AP Exam review tips ppt
advertisement

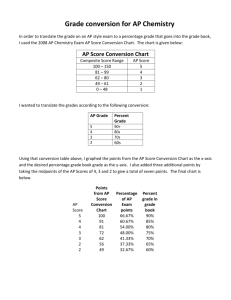
AP Macroeconomics MR. Graham Preparing for the AP Exam Module 44½: What to Expect on the AP Exam 2 The Exam • Multiple-Choice Section (2/3 of final score) – 60 questions, 70 minutes – Plan on answering 15 questions per 15 minutes— write timing on your test – TIPS: • Select the best answer • Answer easy questions first • Skip questions that are completely unfamiliar • No “guessing penalty,” so don’t leave any blank The Exam • Multiple-Choice Section (2/3 of final score) – Basic Economic Concepts 8-12% – Measurement of Economic Performance 12-16% – National Income and Price Determination 10-15% – Financial Sector 15-20% – Stabilization Policies 20-30% – Economic Growth 5-10% – International Trade and Finance 10-15% The Exam • Free-Response Section (1/3 of score) – 3 questions, 60 minutes (including 10-minute reading period) – Plan on spending 25 minutes answering question 1 and 12.5 minutes answering questions 2 and 3— write timing on your test – TIPS: • Models can provide or enhance an explanation to be correctly labeled) • Number your responses (e.g. “2 (c) ii”) • Answer need to be definite and consistent (need 2009 AP MACROECONOMICS FREE-RESPONSE QUESTION The Exam 2009 AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Question • What are students asked to do? – (a) Using model, show… – (b) Calculate. – (c) What OMO? – (d) Using model, show… – (e) How will…? Explain. – (f) What will happen to: i) and ii)? Explain. The Exam 2009 AP Macroeconomics Free-Response Question • Guess how many points for each part? (a) Using model, show… (a) 2 points (b) Calculate. (b) 1 point (c) What OMO? (c) 1 point (d) Using model, show… (d) 2 points (e) How will…? Explain. (e) 2 points (f) What will happen to: i) and ii)? Explain. (f) 3 points Scoring Breakdown • Multiple-Choice Section – 60 points (1 point per question) • Free-Response Section – 30 points (15 points for 1, 7.5 points for 2 and 3) AP Score Conversion Chart Macroeconomics (2000) Composite Score Range AP Score 72-90 5 58-71 4 50-57 3 36-49 2 0-35 1 Module 44¾: All the Graphs You Need to Know 12 The Circular-Flow Diagram The Production Possibilities Curve Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium The Money Market The Loanable Funds Market The Foreign Exchange Market Module 45: Putting It All Together 19 A Starting Point • To analyze any situation, you have to know where to start… The Pivotal Event – This might be a change in the economy or a policy response to the “starting point”. The Initial Effect of the Event – The “pivotal event” will generally have some initial, short-run effects. The Long-Run Effects of the Event – We know that in the long run, monetary policy affects only the aggregate price level, not real GDP. – Because money is neutral, changes in the money supply have no effect on the real economy. – The aggregate price level and nominal values will be affected by the same proportion, leaving real values (including the real interest rate as mentioned in our scenario) unchanged. Analyzing our Scenario Sample Question—“A Structure for Macroeconomic Analysis” • What are students asked to do? 1. Using model, show… 2. What OMO? 3. Using model, show… 4. Using model, show…Explain. 5. Using model, show… 6. What will…? 7. How will…? Explain. Analyzing Our Scenario 1. “Draw a correctly labeled graph showing aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, long-run aggregate supply, equilibrium output, and the aggregate price level” 2. “Identify the open-market operation the Fed would conduct” The Fed would sell U.S. Treasury securities Analyzing Our Scenario 3. “Draw a correctly labeled graph of the money market to show the effect of the monetary policy on the nominal interest rate.” Analyzing Our Scenario 4. “Show and explain how the Fed’s actions will affect equilibrium in the aggregate demand and supply graph you drew previously. Indicate the new aggregate price level on your graph.” A higher interest rate will lead to decreased investment and consumer spending, decreasing aggregate demand. The equilibrium price level and real GDP will fall Analyzing Our Scenario 5. “Draw a correctly labeled graph of the foreign exchange market for the U.S. dollar showing how the change in the aggregate price level you indicate on your graph above will affect the foreign exchange market.” The decrease in the U.S. price level will make U.S. exports relatively inexpensive for Canadians to purchase and lead to an increase in demand for U.S. dollars with which to purchase those exports Analyzing Our Scenario 6. “What will happen to the U.S. dollar relative to the Canadian dollar?” – The U.S. dollar will appreciate. 7. “How will the Federal Reserve’s contractionary monetary policy affect the real interest rate in the United States? Explain.” – There will be no effect on the real interest rate in the long run because, due to the neutrality of money, changes in the money supply do not affect real values in the long run.