Topic 3.8 Photosynthesis
advertisement

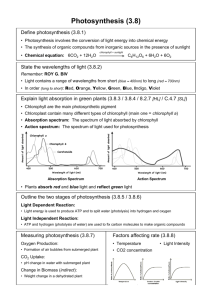
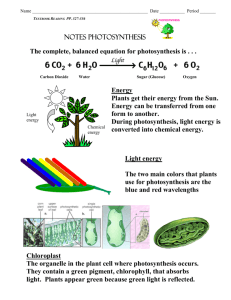
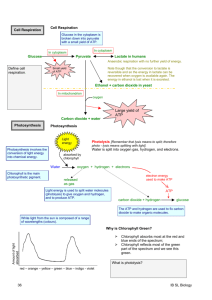
3.8.1 State that photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy 3.8.2 State that light from the sun is composed of a range of wavelengths (colors) 3.8.3 State that chlorophyll is the main photosynthetic pigment 3.8.4 Outline the differences in absorption of red, blue, and green light by chlorophyll 3.8.5 State that light energy is used to produce ATP, and to split water molecules (photolysis) to form oxygen and hydrogen 3.8.6 State that ATP and hydrogen (derived from photolysis of water) are used to fix carbon dioxide to make organic molecules 3.8.7 Explain that the rate of photosynthesis can be measured directly by the production of oxygen or the uptake of carbon dioxide, or indirectly by an increase in biomass 3.8.8 Outline the effects of temperature, light intensity, and carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis Plants produce foods that begin food chains ◦ The sunlight that strikes our planet must be converted into a form of chemical energy to be useful to all non photosynthetic organisms Most common chemical energy produced from photosynthesis is the molecule glucose The vast majority of plant leaves appear green to our eyes ◦ Plants contain a variety of pigments in chloroplasts ◦ The photosynthetic pigment that dominates in most plant species in the molecule chlorophyll Plants make use of the same part of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes are able to see Sunlight is actually a mixture of different colors of light The visible light spectrum includes many colors, but for the purpose of considering how chlorophyll absorbs light energy Three regions of spectrum ◦ Red end of spectrum ◦ Green middle of spectrum ◦ Blue end of spectrum Substances can do one of only two things when they are struck by a particular wavelength of light, they can: ◦ Absorb that wavelength (if so, energy is being absorbed and may be used) ◦ Reflect that wavelength (if so, the energy is not being absorbed and you will see the color) Chlorophyll is a green pigment ◦ This means that chlorophyll reflects green light and therefore must absorb the other wavelengths of the visible light spectrum When a plant leaf is hit by sunlight, the red and blue wavelengths of light are absorbed by chlorophyll and used for photosynthesis Photosynthesis produces sugar molecules as a food source for the plant. Glucose molecules are held together by covalent bonds ◦ It requires energy to create those covalent bonds and the source of that energy can ultimately be traced back to the sun The first stage of photosynthesis is a set of reactions typically referred to as the lightdependent reactions ◦ Chlorophyll absorb light energy and convert that energy to a form of chemical energy (ATP) In additions, light energy is also used to accomplish a reaction that is called photolysis of water Photolysis-water molecule is split into its component elements: hydrogen and oxygen The oxygen that is split away due to photolysis of water is typically released from the plant leaf as a waste product The useful products formed during this stage of photosynthesis are ATP and hydrogen The second stage of photosynthesis is a series of reactions collectively referred to as the light-independent reactions ◦ ATP and hydrogen are used as forms of chemical energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into useful organic molecules for the plant CO2 is inorganic Glucose is organic (requires 6 CO2 molecules to form one glucose molecule) 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 This conversion of an inorganic form of an element to an organic form is known as fixation Photosynthesis can be described as a series of reactions in which carbon dioxide and water are fixed into glucose, and oxygen is produced as a by-product Fixation reaction requires energy ◦ The energy to create the glucose comes directly from the ATP and hydrogen created in the first stage of photosynthesis This energy can be traced back to sunlight Knowing that plants do both photosynthesis can cell respiration might lead you to the conclusion that the two processes ‘cancel each other out’ At any given time of year, any one plant has a fairly consistent throughout the day and night. ◦ Plants do not have muscle and other ATPdemanding tissues as do animals. They need ATP for various biochemical process, but the level is typically far below that required by an animal Photosynthetic rate is highly dependent on many environmental factors including intensity of light and air temperature During the daytime, especially on a warm sunny day. The rate of photosynthesis may be very high for a particular plant If so, the rate of carbon dioxide taken in by the plant and the rate of oxygen released will both be very high At night, the rate of photosynthesis may drop to zero. At this time, a given plant may be giving off carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen to maintain its relatively low and consistent rate of cell respiration Measuring the rate of oxygen production or carbon dioxide intake is considered to be direct measurement of photosynthetic rate as long as a correction is made for cell respiration ◦ Another common approach is to measure photosynthesis by keeping track of the change in biomass of experimental plants. Massing of plants is considered to be an indirect reflection of photosynthetic rate as the increase or decrease in biomass may be traced to a whole variety of factors besides photosynthetic rate The effect of increasing light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis ◦ Figure 3.27 Effects of Changing temperature ◦ Figure 3.28 Effect of changing carbon dioxide concentration ◦ Figure 3.29