2.3 Cellular Transport
advertisement
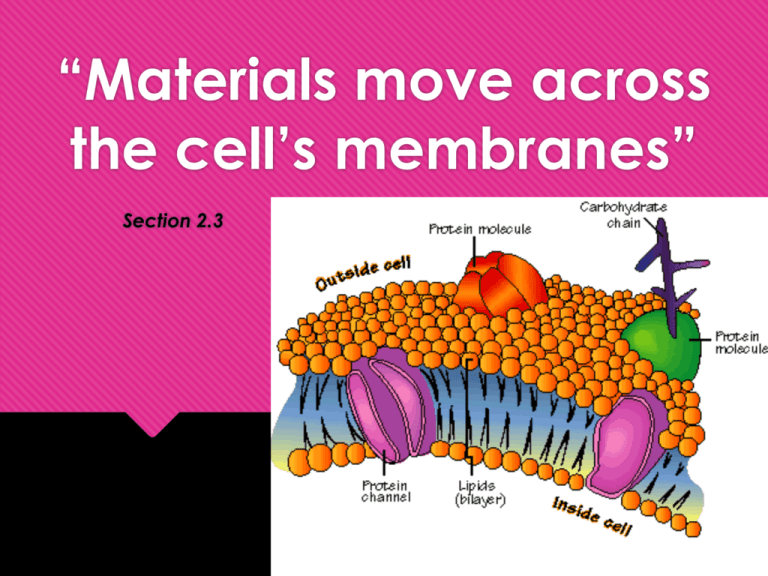
“Materials move across the cell’s membranes” Section 2.3 Do Now!! What is the purpose of the cell membrane? What would happen if we didn’t have cell membranes? What goes in and out of our cells? Objectives To explain the different functions of the macromolecules in the plasma membrane. To understand the process of diffusion. To compare and contrast active and passive transport. The Cell Membrane Called a “Fluid Mosaic Model” Proteins and other components embedded like a mosaic http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= Qqsf_UJcfBc Membrane Components Phospholipids: Give the general structure of the membrane Composed of: Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tails Please draw a phospholipid! Draw a phospholipid and label its parts! Membrane Components Proteins: Allow bigger substances to pass through Provide structure: Ex: Microtubules and microfilaments (cytoskeleton) Membrane Components Cholesterol: helps maintain structure of phospholipids prevents the tails from sticking together Membrane Components Carbohydrates: receptors that send and receive signals from other cells Attached to proteins (glycoprotein) and phospholipids (glycolipid) Explain what’s happening… Types of Transport across a cell membrane Passive Transport Active Transport Vesicular Transport Passive Transport Does NOT require energy Molecules go from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration “Go with the flow” 3 Types of Passive Transport 1. Simple diffusion 2. Facilitated diffusion 3. Osmosis Simple diffusion? Movement of particles from area where there are many to area where there are fewer Moves from high to low concentration Simple diffusion (cont.)? Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration to create DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM Concentrations are the same in all areas Affected By… Heat- higher temp increases rate State of Matter Solid- slow Liquid- faster Gas- fastest Size and Concentration Bigger= slower More concentration = faster Do Now!! Explain what happens when you put a sugar cube in your tea in regards to diffusion. Objectives Explain facilitated diffusion Define solute, solvent and solution Identify different types of solutions Facilitated Diffusion Certain molecules need a “helper” or “facilitator” to allow them to cross the membrane when they are too big. Osmosis o The flow of WATER from a high concentration to a low concentration Solution o A mixture in which you cannot separate the components (ex: iced tea) o solute: the substance being dissolved o Ex: iced tea powder o solvent: The substance doing the dissolving o Ex: water Isotonic Solutions Same amount of solute inside the membrane as there is outside. Cell in this solution: NOTHING Plant Cell Blood Cell HYPERtonic Solutions More solute, less water on outside of the membrane Cell in this solution: shrinks/shrivels Plant Cell Blood Cell HYPOtonic Solutions Less solute, more water on outside of membrane Effect: cell swells or bursts! / Plant Cell Blood Cell Identify the type of solution! Cell in ________ Solution H2O H 2O Cell in ________ Solution H 2O H 2O Cell in ________ Solution H 2O H 2O Answer key! Cell in hypotonic Solution H2O H 2O Cell in isotonic Solution H 2O H 2O Cell in hypertonic Solution H 2O H 2O Let’s try another… For the following examples: Which way is the water moving? What kind of solution is it? What is going to happen to the cells? A. B. C. 2% Salt 3% Salt 12% Salt 9% Salt 28% Salt 28% Salt Real life osmosis situations A salt water fish is put into a freshwater aquarium. What type of solution is the freshwater? What is going to happen to the cells of the fish? Real life osmosis examples A patient is given an IV, which contains the perfect balance of saline. What type of solution is in the IV? What is going to happen to the cells of the human? Real life osmosis examples Your garden is infested with slugs so you go around pouring salt on them What type of solution is this salt? What is going to happen to the cells of the slug? (don’t do this to the poor slugs ) Do Now!! What is diffusion? What do you think “passive” transport is? What do you think the difference is between passive and active transport? Objectives To define active transport To compare and contrast endocytosis and exocytosis To complete a gummy bear osmosis lab activity Active Transport When molecules move from a low concentration to a high concentration and must use ENERGY (ATP). Example- Sodium Potassium Pump http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chap ter2/animation__how_the_sodium_potassium_ pump_works.html Vesicular Transport Sometimes things enter and exit the cell by forming vesicles. For example… Endocytosis: When cells absorb molecules by engulfing them. (like pacman) Endocytosis Pinocytosis: when the substance being engulfed is a LIQUID. Phagocytosis: when the substance being engulfed is a SOLID. Vesicular Transport Exocytosis: When cells expel unwanted materials from vesicles. Vesicular Transport http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olc/dl/120068/bio02.swf Let’s review osmosis… What is osmosis?? What are the three types of solutions?? Identify the following: A. B. 2% Salt 3% Salt C. 12% Salt 9% Salt 28% Salt 18% Salt