Reactions in Aqueous Solutions

9.1 Net Ionic Equations and
Qualitative Analysis
Learning Goals …
… write an ionic and net ionic equation
… use qualitative analysis (flame test, solution colour and solubility) to identify ions in a solution
Let’s take a closer look at the reaction between
NaCl
(aq)
+ AgNO
3 (aq)
NaNO
3 (aq)
+ AgCl
(s)
What actually happened?
Cl -
(aq)
+ Ag +
(aq)
AgCl
(s)
SPECTATOR
IONS
The Na + and NO
3
are still in the solution
A chemical equation written without the spectator ions is called a net ionic equation . A net ionic equation includes only those ions or compounds that undergo chemical change.
TYPES OF EQUATIONS i.
Balanced Chemical equation ii.
Ionic equation iii.
Net ionic equation
Zinc + sodium chloride phosphate zinc + sodium phosphate chloride i.
Na
3
PO
4(aq)
Zn
3
(PO
4
)
2 (s)
+ NaCl
(aq) ii.
iii.
3Zn +2
(aq)
+ 6Cl -
(aq)
+ 6Na +
(aq)
+ 2PO
4
-3
(aq)
Zn
3
(PO
4
)
2(s)
6Na +
(aq)
+
+ 6Cl -
(aq)
3Zn +2
(aq)
+ 2PO
4
-3
(aq)
Zn
3
(PO
4
)
2(s)
Spectator ions: Na + and Cl -
No w you try one …
Lead (II) + sodium nitrate sulfide
Lead (II) + sodium sulfide nitrate i.
Pb(NO
3
)
2 (aq)
+ Na
2
S
(aq)
PbS
(s)
+ NaNO
3(aq) ii.
Pb +2
(aq)
+ 2 NO
3
-
(aq)
+ 2Na +
(aq)
+ S -2
(aq)
PbS
(s)
+
2Na +
(aq)
+ 2NO
3
-
(aq) iii. Pb +2
(aq)
+ S -2
(aq)
PbS
(s)
Spectator ions: Na + and NO
3
-
Qualitative Analysis
• Qualitative Analysis identifies a substance in a sample by observation of physical and chemical properties.
• You can often identify whether a cation ion is in a sample by observing one or more of the following:
• Flame Test results
• solution colour
• precipitates formed with select aqueous solutions.
• Qualitative analysis can tell you what ions are present in a solution.
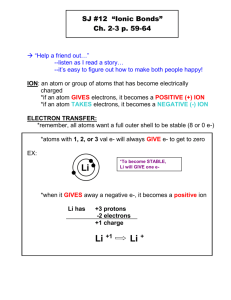
1. Flame Test
Uses the colour that a sample produces in a flame to identify the metal ion in the sample
Flame Colours of Some Metals
Ion
Li +
Na +
K +
Cs +
Ca 2+
Sr 2+
Cu 2+
Pb 2+
Colour
Crimson Red
Yellow-orange
Purple
Blue
Red-orange
Bright red
Bluish-green
Bluish-white
Fast forward video file to 25 seconds in…
2. Colours of Ions in Solution
Uses the colour of a solution to identify the metal ion in the sample
Ion
Cr 2+
Cu 2+
Cr 3+
Cu +
Fe 2+
Ni 2+
Fe 3+
Co 2+
Mn 2+
Pb 2+
Colour blue green
Pale yellow
Pink
Bluish-white
3. Precipitate Formation
Uses the solubility properties of ions to identify an unknown ion. We can add a known reactant to a solution and observe whether a precipitate forms.
Let’s say we wanted to precipitate Pb 2+ out of a water sample…
Let’s look at our Solubility Table …
Lead (II) ions can be precipitated with sulfate ions to yield solid lead (II) sulfate.
Pb 2+ + SO
4
2 PbSO
4
(s)
We can filter off the precipitate and separate it out of the solution.
SO
4
2could be obtained from a solution of Na need a nonreactive cation)
2
SO
4
(we would
Ex) An ion in solution forms a yellow precipitate when sodium iodide, NaI (aq), is added to the solution. The precipitate produces a blue-white colour when it is heated in a flame. What metal ion might be present in the solution?
According to the Solubility Rules ,
iodides are soluble except if it contains Pb 2+ , Ag + , and
Hg + and Hg
2
2+ . So the ion must be one of these four.
We can then look to the
results to narrow the ion down.
Pb 2+ has a blue-white flame so this must be the ion present.
CAN I …
… write an ionic and net ionic equation
… use qualitative analysis (flame test and solubility) to identify ions in a solution
HOMEWORK
p410 #5-10 p414 #12-14
Flame Colours of Some Metals
Ion
Li +
Na +
K +
Cs +
Ca 2+
Sr 2+
Cu 2+
Pb 2+
Colour
Crimson Red
Yellow-orange
Purple
Blue
Red-orange
Bright red
Bluish-green
Bluish-white