Chapter 2 - BC Open Textbooks
advertisement

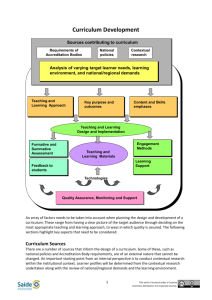
Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2 Leading Strategically This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Add to 15 • • • • In pairs, set out cards face up, numbered 1 to 9 Take turns, select a card Goal select cards which add to 15 (exactly) Secondary goal, block your opponent from succeeding! Identify your Strategies! This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Learning Objectives • Define vision and mission and distinguish between them • Understand SMART & be able to write a SMART goal • Understand the complexities associated with assessing organizational performance • Learn each dimensions of balanced scorecards • Learn what is meant by a ‘triple bottom line’ • Understand the benefits & costs of CEO celebrity status • Understand how thinking and acting entrepreneurially can help organizations and individuals • List and define the five dimensions of an entrepreneurial orientation This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically BIG Social Changes What big social changes have occurred in the last 10-20 yrs (generally social changes take lot of time to catch on…) • Cel phones etiquette • ‘Sins’: Smoking, drinking, social drug use • Marriage • Internet • Informality (no more ‘Mr’!) Think Business Ops? This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statements Mission: captures basic purpose of company – What business are we in? Should be motivating, stimulating, shared, and consistent with the Vision Statement This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statements • Mission, with Vision statements, seek to answer how and why organization exists & what role it seeks to play in society • Declaration of Organization’s key • Purpose, Business, Values • Serves as a ‘strategic compass’ • Sense of direction • May include basis of competition advantage This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statement – Harley Davidson “We fulfill dreams through the experience of motorcycling, by providing to motorcyclists and to the general public an expanding line of motorcycles and branded products and services in selected market segments.” This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statement – CRA CRA Mission To administer tax, benefits, and related programs, and to ensure compliance on behalf of governments across Canada, thereby contributing to the ongoing economic and social well-being of Canadians This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statement - Starbucks Our mission: to inspire and nurture the human spirit – one person, one cup and one neighborhood at a time. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically More Mission Statements HBC… best serve the needs of Canadian consumers through several highly focused formats, linked by customer bridges and enables by common and integrated support services This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Fender (Music) - Our mission to exceed the expectations of music enthusiasts worldwide. Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Stakeholders • Organizations also need support from their key stakeholders, such as employees, owners, suppliers, & customers, if they are to prosper • A mission statement should explain to stakeholders why they should support the organization by making clear what important role or purpose the organization plays in society This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statements Might Consider • Customers: Who are organization’s customers? • Products or services: What are the org’s major products or services? • Markets: Where does org. compete geographically? • Technology: How technologically current is org? • Concern for survival growth, & profitability: Is the org committed to growth & financial stability? This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Mission Statements Might Consider • Philosophy: What are the org’s basic beliefs, values, aspirations, & ethical priorities? • Self-concept: What is the org’s major competitive advantage & core competencies? • Concern for public image: How responsive is the org to societal & environmental concerns? • Concern for employees: Does the org consider employees a valuable asset? This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Food for Thought… This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically The Importance of Vision • A Mission statement tends to focus on what the organization is, what it is currently doing / being • Sometime with a goal of doing it better • Vision Statements focus on what the organization aspires to become in the future • A key tool for inspiring the people in an organization • Well-constructed visions clearly articulate an organization’s aspirations and can give an organization an edge over its rivals This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Vision Statements • In an ideal world, what is your vision for (your) future • Focus everyone’s attention on same target, as well as inspiring them to reach it. • Dr. King -‘I have a dream’ • Expression of what the org aspirations, beliefs & values • A clearly defined vision: • Provides direction • Determines decisions • Motivates people This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Vision Statements Alcoa – (Aluminum) to be the best company in the world, in the eyes of our customers, stakeholders, communities and people This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Petro Canada - To be the leader in the development of some of the purest base oils and innovative, superior products that customers trust for productivity improvements around the world. Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically More Vision Statements • Microsoft - Create experiences that combine the magic of software with the power of Internet services across a world of devices • Pepsi - PepsiCo’s responsibility is to continually improve all aspects of the world in which we operate – environment, social, economic – creating a better tomorrow than today • Google - To develop a perfect search engine • Amazon - to be earth's most customer centric company; to build a place where people can come to find and discover anything they might want to buy online This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically More Vision Statements • FedEx - Leading the way • Walt Disney - We create happiness by providing the finest in entertainment for people of all ages, everywhere. • eBay – to provide a global online marketplace where practically anyone can trade practically anything, enabling economic opportunity around the world This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Vision Statements – Whose? • To be the happiest place on earth • We build Gr-r-reat brands and make the world a little happier by bringing our best to you • The world on time • To be the number one athletic company in the world • A computer on every desk and in every home; all running Microsoft software • The world’s best quick service restaurant • …exists to share the love of Jesus Christ, meet human needs and be a transforming influence in the communities of our world This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Characteristics of Strategic Vision A roadmap of a company’s future • Future technology-product-customer focus • Geographic and product markets to pursue • Capabilities to be developed • Kind of company management is trying to create This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Ing Direct’s Advice (now Tangerine Bank) When creating Mission and Vision statements: • Advocate for somebody • Make it next to impossible, but with milestones to note progress • It’s the journey that inspires; the horizon should always be just out of reach • Make it poetry • Music to hear & read, sticky & difficult to walk away from • Bring it down from the mountain • It’s Leadership… • Takes Quality Time to develop This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Statements (V&M) Fail when… • • • • • • The walk doesn’t match the talk Irrelevance - created in a vacuum Not the Holy Grail - ‘Flavour of the month’ Everything to Everybody An ideal future not ground in present realities Or just poorly written… • Volvo - By creating value for our customers, we create value for our shareholders. We use our expertise to create transportrelated products and services of superior quality, safety and environmental care for demanding customers in selected segments This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically V & M - Nuts & Bolts If you are tasked with creating: • Hold the Pen (firmly!) • 1st step – Know yourself & your key strategies… • Who are we? Who do we want to be? BHAGs • • • • 2nd step – Consult, consult, consult… 3rd step – Write 4th step – Repeat steps 3 & 4 Finally – put it everywhere!! • PS [No Risk, No ‘Stickiness’, no use...] This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically A personal V/M statement What would your own personal vision/mission statement look like? • Try and draft up a couple of bullets or sentences that capture your own goals and aspirations • Remember – the stronger your self-knowledge and the clearer your goals, the more likely you are to achieve them! This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Key Takeaways Organizations need 3 types of aims: • A vision states what the organization aspires to become in the future. • A mission reflects the organization’s past and present by stating why the organization exists and what role it plays in society. • Goals are the more specific aims that orgs pursue to reach their visions & missions Best goals are SMART: specific, measurable, aggressive, realistic, & time-bound. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Key Takeaways Media exposure can give CEO celebrity status, positive benefits but CEO must manage potential for increased public scrutiny Building an entrepreneurial orientation can be valuable to orgs & individuals alike in identifying and seizing new opportunities. EO - 5 dimensions: (1) autonomy, (2)competitive aggressiveness, (3) innovativeness, (4) proactive-ness, and (5) risk taking. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically For teaching in two 90minute classes/wk, possible break point This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Goals • A goal is specific if it is explicit rather than vague • specific goals make it clear how efforts should be directed, vague goals such as “do your best” leave individuals unsure of how to proceed • A goal is measurable to the extent that whether the goal is achieved can be quantified • A goal is aggressive if achieving it presents a significant challenge to the organization (or you!) • easily achievable goals tend to undermine motivation and effort This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically SMART Goals This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically SMART Goals are • Specific – Vague goals lead no where. I should go on vacation… I should loose some weight…. Happy procrastination! • Measurable – A number… in any relevant unit such as cost, quantity, age, etc. • Achievable - It's OK to have "stretch" goals, but must believe goals are achievable. No belief, no action. BTW, control and resources (including time) important! • Relevant - Making sure goal is linked to corporate, work or personal goals – The big picture • Time-Bound - Due when? or never? (But, Don’t worry, we’ll talk about it lots…) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Your Goals Take just a couple of minutes and write down 2 or 3 personal goals for this year • Things that are important to you and that you would like to achieve this year • And willing to invest time and effort to make happen Now, make them SMART goals • (I covered the T for you already – Time – this year) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Why Bother writing down Your Goals? Most people, I would speculate less than 10%, EVER write down goals, and probably less than 5% take the time to regularly review and update their lists… Most people, I would speculate less than 10%, EVER write down goals, and probably less than 5% take the time to regularly review and update their lists… This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 2.2 Assessing Organizational Perf. Organizational performance: How well an organization is doing at reaching its vision, mission, and goals • A multidimensional concept • Vital aspect of strategic management • Assists executives in knowing how well their organizations are performing This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Assessing Org. Performance Too late…. Implicit Future Orientation…. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Performance Metrics • A performance measure is a metric along which organizations can be gauged. • Examines - profits, stock price, and sales • Performance referents or benchmarks enable us to assess how well org. is doing compared to others or itself over time • Suppose, for example, that a firm has a profit margin of 20 percent in 2012. This sounds great on the surface, until you find out the firm’s profit margin was 35% in 2011, or that industry average profit margin was 40% This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 6 Blind Men & the Elephant This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Financial Ratio Analysis • Five types of financial ratios • • • • • Short-term solvency or liquidity Long-term solvency measures Asset management (or turnover) Profitability Market value • Meaningful ratio analysis must include • Analysis of how ratios change over time • How ratios are interrelated This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) An approach to assessing performance that targets managers’ attention on four areas: 1. Financial – “How do we look to shareholders?” 2. Customer – “How do customers see us?” 3. Internal business process – “What must we excel at?” 4. Learning and growth – “Are we continuing to improve and create value?” Helps managers resist temptation to fixate on financial measures,& instead monitor a diverse set of important measures This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically BSC Sample Metrics Customer Perspective This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). • • • • Time Quality Performance and service Cost Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically BSC Sample Metrics Customer Perspective Internal Business Perspective This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). • Processes • • • • • • • • Cycle time Quality Employee skills Productivity Decisions Actions Coordination Resources and capabilities Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically BSC Sample Metrics Customer Perspective Internal Business Perspective Innovation & Learning Perspective This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). • Introduction of new products and services • Greater value for customers • Increased operating efficiencies Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically BSC Sample Metrics Customer Perspective Internal Business Perspective Innovation & Learning Perspective • • • • • Profitability Growth Shareholder value Increased market share Reduced operating expenses • Higher asset turnover Financial Perspective This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 2.3 The CEO as Celebrity • Advantages • Serves as an intangible asset for the CEO’s firm - may increase opportunities available to the firm • Hiring or developing a celebrity CEO may increase stock price, enhance a firm’s image, and improve the morale of employees and other stakeholders • Disadvantages • Magnifies any gaps between actual and expected firm performance • Faces larger and more lasting reputation erosion if their performance and behavior is inconsistent with their celebrity image This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Types of CEOs This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 2.4 Entrepreneurial Orientation • Processes, practices,& decision-making styles of organizations that act entrepreneurially • An organization’s level of EO - five dimensions: • • • • • Autonomy Competitive aggressiveness Innovativeness Pro-activeness Risk taking This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically EO - Autonomy • The degree that individuals or teams have freedom to develop entrepreneurial ideas & see it to completion. • In high autonomy, people have independence required to bring a new idea to fruition, unfettered by the shackles of corporate bureaucracy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically EO – Competitive Aggressiveness • Competitive aggressiveness is the tendency to intensely and directly challenge competitors rather than trying to avoid them. • Aggressive moves can include price-cutting & increasing spending on marketing, quality, & production capacity. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically EO - Innovativeness • Innovativeness is the level of org. creativity and experimentation. • Some innovations build on existing skills to create incremental improvements, while radical innovations require brand-new skills and may make existing skills obsolete. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically EO - Innovativeness • Either way, innovativeness is aimed at developing new products, services, & processes. • Those organizations that are successful in their innovation efforts tend to enjoy stronger performance than those that do not This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically EO - Autonomy • Proactiveness is the focus on anticipating and acting on future needs rather than only reacting • Proactive org. adopt an opportunity-seeking perspective. Such organizations act in advance of shifting market demand and are often either the first to enter new markets or “fast followers” that improve on the initial efforts of first movers. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically EO – Risk Taking • Risk taking refers to the tendency to engage in bold rather than cautious actions. • Starbucks, for example, made a risky move in 2009 when it introduced a new instant coffee called VIA Ready Brew. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Increasing Entrepreneurial Orientation • Org systems & policies must reflect 5 dimensions of EO. • Org’s compensation systems will encourage or discourage taking sensible risks, which must be rewarded, regardless of whether the risks pay off • Corporate debt levels will influence EO • Performance measures implicitly signal what is important • Higher levels of autonomy tend to increase employee satisfaction & reduce turnover. • Innovativeness can be gauged by tracking # of new products or services developed in the last year, & # of patents the firm has obtained This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically Key Takeaways Organizational performance is a multidimensional concept, and wise managers rely on multiple measures of performance when gauging the success or failure of their organizations. The balanced scorecard helps executives understand, monitor & manage org. across a 4 dimensions – The triple bottom line provides another tool to help executives focus on performance targets beyond profits alone; this approach stresses the importance of social & environmental outcomes. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 2.3 The CEO as Celebrity • Advantages • Serves as an intangible asset for the CEO’s firm - may increase opportunities available to the firm • Hiring or developing a celebrity CEO may increase stock price, enhance a firm’s image, and improve the morale of employees and other stakeholders • Disadvantages • Magnifies any gaps between actual and expected firm performance • Faces larger and more lasting reputation erosion if their performance and behavior is inconsistent with their celebrity image This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 2.3 The CEO as Celebrity • Advantages • Serves as an intangible asset for the CEO’s firm - may increase opportunities available to the firm • Hiring or developing a celebrity CEO may increase stock price, enhance a firm’s image, and improve the morale of employees and other stakeholders • Disadvantages • Magnifies any gaps between actual and expected firm performance • Faces larger and more lasting reputation erosion if their performance and behavior is inconsistent with their celebrity image This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically 2.3 The CEO as Celebrity • Advantages • Serves as an intangible asset for the CEO’s firm - may increase opportunities available to the firm • Hiring or developing a celebrity CEO may increase stock price, enhance a firm’s image, and improve the morale of employees and other stakeholders • Disadvantages • Magnifies any gaps between actual and expected firm performance • Faces larger and more lasting reputation erosion if their performance and behavior is inconsistent with their celebrity image This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 2: Leading Strategically