THE PERIODIC TABLE
advertisement

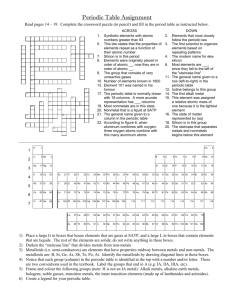
OUTLINE History of Periodic Table Periodic Table Organization Period Group/Family Representative Elements Transition Elements Inner Transition Elements Types of Elements Metals Nonmetals Metalloids HISTORY OF PERIODIC TABLE By the Mid-1800s, there were 65 known elements. Scientists began to recognize patterns after recording information such as: chemical reactivity (ex: bonding patterns) physical properties (ex: state of matter, mass) HISTORY . . . DMITRI MENDELEEV (1834-1907) Wrote out elements in order of increasing ATOMIC MASS, and ended up with a table! Now organized according to: ATOMIC NUMBER NUMBER OF ELECTRONS Why “PERIODIC”? Periodic means repeating patterns and properties. PERIODIC TABLE ORGANIZATION The periodic table is arranged in rows and columns. PERIOD Horizontal rows on table 7 in total Atomic Mass and Atomic Number increase from LEFT TO RIGHT ORGANIZATION . . . GROUP Also known as FAMILY Vertical columns on table Elements of the same group have similar but not identical properties. There are two number systems for groups: CURRENT: OLD: 1-18 ROMAN NUMERALS IA – VIIIA IB - VIIIB ORGANIZATION . . . GROUP 1 – Alkali Metals LINK Soft, silver, react violently with water GROUP 2 – Alkaline Earth Metals Shiny, silver, light, reactive GROUP 17 – Halogens Extremely reactive, poisonous GROUP 18 – Noble Gases INERT Not reactive under normal laboratory conditions ORGANIZATION Organization . . . REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS AKA Group A elements Groups IA-VIIIA, or 1, 2, 13-18 These elements illustrate the ENTIRE RANGE OF PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS. ORGANIZATION . . . TRANSITION ELEMENTS AKA Group B elements Group IB-VIIIB, or the “lower” groups Metallic elements that exhibit some different properties due to their electron arrangements. ORGANIZATION . . . INNER TRANSITION ELEMENTS Removed from the main table as a matter of convenience in organizing table Two names: 57-71 LANTHANIDES (rare earth) 89-103 ACTINIDES (radioactive) TYPES OF ELEMENTS 1 2 3 H He 1 2 Li Be B C 3 4 5 Na Mg 11 4 K 19 5 7 Ca Sc O F Ne 6 7 8 9 10 Al Si P S Cl Ar 13 14 15 16 17 18 Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 23 24 35 36 I Xe 53 54 20 21 22 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In 39 40 41 42 49 Hf Ta W 72 73 74 37 6 12 N 38 Cs Ba 55 56 Fr Ra 87 88 * W Nonmetals 25 26 27 28 29 30 METALS 43 44 Re Os 75 76 47 45 46 Ir Pt Au Hg Tl 77 78 81 79 48 31 80 32 33 34 Sn Sb Te 50 51 Pb Bi 82 83 52 Po At Rn 84 85 86 Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt 104 105 106 107 108 Metalloids 109 La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 57 58 59 Ac Th Pa 89 90 91 60 U 92 61 62 63 64 65 66 Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf 93 94 95 96 97 98 67 68 69 70 71 Es Fm Md No Lr 99 100 101 102 103 TYPES OF ELEMENTS There are three types of elements on the periodic table: Metals Nonmetals Metalloids The STAIRCASE LINE on the periodic table divides the METALS and the NONMETALS. The ratio of metals to nonmetals is about 4:1. METALS Substances found on the Left Hand Side of the staircase on the periodic table. Physical properties include: Shiny Solids at room temperature (except Hg) Good conductors of electricity Ductile (can be stretched into wire) Malleable (can be hammered in shapes) NON-METALS Substances found on the Right Hand Side of the staircase on the periodic table. Physical properties include: Dull Brittle S, L, or G at room temperature Poor conductors/good insulators METALLOIDS AKA semi-metals Substances that are found ON the staircase on the periodic table. Have properties of BOTH metals and nonmetals. In general, Hard, but sometimes brittle Solid High melting points Weak (or not at all) conductors of electricity HYDROGEN The “rebel” of the periodic table! It does not really “belong” anywhere. Hydrogen is usually located on the top left hand corner of the table, even though it has both metallic and nonmetallic properties. HOMEWORK 1. 2. What do calcium chloride, potassium bromide, and magnesium oxide have in common? (Hint: the answer is NOT that they end in “-ide”!) Give an example of each of the following: 1. Alkali metal 2. Halogen nonmetal 3. Transition element 4. Lanthanide 5. Representative element 6. Noble gas 7. Alkaline Earth Metal 8. Inner Transition element 9. Metalloid 10. Actinide