. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1136099 Networking is important Start early, make use of Social Networking tools ● Facebook ● LinkedIn ● Social networks for scientists ● SSRN, Academics.edu, Researchgate On social networking On using social media McKenzie and Özler (2011) The impact of economics blogs Consider the Wikipedia For better or worse, people are guided to Wikipedia when searching the Web for biomedical information. So there is an increasing need for the scientific community to engage with Wikipedia to ensure that the information it contains is accurate and current. Logan, D.W., M. Sandal, P.P. Gardner, M. Manske & A. Bateman (2010). Ten Simple Rules for Editing Wikipedia. PLoS Comput Biol, 6(9): e1000941 http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000941 Self citations and more Self citations The model [...] implies that external citations are enhanced by self-citations, so that we have the “chain reaction:” Larger size leads to more selfcitations, which lead to more external citations. van Raan, A. F. J. (2008). Self-citation as an impact-reinforcing mechanism in the science system. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 59(10): 1631-1643. 11/28 More on references Articles that cite more references are in turn cited more themselves Webster, G. D., P. K. Jonason, et al. (2009). Hot Topics and Popular Papers in Evolutionary Psychology: Analyses of Title Words and Citation Counts in Evolution and Human Behavior, 1979 – 2008. Evolutionary Psychology 7(3): 348-362. http://www.epjournal.net/filestore/ep07348362.pdf To be the best, cite the best Borrowed from: Corbyn, Z. (2010). "To be the best, cite the best." Nature News, 13 October 2010, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/news.2010.539 Reporting on the publication of Bornmann, L., F. de Moya Anegón, et al. (2010). Do Scientific Advancements Lean on the Shoulders of Giants? A Bibliometric Investigation of the Ortega Hypothesis. PLoS ONE 5(10): e13327 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013327. More articles per research project? Publishing more articles results in higher citation counts if the articles provide sufficient substantive content to other researchers. ● Beware of the ethical standards ● Bornmann looked at total citations, not to relative impact Bornmann, L. & H.-D. Daniel (2007). Multiple publication on a single research study: Does it pay? The influence of number of research articles on total citation counts in biomedicine. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 58(8): 1100-1107 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/asi.20531 Journal selection and referencing with multidisciplinary research Higher citations are linked to the citation-intensive disciplines. ● But Larivière et al. looked at absolute citations rather that relative to the field Articles citing citation-intensive disciplines are more likely to be cited by those disciplines and, hence, obtain higher citation scores than would articles citing noncitation-intensive disciplines. Larivière, V. & Y. Gingras (2010). On the relationship between interdisciplinarity and scientific impact. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 61(1): 126-131 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/asi.21226 Consider Open Access publishing Be aware of your copyrights when publishing Golden Road ● PloS Journals, BMC, etc. Green Road ● Self archived copies (final author’s version) ● TU Repository, RePec, SSRN etc. Open Choice ● Hybrid system, author pays and library pays ● Sage model (only 10% of standard fees) Is there a citation advantage for OA? Evidence is mounting ● There is certainly no dis-advantange ● Van Raan has started to self archive his preprints ● Publishers allow self archiving of the final peer reviewed authors version ● Open Citation Project OA is important for developing countries Evans, J.A., Reimer, J., 2009. Open access and global participation in science. Science. 323, 1025. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1154562 Publish your data! Henneken et al. (2011) "articles with links to data result in higher citation rates than articles without such links" http://arxiv.org/abs/1111.3618 Piwowar et al. (2007) "Sharing detailed research data is associated with increased citation rate http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000308 Also relevant in the view of the latest developments (KNAW) Library assists in curating datasets What is in a name? Who is the author of this thesis? On the inside On her own publication list Final word of warning! Publishing strategies are meant to improve the impact of good quality research. Using these techniques to upgrade CVs or boosting research performance ratings of research groups is a dangerous tactic. Tijssen, R.J.W. (2003). Scoreboards of research excellence. Research Evaluation, 12(2): 91-104; p.16 is especially relevant for Tilburg University Thank you! http://tinyurl.com/7r67fmm On the Web: @wowter wowter.net www.slideshare.net/wowter