Chapter 10, Section 2
advertisement

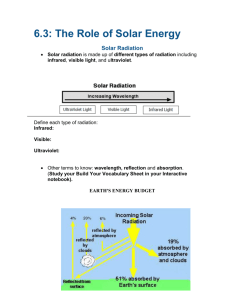
Chapter 22, Section 2 Standards Chapter 10, Section 2 4b. Students know the fate of incoming solar radion in terms of reflection, absorption, and photosynthesis 4c. Students know the different atmospheric gases that absorb the Earth’s thermal radiation and the mechanism and significance of the greenhouse effect. 8a. Students know the thermal structure and chemical composition of the atmosphere. Objective 1 Explain how radiant energy reaches Earth. Objective 2 Describe how visible light and infrared energy warm Earth. Objective 3 Assessment Summarize the processes of radiation, conduction, and convection. Group Posters, Chapter Test Review Daily Bellwork, Science Starters, Standards Practice Solar Energy Key Terms: Create a flashcard for each. The words can be found starting on page 555 or use the glossary. If you finish early, study your new words! • • • • • Electromagnetic Spectrum Albedo Greenhouse effect Conduction Convection Solar Energy Heat in the atmosphere comes from the absorption of the sun’s rays by gases in the atmosphere and indirectly as the ocean and land surfaces absorb solar energy and then give off that energy as Radiation • Radiation= all forms of energy that travel through space as wave. • Visible light is a form of radiation the human eye can see • UV rays, x-rays, radio waves are also radiation • Electromagnetic Spectrum= all of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation INTERACTIVE The Atmosphere and Solar Radiation • As solar radiation passes through the atmosphere: • 30% is reflected back into space • 20% absorbed by clouds, dust, and gases • 50% absorbed by Earth’s surface Scattering Clouds, dust, water droplets, and gas molecules in the atmosphere disrupt the paths of radiation from the sun and scatter them. This deflection causes the rays to change direction and some reflects back to space. Why is the sky blue?? As light travels through the atmosphere the smaller wavelengths (Blues) hit small particles of gas and dust, which then scatter the blue light in all directions across the sky. Longer wavelength light (Reds) usually pass straight through the sky, however when the sun is low in the sky (sunset), only the reds can get through so we see only shades of red, not blue. Demo Reflection When solar energy reaches the surface it is either absorbed or reflected. The fraction of solar radiation that is reflected = abledo Amount of energy absorbed or reflected depends on color, texture, composition, volume, mass, etc. INTERACTIVE Tell me about the GREENHOUSE EFFECT Greenhouse Effect • The Earth’s atmosphere allows radiation to pass through but it slows the escape of energy the radiates from the Earth’s Surface • Car example… • Generally the amount of solar energy that enters the atmosphere is equal to the amount that escapes into space • Human activities may change this balance (CO2 has increased, which prevents energy BrainPop GreenHouse Effect Conduction and Convection Conduction: Transfer of energy as heat through direct contact of one object to another Convection: Movement of matter (liquids and solids) due to different densities and temperature differences, which as a result transfers heat Cool air sinks, warm air rises Assessment/INTERACTIVE Answer # 1 and # 8 on page 560 Solar Energy





![Applied Heat Transfer [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008526779_1-b12564ed87263f3384d65f395321d919-300x300.png)



