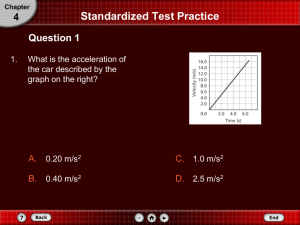
When you drop an object, gravity starts pulling it down Acceleration

Free fall
Definition: downward movement under the force of gravity only
Gravity
Definition: the force that attracts a body toward the center of the earth, or toward any other physical body having mass
When you drop an object, gravity starts pulling it down
Acceleration due to gravity is always down toward the center of the earth
Acceleration due to gravity represented as “g” and is equal to….
The wonders of free fall
In the absence of air resistance, all objects fall at a constant acceleration, regardless of their size or weight.
Lab
Using the photo-gates, design an experiment to calculate the acceleration due to gravity.
Lab Report: Title, Purpose, Materials, Procedure,
Data Table (three trials!), Analysis, Conclusion
Analysis: Get the true value of g from Ms. Rippey and calculate your percent error
The acceleration is the same at all points – only the velocity changes.
Even though the velocity is zero at the top of the ball’s flight, its acceleration is still -
9.8 m/s 2.
If you know the initial velocity at which the ball was thrown, you can calculate how fast it is going and how far it goes at any point during its flight.
So let’s say the ball was thrown with an initial velocity of 10.5 m/s. How fast was it going after 1 s?
While watching the DHJ football team play at
Farrington Field, I accidentally dropped my cell phone from my seat at the top of the bleachers. I heard it crack 3.3 seconds later. How high up was my seat?
A ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 19.5 m/s. What is the maximum height reached by the ball?
A 30 lb weight falls freely from rest from the roof of a building. What is the total distance the weight falls after 3 seconds?
CHALLENGE QUESTION
David throws a baseball into the air at 10 m/s.
How long will it be before the baseball comes back and hits him in the head?
Closing Question
Knowing what you know about free fall, predict what the position vs. time graph and velocity vs. time graph would look like for an object in free fall?