C.P. Algebra II

The Conic Sections Index
Parabola
The Conics
Ellipse
Circle
Click on a Photo
Hyperbola
The Parabola
A parabola is formed when a plane intersects a cone and the base of that cone
Parabolas
A Parabola is a set of points equidistant from a fixed point and a fixed line.
The fixed point is called the focus .
The fixed line is called the directrix .
Parabolas Around Us
Parabolas
Parabola
FOCUS
Directrix
Standard form of the equation of a parabola with vertex (0,0)
•Equation •Focus •Directrix •Axis
•x 2 =4py •(0,p) •y = -p
•y 2 =4px •(p,0) •y = p
To Find p
4p is equal to the term in front of x or y. Then solve for p.
Example: x 2 =24y
4p=24 p=6
Examples for Parabolas
Find the Focus and Directrix
Example 1 y = 4x 2 x 2 = ( 1 /
4
)y
4p = 1 /
4 p = 1 /
16
FOCUS
(0, 1 /
16
)
Directrix
Y = 1 /
16
Examples for Parabolas
Find the Focus and Directrix
Example 2 x = -3y 2 y 2 = ( -1 /
3
)x
4p = -1 /
3 p = -1 /
12
FOCUS
( -1 /
12
, 0)
Directrix x = 1 /
12
Examples for Parabolas
Find the Focus and Directrix
Example 3
(try this one on your own) y = -6x 2
FOCUS
????
Directrix
????
Examples for Parabolas
Find the Focus and Directrix
Example 3 y = -6x 2
FOCUS
(0, 1 /
24
)
Directrix y = 1 /
24
Examples for Parabolas
Find the Focus and Directrix
Example 4
(try this one on your own) x = 8y 2
FOCUS
????
Directrix
????
Examples for Parabolas
Find the Focus and Directrix
Example 4 x = 8y 2
FOCUS
(2, 0)
Directrix x = -2
Parabola Examples
Now write an equation in standard form for each of the following four parabolas
Write in Standard Form
Example 1
Focus at (-4,0)
Identify equation y 2 =4px p = -4 y 2 = 4(-4)x y 2 = -16x
Write in Standard Form
Example 2
With directrix y = 6
Identify equation x 2 =4py p = -6 x 2 = 4(-6)y x 2 = -24y
Write in Standard Form
Example 3 (Now try this one on your own)
With directrix x = -1 y 2 = 4x
Write in Standard Form
Example 4 (On your own)
Focus at (0,3) x 2 = 12y
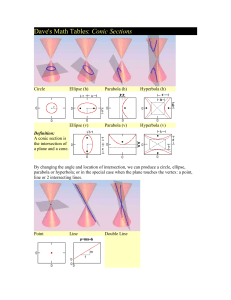
Circles
A Circle is formed when a plane intersects a cone parallel to the base of the cone.
Circles
Standard Equation of a
Circle with Center (0,0)
x 2 y 2 r 2
Circles & Points of
Intersection
Distance formula used to find the radius
( x
1
x
2
) 2 ( y
1
y
2
) 2 r
Circles
Example 1
Write the equation of the circle with the point (4,5) on the circle and the origin as it’s center.
Example 1
Point (4,5) on the circle and the origin as it’s center.
( x
1
x
2
) 2 ( y
1
y
2
) 2 r
(4 0) 2 (5 0) 2
16 25 r
r
41 r x 2 y 2 41
Example 2
Find the intersection points on the graph of the following two equations x 2 y 2 25 y 2 x 2 x 2 (2 x 2) 2 25 x 2 4 x 2 8 x 4 25
(5 x 7)( x 3) 0
(5 x 7) 0 ( x 3) 0
5 x 2
5 x 2
8 x 4 25
8 x 21 0 x
7
5 x 3
Now what??!!??!!??
Example 2
Find the intersection points on the graph of the following two equations x 2 y 2 25 y 2 x 2 x
7
5 x 3
Plug these in for x
.
Example 2
Find the intersection points on the graph of the following two equations x 2 y 2 25 x
7
5 y 2( y
7
5
) 2
24
5 y 2 x 2 x 3 y 2( 3) 2 y 4
7
5
,
24
5
3, 4
Ellipses
Ellipses
Examples of Ellipses
Ellipses
Horizontal Major Axis
FOCI
(-c,0) & (c,0)
CO-VERTICES
(0,b)& (0,-b)
CENTER (0,0) x 2 a 2
y 2 b 2
Vertices
(-a,0) & (a,0)
1
Ellipses
Vertical Major Axis
FOCI
(0,-c) & (0,c)
CO-VERTICES
(b, 0)& (-b,0)
CENTER (0,0) x 2 b 2
y 2 a 2
1
Vertices
(0,-a) & (0, a)
Ellipse Notes
Length of major axis = a (vertex & larger #)
Length of minor axis = b (co-vertex & smaller#)
To Find the foci (c) use: c 2 = a 2 b 2
Ellipse Examples
Find the Foci and Vertices x 2
144 y 2
169
0 a vertices a 13 vertices (0,13),(0, 13) c 2 c 2
a 2 b 2
169 144 c 2 25 c 5 foci (0,5),(0, 5)
Ellipse Examples
Find the Foci and Vertices x 2
81
y 2
9
0 a vertices a 9 vertices (9,0),( 9,0) c 2 c 2
a 2
81 9 b 2 c 2 72 c 72 foci ( 72,0),( 72,0)
Write an equation of an ellipse whose vertices are (-5,0) & (5,0) and whose co-vertices are (0,-3) & (0,3). Then find the foci.
a 5 a 2 b 3 b 2 x 2
25
9
c 2 c c
2
2 foci
a 2 b 2
25 9
16
c 4
(4,0),( 4,0)
25 y
9
2
1
Write the equation in standard form and then find the foci and vertices.
49 x 2 64 y 2 3136 c 2 a 2 b 2
49 x 2
3136 x 2
64
64 y 2
3136
3136
3136 c 2 c 2
15
64 49 c 15
y 2
49
1 vert .
(8,0),( 8,0) foci ( 15,0),( 15,0)
The Hyperbola
Hyperbola Examples
Hyperbola Notes
Horizontal Transverse Axis
Center (0,0)
Asymptotes
Vertices (a,0) &
(-a,0)
Foci (c,0) &
(-c, 0)
Hyperbola Notes
Horizontal Transverse Axis
Equation x 2 a 2
y 2 b 2
1
Foci : c 2 a 2 b 2
Hyperbola Notes
Horizontal Transverse Axis
To find asymptotes y y
b a
b x x a
Hyperbola Notes
Vertical Transverse Axis
Center (0,0)
Vertices (a,0) &
(-a,0)
Asymptotes
Foci (c,0) &
(-c, 0)
Hyperbola Notes
Vertical Transverse Axis
Equation y 2 a 2
x 2 b 2
1
Foci : c 2 a 2 b 2
Hyperbola Notes
Vertical Transverse Axis
To find asymptotes y y
a b
a x b x
Write an equation of the hyperbola with foci (-5,0) & (5,0) and vertices
(-3,0) & (3,0) a = 3 c = 5 c 2 a 2 b 2
5 2 3 2 b 2
25 9 b 2 b 2 16 x 2
9
y
16
2
1
Write an equation of the hyperbola with foci (0,-6) & (0,6) and vertices
(0,-4) & (0,4) a = 4 c = 6 c 2 a 2 b 2
6 2 4 2 b 2
36 16 b 2 b 2 20 y 2
16
x 2
20
1
Translations
What happens when the conic is NOT centered on
(0,0)?
Translations
Circle
( x h ) 2 ( y k ) 2 r 2
Translations
Parabola
( y k )
( x h )
4 p ( x h ) or
4 p ( y k )
Translations
Ellipse
( x h ) 2 a 2
( y k ) 2 b 2 or
1
( x h ) 2 b 2
( y k ) 2 a 2
1
Translations
Hyperbola
( x h ) 2 a 2
( y k ) 2 b 2 or
1
( y k ) 2 a 2
( x h ) 2 b 2
1
Translations
Identify the conic and graph
( x 1) 2 ( y 2) 2 3 2 r= 3 center (1,-2)
Translations
Identify the conic and graph
( x 2) 2
3 2
( y 1) 2
2 2
1
Translations
Identify the conic and graph
( x 3) 2
1 2
( y 2) 2
3 2
1 center asymptotes vertices
Translations
Identify the conic and graph
( x 2) 2 4 ( 1)( y 3)
Conic center
Completing the Square
Here are the steps for completing the square
Steps
1) Group x 2 + x, y 2 +y move constant
2) Take # in front of x, ÷2, square, add to both sides
3) Repeat Step 2 for y if needed
4) Rewrite as perfect square binomial
Completing the Square
Circle: x 2 +y 2 +10x-6y+18=0 x 2 +10x+____ + y 2 -6y=-18
(x 2 +10x+25) + (y 2 -6y+9)=-18+25+9
(x+5) 2 + (y-3) 2 =16
Center (-5,3) Radius = 4
Completing the Square
(
Ellipse: x 2 +4y 2 +6x-8y+9=0 x 2 +6x+____ + 4y 2 -8y+____=-9
(x 2 +6x+9) + 4(y 2 -2y+1)=-9+9+4
(x+3) 2 + (y-1) 2 =4 x
4
3) 2
( y 1) 2
1
1
C: (-3,1) a=2, b=1
Classifying Conics
Classifying Conics
Given in General Form
Ax 2 Bxy Cy 2 Dx Ey F 0
Classifying Conics
Given in General Form
Ax 2 Bxy Cy 2 Dx Ey F 0
Classifying Conics
Given in general form, classify the conic
5 x 2 2 y 2
A 5
B 0
C 2
20 x 4 y 24 0
B 2
0 2
4 AC
4(5)(2)
40
Ellipse
Classifying Conics
Given in general form, classify the conic y 2 8 x 12 y 0
A 0
B 0
C 1
B 2
0 2
4 AC
4(0)(1)
0
Parabola
Classifying Conics
Given in general form, classify the conic
24 x 2 18 y 2 18 0
A 24
B 18
C 0
B 2 4 AC
0 2 4( 24)(18)
1728
Hyperbola
Classifying Conics
Given in general form, classify the conic
16 xy 0
A 0
B 1
C 0
B 2 4 AC
( 1) 2 4(0)(0)
1
Hyperbola
Classifying Conics
Given in General Form
Then
Ellipse
Circle
Classifying Conics
Given in General Form
Then
Classifying Conics
Given in General Form
Then
Hyperbola