File
advertisement

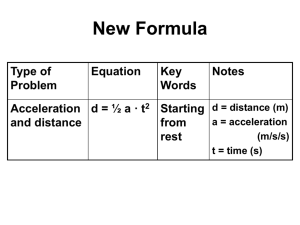
Physics Activity #4 9/30/14 Objective: To measure the acceleration of gravity in the lab, by using two different methods. Pre Lab: Use the “Acceleration and Distance” formula and solve for a. Given: d = ½ a · t2 Solve for a Materials: Ping Pong ball 2 Meter Sticks Stopwatch Procedures: (Part 1) 1. Find a location suitable for dropping your ping pong ball to minimize the relative fraction of time it takes to start and stop the stopwatch. 2. Measure the distance the object will fall in meters. The tennis ball should start from 0.75 m and reach 2.00 m by 0.25 m increments 3. Time the object's fall 5 times from each distance and record in the data table. *** NOTE: The person that drops the ball should also time it!!! *** Data: [in Excel] Drop Time Time Time Time Time Distance 1 2 3 4 5 (m) (s) (s) (s) (s) (s) 0.75 1.00 1.25 1.50 1.75 2.00 Ave. Time (s) In Excel or by calculator Calculate: Average times Acceleration at each height Final velocity as it hits the ground Lab Day 2 10/1/14 Title and Names Objective: To measure the acceleration of gravity in the lab, by using two different methods. Materials: (Part 1) Ping Pong ball 2 Meter Sticks Stopwatch Materials: (Part 2) Go Motion Sensor Ping Pong Ball Computer Lab Day 3 10/2/14 Review Check off and go over Procedures: (Part 2) Turn on the computer & open up “Logger Pro” Plug in the Go Motion Sensor Place sensor on ground Hold ping pong ball over the sensor between 1.5 - 2.0 m and just off to the side 5. Click on “Collect” wait 1 second then drop the ball without moving your hand 6. Once the ball hits the ground click on “Stop” 7. Save you data EXCEL (time and position only) as part of your lab report 1. 2. 3. 4. Data: (Part 2) A GOOD data trial Copy and paste time and position data into Excel Calibrate time and position to zero Calculate the velocity in Excel Graphs: (Part 2) 2 Graphs in Excel Trendlines should be on both graphs d-t graph Poly. 2 trendline With the equation v-t graph Linear trendline With the equation Analysis Find the percent error for all trials (6 total) Where g = -9.80 m/s2 (actual value) Conclusion: [In paragraph form] Compare the 2 methods for finding the acceleration of gravity Compare you percent errors from part 1 to part 2 (was one method more accurate then the other) Explain what your graphs mean What errors were in this activity?