Cardiac anatomy using models
advertisement

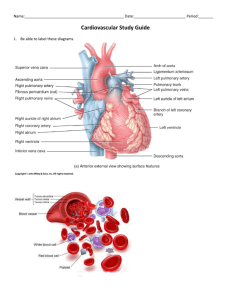
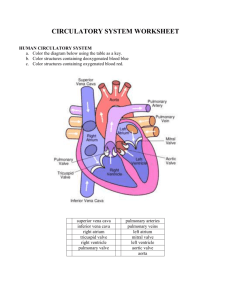
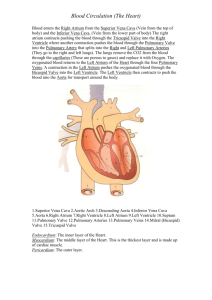
Heart Anatomy & ECG KAAP 310 The Electrocardiogram (ECG) • As we discussed last week, the electrical activity of the heart is determined by pacemakers (SA, AV node) • By placing sensitive electrodes on certain parts of the body, we can recognize and record the “echoes” of the heart depolarizing and repolarizing • Heart rate, Axis deviation (heart position), cardiac arrthymias and mechanical activity of heart can all be seen on a standard ECG. A normal ECG reading T Wave: QRS Complex: Repolarization R & L ventriular of right and depolarization, left ventriclesAtrial repolarization P Wave: Depolarization of the right and left atria (atrial depolarization) masked by QRS complex Reading & Interpreting an ECG Segments: Isoelectric Interval: Period Line: Periods of Point electrical of no of departure recorded activityofwithin the depolarizing and activity between in the heartbeats heart and repolarizing actions of the heart. ECG Leads • Particular arrangement of the electrodes with respect to one another is called a lead. • We will be using a 3-lead model – A positive, negative and ground electrode will be placed on the subject • + on left ankle • - on right wrist • Ground on right ankle ECG Notes • QRS complex generally dominant in any ECG recording – Affected by many factors: Body mass, fat mass, height, cardiovascular health (large LV mass will change the look of the complex) Large & Small Block Calculations BioPac Lab • Four conditions will be recorded: Supine, Seated, Breathing deeply, and After exercise. Minimize EMG artifact and baseline drift: • Subject’s arms and legs must be relaxed. • Subject must remain still and should not talk during any recordings. • Make sure electrodes do not peel up and that the leads do not pull on the electrodes. BioPac Lab • First condition: Supine, eyes closed, relaxed • Second condition: Stand up quickly, settle back down into seated position • Third condition: Five (5) deep inhales/exhales with recorder counting • Fourth condition: Exercise – 15 pushups or 15 jumping jacks. Mind the cables – may unclip if necessary…don’t forget to re-attach! • Optional active learning portion not required • Call your TA when you have collected all data Data Review • After your data file has been transferred to your laptop, open it with your BioPac analysis software and begin analyzing your data • Data & questions can be completed on your computer and emailed to your TA (due next week) Heart Models • While your group is waiting to work with the BioPac software please use this time to begin reviewing the heart models • These same models will be used for your first long quiz • Feel free to use online resources and this presentation • Models will be available next week during our dissection lab as well Cardiac Anatomy Interatrial Septum Interventricular Septum Brachiocephalic trunk Superior vena cava Right pulmonary artery Ascending aorta Pulmonary trunk Right pulmonary veins Right atrium Right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus) Anterior cardiac vein Right ventricle Right marginal artery Small cardiac vein Inferior vena cava (b) Anterior view Left common carotid artery Left subclavian artery Aortic arch Ligamentum arteriosum Left pulmonary artery Left pulmonary veins Auricle of left atrium Circumflex artery Left coronary artery (in coronary sulcus) Left ventricle Great cardiac vein Anterior interventricular artery (in anterior interventricular sulcus) Apex Figure 18.4b Aorta Left pulmonary artery Left pulmonary veins Auricle of left atrium Left atrium Great cardiac vein Posterior vein of left ventricle Left ventricle Ape x Superior vena cava Right pulmonary artery Right pulmonary veins Right atrium Inferior vena cava Coronary sinus Right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus) Posterior interventricular artery (in posterior interventricular sulcus) Middle cardiac vein Right ventricle (d) Posterior surface view Figure 18.4d Superior vena cava Anastomosis (junction of vessels) Aorta Pulmonar y trunkLeft atrium Right atriu m Right coronar y artery Right ventricle Right marginal Posterior artery interventricula r artery (a) The major coronary arteries Left coronar y artery Circumfle x artery Left ventricle Anterior interventricula r artery Figure 18.7a Superior vena cava Anterio r cardiac veins Great cardia c vein Coronary sinus Small cardiac vein (b) The major cardiac veins Middle cardiac vein Figure 18.7b Aorta Superior vena cava Right pulmonary artery Pulmonary trunk Right atrium Right pulmonary veins Fossa ovalis Pectinate muscles Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Chordae tendineae Trabeculae carneae Inferior vena cava Left pulmonary Left artery atrium Left pulmonary veins Mitral (bicuspid) valve Aortic valve Pulmonary Left valve ventricle Papillary muscle Interventricular septum Epicardiu Myocardiu m Endocardium m (e) Frontal section Figure 18.4e Myocardium Pulmonary valve Aortic Tricuspid Area valveof (right atrioventricular) cutaway Mitral valve valve Tricuspid Mitral valve (left atrioventricular) valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve Fibrous skeleto n (a ) Pulmonary valve Aortic Area valveof cutaway Mitral valve Tricuspid valve Anterio r (b ) Myocardiu m Tricuspid (right atrioventricular) valve Mitral (left atrioventricular) Aortic valve valve Pulmonary valve Figure 18.8a