low pressure - Mercer Island School District
advertisement

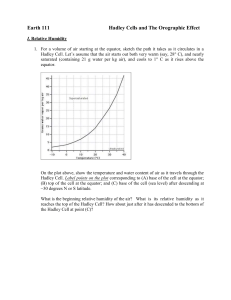
1. The land at the equator has the highest average annual temperatures primarily due to the fact that It h as th e re . .. rp ai hi g he st hi g th e as It h he st hu m id at is su n da y Th em id It i it. .. o. . m a th e o se rt lo sc A. It is closer to the sun B. The midday sun is at a more direct angle (closer to 90°) on average. C. It has the highest humidity level D. It has the highest air pressure su n 25% 25% 25% 25% 2. On December 21 at midday, the sun is directly over head which latitude? 30 °N 23.5 °N (Tropic of Cancer) 0 ° (the Equator) 23.5 °S (Tropic of Capricorn) 30 °S °S 30 ap r ic fC co ro pi (T °S 23 .5 or n) or ) qu at (th ° 0 °N (T ro pi co eE fC 30 an ce r) °N 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 23 .5 A. B. C. D. E. rc on di ti e de cr ea s e th Bo Bo th in cr ea s ea se .. . on er s in cr de cr on er s Ai Ai rc on di ti A. Air conditioners decrease the relative humidity and furnaces increase it. B. Air conditioners increase the relative humidity and furnaces decrease it. C. Both increase D. Both decrease ea s.. . 3. Which of the following is correct about how cooling air, such as with an air conditioner, and heating air, such as with a furnace, affects the relative humidity of the air? 25% 25% 25% 25% Cold air = lower water vapor capacity Relative Humidity= the percentage of water vapor in the air as a percentage of the maximum it can hold at that temperature. 10 °C air can hold 8 g/kg 20 °C air can hold 15 g/kg If 7 g/kg then 88% relative humidity for 10 ° C. 7 g/kg is 47 % relative humidity in 20 °C air. Cooling increases relative humidity and can lead to precipitation if increases above 100% 30 °C air can hold 27 g/kg 7 g/kg is 26% relative humidity for 30 ° C air. Heating decreases the relative humidity, if no additional source of water vapor. 4. Which type of air pressure is often associated with precipitation, and why? r; ai Lo w Lo w ai rr pr ise es . .. su re ;a Hi ir gh sin pr ks es a. su . re ;a i rr Hi ise gh sa pr es n. su .. re ;a ir s in ks a. . 25% 25% 25% 25% pr es su re A. Low pressure air; air rises and cools in the upper troposphere B. Low pressure; air sinks and cools as it moves closer to Earth C. High pressure; air rises and cools in the upper atmosphere D. High pressure; air sinks and cools as it moves closer to Earth. Low pressure zones are created when hot air rises. (As air rises there is less pressure at the Earth’s surface). But as that warm air rises, it cools in the upper atmosphere. The colder air can no longer hold as much moisture, which can result in precipitation. At an altitude of 10 km in the troposphere, the average temperature is – 60 °C. COOLING in the Upper Atmosphere leads to Condensation and Precipitation HEATING at the Surface of the Earth leads to air expanding and rising creating a LOW PRESSURE zone. 5. Water has a _____ specific heat, which means that compared to most other substances it require ________ energy to increase its temperature. 25% or e m gh ; hi hi gh ; or e ;m w lo ;l w 25% le ss 25% es s low; less low; more high; less high; more lo A. B. C. D. 25% 6. The temperature of water will increase _______ compared to most other substances given an equal amount of energy and it tends to ______ temperatures. 25% 25% 25% 25% am pl ify le ss ; ify m pl or e; a m m od er a le ss ; or e; m od er at e te more; moderate less; moderate more; amplify less; amplify m A. B. C. D. 7. At a lake during the daytime, the wind usually blows _____ because of ______ pressure over the land. 25% 25% 25% 25% A. B. C. D. from the lake (sea breeze); low from the lake (sea breeze); high from the land (land breeze); low from the land (land breeze); high m fro e th la ke a (se m fro .. ze e e br e th l e ak a (se b ... e) z e re m fro e th l d an (l d an b m fro . e. z e re e th l d an (l d an b . z.. e re The land is warmer than water during the day. (sand/soil have lower specific heat- take less energy to heat than water/ greater temperature change with equal energy). This differential in heating results in lower pressure over the land. Air moves towards this lower pressure. At night, the water does not cool off as quickly as the land (retains its heat). Thus there is lower pressure over the sea at night. 8. In the Hadley convection cell, air _____ at the equator, creating a _____ pressure zone at the equator. h 25% r is es ;l ow sin ks ;l igh ks ;h 25% r is es ;h ig 25% ow 25% sinks; high sinks; low rises; high rises; low sin A. B. C. D. 0 9. In the Hadley convection cell, air begins to sink at latitudes of ____ N and S. Sinking air warms as it moves closer to the Earth and therefore 25% latitudes. 25% 25% precipitation is ________ likely25% at these es s 30 °; l e °; m or 30 °; l 23 .5 °; m or e es s 23. 5 °; more 23. 5 °; less 30 °; more 30 °; less 23 .5 A. B. C. D. 10. The term westerly winds comes from the fact that these winds 25% 25% 25% ep ic t ed ed ar c. . . in af te r ed am en ar m Jo hn he ds t ar to w ov e m an y w w th e n ei in at W e. .. es t es t 25% originate in the west move towards the west are named after John Westerly are depicted in many cowboy movies or ig A. B. C. D. 11. The Coriolis Effect causes wind and ocean currents to be deflected A. to the right in the northern hemisphere and the left in the southern hemisphere. B. to the left in the northern hemisphere and the right in the southern hemisphere C. to the right in both hemispheres D. to the left in both hemispheres th e to to th e rig is. .. he m le ft i n ht i n bo th bo th no r th e n le ft i th e to he m th er ... ... no rth th e n ht i rig th e to . .. 25% 25% 25% 25% On a piece of paper • Draw a sphere • Draw lines for the equator, 30° N and S, 60 ° N and S • Discuss with the person next to you how to draw the 6 major bands of prevailing winds Hints: Remember that the Coriolis effect deflects to the right in the Northern hemisphere To draw the bands between 0-30 °, remember that there is a LOW Pressure zone at the equator (due to Hadley cell) To draw the bands between 30 °-60 °, remember there is a high pressure zone at 30 °. 12. Recall the direction of the wind along the surface of the earth between 0 and 30 N (Hadley cell) and the deflection of the Coriolis effect. These combine for ________ winds in the 0- 30 N zone. 25% 25% 25% ut he as te rly es te r ly ut hw ea st er ly or th w es te r ly Northwesterly Northeasterly Southwesterly Southeasterly rth A. B. C. D. 25% 13. The Great Barrier Mountain Range in Australia is at a latitude of about 25° S. You would expect the _______ side of this mountain range to be rainier because it is on the ______ side. 25% 25% 25% ar d d ea st ; w in dw ar le ew ea st ; in dw w es t; w es t; le ew ar ar d d west; leeward west; windward east; leeward east; windward w A. B. C. D. 25% Note- in Australia (at 25S) the direction of the winds would be reversed from the diagram above since it is in the trade winds zone. See diagram below. Between 30 S and the equator- east side of mountains is the windward side. 14. The tropical rainforest has ___ soil due to _______. ut ... of n ng ec yc li ng o fa st r re cy c li r ic h; w ;s lo po or fn . .. u. .. go fn ... cli n tr ec y po s it io po or ;f as de co m w ;s lo po or fa st d ec om po sit i on .. 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% r ic h; A. rich; fast decomposition of dead organisms B. poor; slow decomposition of dead organisms C. poor ; fast recycling of nutrients D. poor; slow recycling of nutrients E. rich; fast recycling of nutrients 0 The hot, moist conditions in a tropical rainforest allow many living things, including decomposers, to thrive. Organic matter is quickly decomposed. However, these nutrients are quickly recycled into all living things. Thus most of the nutrients in a tropical rainforest are found in the living organisms. Note the very thin layer of dark organic matter in this tropical rainforest soil profile. 15. Which biome typically has the richest soil? A. B. C. D. Taiga Chaparral Grasslands Temperate Deciduous Forest E. Tundra uo u ec id eD nd ra Tu ss la Gr a pe ra t sF o. .. nd s l ra pa r Te m Ch a Ta iga 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 16. The two biomes with the lowest precipitation are the desert and the ________________ 1. grasslands 2. tundra 3. temperate deciduous forest 4. chaparral de cid l ar ra ch ap uo u sf or es t tu nd ra te te m pe ra gr as sla nd s 25% 25% 25% 25% Cold air can not hold much moisture. Due to this fact the tundra (and also to a lesser extent the taiga) receive very little precipitation. But due to the year round cold temperatures, the snow that does fall accumulates. 17. A TROPICAL deciduous forest is one that ______________ in order to conserve water in the ___________________ . ... ... ly; ua l es an n le av its ea v es an n ua l ly; le ... of ts l si es i ee dl es i ee dl ns te ad of le ... 25% 25% 25% 25% ns te ad A. has needles instead of leaves ; colder season B. has needles instead of leaves ; drier season C. sheds its leaves annually; colder season D. sheds its leaves annually; drier season Deciduous means to shed leaves. Tropical rainforests have broad leaved trees that are evergreen (do not shed their leaves) Note that we often use the terms coniferous and evergreen as synonyms since they are the cone-bearing trees are generally the only evergreen trees at our latitude. But these two terms are not the same. At latitudes near the tropics (23.5 N or S), where the temperatures are quite hot year round, but there is a more pronounced dry season. Tropical deciduous forests are often found near these latitudes. 18. What is the approximate relative humidity of air that is 30 °C and has 10 g/m3 of water vapor? A. B. C. D. 100 % 66 % 33 % 10 % 25% 25% 25% 25% 19. If the air cools to 10 C, (but still has 10 g/m3 of water vapor) its relative humidity Increases to 100 % Increases to 66% Stays the same Decreases to 10 % % st o 10 e m sa he 66 % st o 10 0% 25% 25% 25% 25% to A. B. C. D. 1. B 2. D 3. B 4. A 5. D 6. B 7. A 8. D 9. D 10.A 11.A 12.B 13.D 14.C 15.C 16.B 17.D 18.C 19.A