Period 4 1800-1848 - Marblehead High School
advertisement

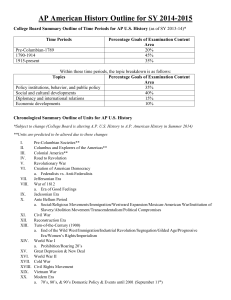
AP Review Session 4 • Agenda – Review Big Idea and Key Concepts for the Period. 15 Min – Consider connections to other time periods. 5 Min – Answer short answer questions from the time period – 10 Min • Share answers / Address good – Open for questions Period 4 1800-1848 • THE BIG IDEA: The new republic struggled to define and extend democratic ideals in the face of rapid economic, territorial, and demographic changes. • Key Concept 4.1: The United States developed the world’s first modern mass democracy and celebrated a new national culture, while Americans sought to define the nation’s democratic ideals and to reform its institutions to match them. • Key Concept 4.2: Developments in technology, agriculture, and commerce precipitated profound changes in U.S. settlement patterns, regional identities, gender and family relations, political power, and distribution of consumer goods. • Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European conflicts shaped the nation’s foreign policy and spurred government and private initiatives. Period 4 1800-1848 THE BIG IDEA: The new republic struggled to define and extend democratic ideals in the face of rapid economic, territorial, and demographic changes. • • • New Republic – Early Polit parties – Jefferson v. Hamilton, v Adams – 1812, Era of Good Feelings, Monroe Doctrine – Jackson – Manifest Destiny – Marshall Court Cases Democratic Ideals – Who has suffrage? – Republican Motherhood – Slavery v. Democratic Ideals Econ Changes – Growth of cotton industry – Start of manufacturing – Internal improvements debate • • Territorial Changes – LA Purchase – Misouri Compromise – Annexation of TX – Mex War Demographic Changes – Small scale immigration – Shift toward the west – Increased division between regions Key Concept 4.1: The United States developed the world’s first modern mass democracy and celebrated a new national culture, while Americans sought to define the nation’s democratic ideals and to reform its institutions to match them. • • Founding fathers to Jacksonian era – Generational power shift Jacksonian Democracy – Universal Manhood suffrage – Era of mass campaigning • Antebellum Reform Movements – Abolition – Women’s Rights – Seneca Falls – Temperance, Mann, Dix, Garrison, Mott • Second Great Awakening – Wave of Protestant Evangelical Fervor – New Denominations – Camp Meetings • Art / Literature of the Era – Hudson R. School – Romanticism (Irving, Longfellow, Hawthorne, Cooper) – Transcendentalism (Emerson, Thoreau) Key Concept 4.2: Developments in technology, agriculture, and commerce precipitated profound changes in U.S. settlement patterns, regional identities, gender and family relations, political power, and distribution of consumer goods. • Tech Changes of Era – Influence agriculture and commerce – Cotton Gin (1790s), Interchangeable parts, steam engines (ships), canals and later railroads – Textile Manufactures – Ex. Erie Canal impact on farming – Jackson and the Bank • Where people live C/T Colonial Era to Antebellum Era – Demographic center shifts west of Applachians – Manifest Destiny --- Expansion • Regional ID – Tension – How were regions different – Why was there tension between regions • Gender / Family Relations – – – – Women’s advocates / Seneca falls Republican Motherhood - Cult of Domesticity Emphasis on Romantic / Family love Care of children, definition of childhood Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European conflicts shaped the nation’s foreign policy and spurred government and private initiatives. • • • • • Wash – Neutrality Barbary War Embargo / War of 1812 Monroe Doctrine Mex Am War Connections (Context / Synthesis) • • • • • • • • • • • LA Purchase v. Mex War v. Alaska v. Span Am War Antebellum Reform v. Progressive Era Republican Motherhood – Cult of Domesticity – Settlement Houses – 19th Amendment – Betty Friedan – Title IX – ERA 1st v. 2nd Great Awakening v. 1920s Creationism v. 1980s Wave of Protestant Evangelical Fervor For Policy – Neutrality – Monroe – Roosevelt Corollary – Big Stick, Dollar Diplomacy, Wilson, WWII Neutrality, Containment, Truman Doctrine, Bush Doctrine Voting Rights - Jackson Era – Freedmen / Reconstruction – Women’s Suffrage – Civil Rights Era – Contemporary Undocumented Immigrant Status debate Political Parties - Change through the eras Agriculture Manufacturing Service Econ / Intel – Different Eras / Different Industries Jackson Era Indian Removal Colonial Era / Late 1800s Internal Migrations – Dustbowl, Suburbs, Sun belt Indian Removal compared to other nations dealing with internal groups – Australia / Mexico / Israel / Russia / Rwanda Short Answer Questions • • • • 4 – Questions 20% of test Each question has 3 parts (Easy, Moderate, Difficult) Answers must be in sentences, but no grammar grading. (Must have a verb) • Answers do not need to be in paragraphs. • Answers MUST fit in the box. • Often address Point of View, Interpretation, Factual Knowledge. • Go to http://mhs.marbleheadschools.org/teachers/mtangney/apushistory • Click on AP Review Session Practice Answers - Write your answer on one particular slide. • Practice Short Answer Question - Per 4 • A. Briefly explain ONE Supreme Court case during the Marshall court that asserted federal power over state laws. • B. Briefly explain another Supreme Court case during the Marshall court that asserted federal power over state laws. • Briefly explain an effect or challenge in enforcement of ONE of the aforementioned court cases in the period 1800-1848. • • • • Using this 1833 image, address all three of the following parts: A. Briefly explain the point of view about the National Bank from the perspective of the author B. Briefly explain ONE development from the period 1800-1848 that could be used to support the point of view expressed by the author. C. Briefly explain ONE development from the period 1800-1848 that could be used to challenge the point of view expressed by the artist.