3.1 Introduction to Photosynthesis
advertisement

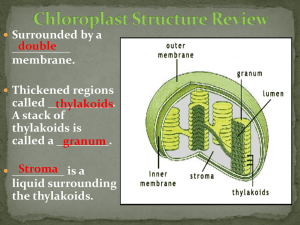
Photosynthesis Overview 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O(I) + light energy C6 H12 O6 (aq) + 6 O2 (g) Light Only 5% of the light that hits earth's surface is converted to organic compounds by photosynthesis. Light travels in wave packets called photons Light from the sun is a mixture of photons of different energies (called wavelengths, measured in nanometers). Photons are captured in plants by plastids (ex. Chloroplasts). Chloroplasts Functions: Photosynthesis factories for plants and algae Store excess glucose as starch Chloroplasts Structure: 2 membranes (like mitochondria) Interior space filled with stroma (protein-rich fluid) In the stroma are thylakoids (membrane bound sacs) The thylakoid membrane contains light gathering (photosynthetic) pigments Thylakoids Grana: stack of thylakoids (~60 grana per chloroplast with 30-50 thylakoids each) Lamellae: unstacked thylakoids that link grana together. Lumen: interior of the thylakoid, water- filled Pigments Green plants contain chloroplasts with the pigments chlorophyll a and b both absorb blue and red light and reflect green light, so we assume blue and red light is used in photosynthesis Chloropyhll a is used to transfer energy from light into chemical energy. Chlorophyll b is an accessory pigment. It absorbs photons that a misses. Accessory Pigments In addition to chlorophyll b there are other accessory pigments. Their job is to absorb light that can damage chlorophyll and lose it as heat instead. Carotenoids: appear yellow/orange (ie. Carrots). Betacarotene protects our eyes Xanthophylls: reflect yellow light, also found in the thylakoid Photosystems Photosynthetic pigments are embedded in the thylakoid membrane clustered in groups called photosystems. A photosystem contains a chlorophyll a molecule called a reaction centre, surrounded by accessory pigments called the antenna complex. The antenna complex harvests the light and passes it to the reaction centre. Photosystem Diagram PI (P700) and PII (P680) Two types of photosystems exist: Photosystem I (PI) and Photosystem II (PII). They have identical reaction centres, but they absorb light at slightly different wavelengths because of the proteins the reaction centre is associated with. The reaction center in PI is called P700; absorption peaks at 700nm. The reaction centre in PII is called P680, absorption peaks at 680nm. Photosystem Diagram