Evaporation
H2O(g)
molecules
(water vapor)
H2O(l)
molecules
Evaporation
H2O(g)
molecules
(water vapor)
H2O(l)
molecules
Evaporation
H2O(g)
molecules
(water vapor)
H2O(l)
molecules
How Vapor Pressure is Measured
760 mm + 120 mm = 880 mm Hg
1 atm = 760 mm Hg
Animation by Raymond Chang
All rights reserved
Manometer
Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 401
Atmospheric Pressure
760 mm Hg
Manometer A
BIG
=
small
+
height
760 mm =
________
small
120 mm
+ __________
Small = 640 mm Hg
h = 120 mm
?
Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 401
760 mm Hg
Manometer B
BIG
=
small
+
height
BIG
760 mm + _________
120 mm
= ________
BIG = 880 mm Hg
h = 120 mm
?
Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 401
The Manometer and Vapor
Pressure
Barometer & Manometer
atmospheric pressure
= 101.3 kPa
atmospheric pressure
= 100.4 kPa
atmospheric pressure
= 101.7 kPa
750 mm
confined
gas
600 mm
confined
gas
confined
gas
500 mm
325 mm
200 mm
(a)
150 mm
(b)
(c)
100 mm
(d)
Pressure and Temperature
STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure)
standard temperature
0 oC
273 K
standard pressure
1 atm
101.3 kPa
760 mm Hg
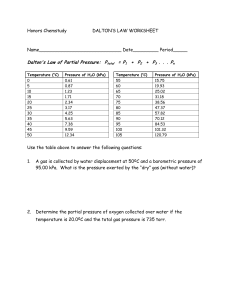
Equations / Conversion Factors:
K = oC + 273
oC = K – 273
1 atm = 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg
Convert 25oC to Kelvin.
K = oC + 273
25oC + 273 =
298 K
How many kPa is 1.37 atm?
X kPa = 1.37 atm
101.3 kPa
= 138.8 kPa
1 atm
How many mm Hg is 231.5 kPa?
X mm Hg = 231.5 kPa
760 mm Hg
= 1737 mm Hg
101.3 kPa
AIR
PRESSURE
CONFINED
GAS
higher
pressure
Pa
manometer: measures the
pressure of a confined gas
Hg HEIGHT
DIFFERENCE
small
96.5 kPa
Atmospheric pressure is 96.5 kPa;
mercury height difference is 233 mm.
Find confined gas pressure, in atm.
BIG
1.26
X atm
SMALL + HEIGHT = BIG
233 mm Hg
96.5 kPa + 233 mm Hg = X atm
96.5 kPa
1 atm
101.3 kPa
+ 233 mm Hg
0.953 atm + 0.307 atm = X atm
X = 1.26 atm
1 atm
= X atm
760 mm Hg
Vapor Pressure
measure of the tendency for liquid particles to enter
gas phase at a given temp.
a measure of “stickiness” of liquid particles to each other
more
“sticky”
less likely to
vaporize
In general:
LOW v.p.
not very
“sticky”
more likely to
vaporize
In general:
HIGH v.p.
NOT all liquids have same v.p. at same temp.
100
CHLOROFORM
80
PRESSURE 60
(kPa)
40
ETHANOL
20
WATER
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
TEMPERATURE (oC)
Volatile substances evaporate easily (have high v.p.’s).
BOILING when vapor pressure = confining pressure
(usually from atmosphere)
atmospheric pressure is 101.3 kPa
b.p. = 78oC
b.p. = 100oC
Vapor Pressure
61.3oC
101.3
78.4oC
100oC
Pressure (KPa)
93.3
80.0
66.6
53.3
40.0
26.7
13.3
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Temperature (oC)
80
90 100
BOILING when vapor pressure = confining pressure
(usually from atmosphere)
At sea level and 20oC…
AIR PRESSURE
(~100 kPa)
VAPOR
PRESSURE
(~5 kPa)
VAPOR
PRESSURE
(~10 kPa)
ETHANOL
WATER
NET
PRESSURE
(~95 kPa)
NET
PRESSURE
(~90 kPa)
ETHANOL
WATER
Water
Molecules in
Liquid and
Steam
Microscopic view of a liquid
near its surface
The high energy
molecules escape
the surface.
Behavior of a liquid in a closed
container
Water rapidly boiling on a stove
Pressure Cooker
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Benjamin Cummings. All rights reserved.
120oC
Formation of a bubble is opposed by
the pressure of the atmosphere
Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 452
Vapor Pressure
61.3oC
101.3
78.4oC
100oC
Pressure (KPa)
93.3
80.0
66.6
53.3
40.0
26.7
13.3
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Temperature (oC)
80
90 100
Boiling Point and Pressure
Heating / Cooling Curve of Water
140
steam
Temperature (oC)
120
water and steam
100
liquid water
80
60
40
ice and
water
20
0
ice
-20
Heat added at a constant rate
Gas Collected Over Water
Measuring the Vapor Pressure
of a Liquid
Davis, Metcalfe, Williams, Castka, Modern Chemistry, 1999, page 376
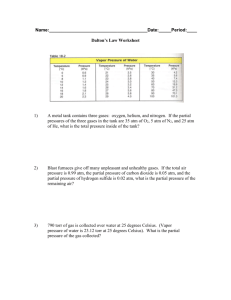
Gas Mixtures
and Dalton’s
Law
Gases Dissolved
in Liquids