Dating - mssarnelli

Earth’s Age +
Evidence
WARM UP
• Write your homework – leave it to be stamped!
• Get your homework out to be checked!
• Update your Table of Contents for today!
• Get something to grade your Vocab Quiz with!
Date Session
#
11/15
&
11/18
7
Activity
Earth’s Age & Evidence Note guide
Page
#
13
The Great Fossil Find Poster Instructions 14
Notes Tips for Today
• Anything in yellow you MUST write on your note guide
• Pictures and diagrams are great things to draw to help you remember vocab and ideas!
• Underlined or bold words that are underlined or bold in PowerPoint
BECAUSE THEY ARE IMPORTANT !
How old is the
Earth?
Earth is around 4.6
BILLION years old.
BIG QUESTION:
HOW DO WE KNOW
HOW OLD THE
EARTH IS?
BIG ANSWER:
Everything coming up in the next few lessons provides an answer to the
BIG QUESTION!
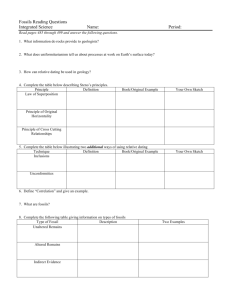
Law of Superposition
• Law of Superposition –
• Under normal conditions, the layers of sediment get older the deeper you go
Examples of Law of
Superposition
• Just like a layered cake…you put the bottom layer down first, so it is the “oldest” and you fill in each layer on top of it! What examples can you come up with?
Draw your own picture illustrate the concept!
We Have a Problem…
• There are several things can mess up the Law of Superposition called unconformities
Types of unconformities:
1 – intrusion
2 – overturning
3 - faults
Unconformity
• Unconformity-
• A break or an irregularity in the geologic time sequence due to a geologic event.
• “Missing Information”
1. Intrusion
• An intrusion is igneous rock that cuts through layers of sedimentary rock.
• The intrusion is younger than any other rock layer it cuts through.
intrusion
2. Overturning
• Overturning is when rock layers are folded due to gravity, erosion, or shifts in Earth’s crust.
3. Faults
• Faults are cracks, fractures or shifts in Earth’s crust
Fault
Law of Superposition
Practice
Which type of unconformity do you see in the diagram?
Can you put the layers in order from oldest to youngest?
Law of Superposition
Practice
Which types of unconformity do you see in the diagram?
Can you put the layers in order from youngest to oldest?
What is This?
Fossils
• Fossil – traces or remains of living things from long ago that help sort out the sedimentary rock record
• Index Fossils – common fossils that are used as a “reference” to date other fossils
Types of Fossils
• BrainPOP Video
The Great Fossil Find
• Choose a partner to work with…I will give you 1 minute to move all of your stuff so that you are sitting with your partner and be ready to listen!
• Work together to determine what type of animal your fossil is! The activity guide must be turned in by the end of class! http://www.indiana.edu/~ensiweb/lessons/g r.fs.fd.html
Homework
1.
Bring a bag of
Skittles next class!
2.
The Great Fossil
Find Poster due in 2 classes!
Warm-Up
• Write your homework – get it stamped!
• Update your Table of Contents for today!
• Make sure you have a cup of Skittles – you may need to arrange for someone to share with you!
Date Session
#
Activity Page
#
11/19
&
11/20
8 Determining Age Note Guide 15
Skittles Half-Life Simulation 16
“Other Ways of Determining Age” Reading
Comprehension & Activity
17
Review
• What were some things we talked about last class that help us determine how old Earth really is?
The Butler walks to work
The Handyman rides a bike
The Cook rides a motorcycle
The Maid drives a car
The Nephew has a seeing-eye dog
(layer E)
R
5
2
4
3
9
7
8
1
6
R
Time for more specific evidence…
Relative Age
• Relative Age - the age of an event or object in relation to other events or objects
– Use words like older, younger, around the same time, etc…
Absolute Age
• Absolute Age - The actual age of an event or object
– Use techniques to figure out actual age
• Radioactive dating, carbon dating
Lived:
1 million years ago
2 million years ago
3 million years ago
4 million years ago
Types of Dating
• Radioactive (Radiometric) Dating – If you know how much radioactive material was initially present in the sample and you know the half-life of the material, you can calculate the age of the sample.
• Carbon Dating – Using the amount of carbon in fossil remains, and the half life to determine the age - sample must have been alive to use carbon dating!
What’s a “half-life?”
• Half-life – the length of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample of a radioactive material to change
• This break down occurs at a constant rate depending on the substance
Carbon Dating
• BrainPOP Video – Carbon Dating
• Half-life Practice
Skittles Half-Life
Simulation
• You will work where you are seated, but you and your table partner can work together.
• I want to see your work before you leave, and I will be checking it off for a grade…then you can tape it into page 16!
Homework
• The Great Fossil Find
Poster – due next class!
• Finish the “Other Ways of
Determining Age” Reading,
Questions & Activity – due in 2 classes!
Warm-Up
• Write a homework reminder – get it stamped!
• Update your Table of Contents for today!
• Put your Great Fossil Find Poster in the basket!
• Get your Skittles Lab out from last class!
Date Session
#
11/21
&
11/22
9
Activity
Silent Stations Answer Sheet –
GRADE
FORMAL
Page
#
18
Skittles Half-Life Simulation
Review
#2 on the back
• What is Iodine-131?
# of Half-Lives
2
3
0
1
4
Time of Half-Life Amount of Iodine-131
Remaining
0 40 mg
8 days
16 days
20 mg
10 mg
24 days
32 days
5 mg
2.5 mg
Skittles Half-Life Simulation
Review
#3 on the back:
• Does it give the name of the radioactive isotope in the question?
• What does it mean to be radioactive?
• What is an isotope?
• What is a half-life? What is the half-life of this isotope?
• What is the significance of this half-life – in other words, why should your mom not be worried?
READY TO FIND OUT
WHAT THE GREAT FOSSIL
•
FIND WAS?
pterosaur, similar to a pterodactyl, that lived during the Late Jurassic Period.
Scaphognathus crassirostris
• What it may have looked like…
•
“SILENT
STATIONS”
practice the concepts we have learned at each station.
• I am the “Answer Key Station,” so once you have completed everything you can come check your answers!
• Be sure to tape the station guide into your notebook on page 18 once you have checked your answers and been checked off for a grade!
• Complete the homework for next class, or work on an extra credit opportunity!!
HOMEWORK
• “Other Ways of Determining Age” –
Article, Questions & Map Activity due next class!
• Extra Credit Opportunity – try to finish it by after Thanksgiving break so you don’t forget about it!
Warm-Up
• No homework over break!
• Update your Table of Contents today!
• Get your “Other Ways of Determining
Age” out to be checked!
Date Session
#
11/25
&
11/26
9
Activity
Ice Cores & Tree Rings – Notes and
Lab
Argumentative Writing Prompt
Page
#
19
20
Just a Few More Pieces of
Evidence…
• Law of Superposition
• Unconformities (Intrusion, Overturning,
Fault)
• Fossils/Index Fossils
• Absolute & Relative Age
• Carbon Dating & Radioactive Dating
We are missing:
• Ice Cores
• Tree Rings
Remember The Law of
Uniformitarianism?
• The earth is a constantly changing place.
• Climate change is part of that and the climate can gradually change over hundreds, thousands or millions of years.
• Ice cores and tree rings are tools to help scientists figure out how the climate has changed in the past.
Ice Cores
• Ice Core - a tubular sample of ice that shows the layers of snow and ice that have built up over thousands of years literally freezing the events of the past
What types of things do you think get “trapped” in these ice cores?
Ice Cores
• temperature records
• atmospheric composition data
• dust, ash or sediment
• plant spores
• bubbles of gas or radioactive material
* All of this information together presents a well rounded picture
Ice Cores
• Day After Tomorrow Clip
• Video Clip at Discovery Education: http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.c
fm?guidAssetId=179C023D-B3CE-46A6-
BECD-
FB5978AB7A01&blnFromSearch=1&prod uctcode=US
Tree Rings
• Another tool for studying climate change over the life span of the tree
• The width of tree rings varies, depending on how much the tree grows in various years
• Thick ring = good year for growth
• Thin ring = poor growth, little rainfall
Tree Ring Practice
B
A
D
C
Argumentative Writing
Prompt
COPY NOW ONTO PAGE 20!
Analyze the information you have learned and researched about ice cores and tree rings to construct an argumentative statement:
1) Opinion/Argument: Which of the two tools is more useful?
2) Research: Defend your answer using 3 pieces of evidence to support your decision that have come from cited resources!
Questions??
The Birth of the Earth
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JQ93Ms
M8KFI
• A great recap as well as a lot we didn’t get a chance to talk about!