simple machines notes
advertisement

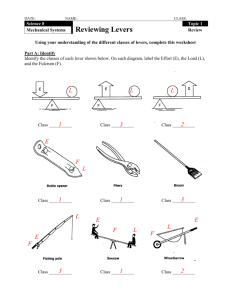
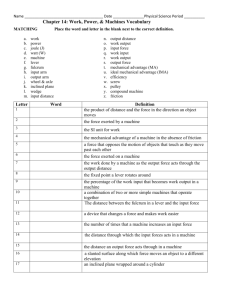
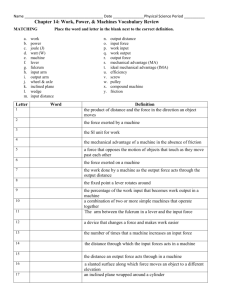
Simple Machines Levers Objectives You will be able to… …explain what a lever is. …distinguish between the different parts of a lever. …describe the difference between a 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Class Lever. …explain the difference between Mechanical Advantage and Disadvantage. …calculate the Ideal and Actual Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of a lever. What is a Lever? All levers are made up of 4 components: LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT LEVER ARM Parts of a Lever EFFORT LOAD FULCRUM LEVER ARM If theE F ULCRUM isthe The LOAD EVER is a L F ULCRUM FFORT isAthe isRM isan located atthat the rigid bar rests on weight pivot outside point of force the or(person, moment midpoint of the and rotates about the object(s) around machine, which that natural isthebeing L EVER ARM and theItto F ULCRUM . It, applied serves moved forces phenonoma) rotate. (displaced). E FFORT the is equal toof transfer represents to the lever. aforce Itforce is also that the L OAD, then the the EFFORT the is measured measured intoin pounds lever be perfectly L OADwill . (lbs) pounds (lbs). balanced. Advantages of Levers: … can be used to change the direction of an applied force (EFFORT) … can increase or decrease an applied force … can increase or decrease the distance travelled by an object (LOAD) 150 lbs Your muscles When Imagine weyou lift are heavyproduce trying must to objects, lift a an box we mustweighs that upward produce force150 of an upward lbs. 150 lbs or force more that in is equal order to to raise or the greater box to the than desired the 150 lbs weight of that height. object. For example... If your Your muscles muscles must produce cannot produceanthe upward force necessary upward of 150 lbs force to or overcome more in order the weight to raise of the box to box, then the desired height. can problems occur. Levers can help! Classes of Levers st 1 Class Levers In a 1st Class Lever, the FULCRUM is located between the LOAD and the EFFORT. LOAD EFFORT FULCRUM st Class Note In a 1that the forces Lever, of thethe FULCRUM LOAD and is the located E FFORT between are moving the in LOAD the same and the direction. EFFORT. EFFORT LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT FULCRUM LOAD Homemade Lift When the FULCRUM is moved to one side, mechanical advantage or disadvantage occurs. EFFORT Note: EFFORT LOAD smaller EFFORT, but greater distance OAD that it must move L FULCRUM Other examples of 1st Class Levers... Tongs Other examples of 1st Class Levers... Paint Can Opener nd 2 Class Levers In a 2nd Class Lever, the LOAD is located between the FULCRUM and the EFFORT. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT Note that the forces from the LOAD and the EFFORT are pointing in opposite directions. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT EFFORT FULCRUM LOAD Bottle Opener Other examples of 2nd Class Levers... Wheelbarrow Other examples of 2nd Class Levers... Nut Cracker A 2nd Class Lever always has mechanical advantage. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT rd 3 Class Levers In a 3rd Class Lever, the EFFORT is located between the FULCRUM and the LOAD. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT As was the case with the 2nd Class Lever, the forces from the LOAD and the EFFORT are pointing in opposite directions. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT Unlike the class 2 lever, a 3rd Class Lever has mechanical disadvantage. The EFFORT must be greater than the force of the LOAD. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT However, the distance moved by the LOAD is greater than the distance moved by the EFFORT. LOAD FULCRUM EFFORT EFFORT LOAD FULCRUM Human Arm Other examples of 3rd Class Levers... Shovel Other examples of 3rd Class Levers... Tweezers Levers in Combination EFFORT FULCRUM LOAD Lever #1 = 2nd Class Lever Nail Clippers EFFORT FULCRUM LOAD Lever #1 = 2nd Class Lever Lever #2 = 3rd Class Lever Nail Clippers Levers & Mathematics Moment: The tendency to produce motion around an axis or point. The turning effect produced by a lever is called a moment. It is the product of the applied force and the distance of that force from the fulcrum. Moment = force x distance = Work 1st Class Lever EFFORT 20 lbs force x distance = Moment = Work 20 lbs x 5 ft = 100 (EFFORT Moment) = 100 Joules 1st Class Lever LOAD force x distance = Moment = Work 50 lbs x 2 ft = 100 (LOAD Moment) = Joules 50 lbs 1st Class Lever EFFORT LOAD 20 lbs EFFORT Moment = LOAD Moment Balanced Lever 50 lbs Ideal Mechanical Advantage: …IMA …also known as Theoretical Mechanical Advantage (TMA) …the ratio between the EFFORT-arm length to the LOAD-arm length. IMA = rE rL IMA = 5 2 2.5 : 1 6 in. 0.75 in. IMA = rE rL 6 IMA = .75 =8 or ratio 8 : 1 IMA = rE rL 2 IMA = 20 = 0.1 or ratio 0.1 : 1 2 in. 20 in. Actual Mechanical Advantage: …AMA …the ratio between the force applied to the LOAD arm and the force applied to the EFFORT arm AMA = EFFORT FL FE LOAD 20 lbs AMA = 50 20 = 2.5 or ratio 2.5 : 1 50 lbs Efficiency: …(Greek lowercase H…pronounced Eta) …the ratio of AMA to IMA …friction at the FULCRUM will cause the AMA to be less than the IMA, resulting in an efficiency less than 1 Efficiency = = AMA IMA