Social Psych Vocab
advertisement
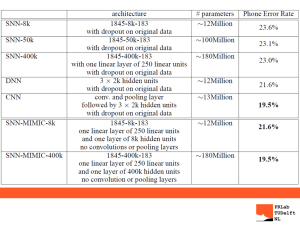
AND MELANIE PATALANO First Period Vocabulary Slides Social Psychology Shallow: the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another Deep: why we do what we do O&E: Psychologist studying how people relate to one another. Objective 2 Attribution Theory Shallow: we explain someone’s behavior by crediting either the situation or persons disposition Deep: Melanie being extremely negative towards me and I wonder if she just has a negative personality or if it a reaction to stress at home O&E: A teacher may wonder whether a student’s hostility reflects an aggressive personality or a reaction to stress or abuse Objective 1 Central Route to Persuasion Shallow: Attitude change path in which interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoughts. Deep: A central route is the fastest path, allowing people to focus on what’s most important. Example: In the Socratic seminar, I listened to the Conner’s point and responded with my thoughts. Objective:4 Peripheral Route to Persuasion Shallow: Attitude change path in which people are influenced by incidental cues. Deep: Your peripheral vision doesn’t focus on the important details, such as the argument, and focuses on other cues. Example: A speaker’s attractiveness may influence the listeners attitude. Objective: 4 Foot-in-the-door Phenomenon Shallow: Tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request. Deep: By getting your foot in the door initially, you will later be able to open bigger doors. Example: I first helped Danielle with her homework, later I agreed to help her murder someone. Objective: 3 Fundamental Attribution Error Shallow: the tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition Deep: Danielle was extremely talkative in class while Conner didn’t say a word. It seems that Danielle is outgoing and Conner is quiet and does not like to share O&E: - A classmate may be quiet in class, while another is constantly raising their hand. Causing you to make the assumption that classmate one is shy while classmate two is outgoing. However, put the classmates in different environments, in which classmate one is the lead role in a play, and classmate two is at coffee and says only a few words - Objective 1 Attitude Shallow: feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people and events Deep: think about 3 different people and the way you act around them each O&E: - After a loss in a game, you feel anger towards a friend that was on the other team, causing you to be rude towards them afterwards - Objective 4 Role Shallow: a set of expectations about a social position, defining how those in position ought to behave. Deep: Think of an actor and the role/character they take on. How must they act and behave? O&E: DECA students often take on the role of a professional acting adult. Objectives (3,4) Conformity Shallow: Adjusting ones behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard. Deep: Think of conforming to the pressures of high school that make you do something you might not on your own. O&E: When everyone dresses spirited at the liberty football games you're more inclined to also dress spiritedly. Objectives (2,3,4) Social Psych Vocab Normative Social Influence Definition: a type of social influence leading to conformity or the influence of other people that leads us to conform to the rules in order to be liked and accepted by them. Example: Fashions styles lean heavily on normative social influence and is seen in religious, and political beliefs along with other situations of persuasion. Informational Social Influence Definition: when you look at the behaviors of others who are also in the same or similar situation to see how to act in order to be accepted Example: The situation is ambiguous. We have choices but do not know which to select We have no time to think and experiment and a decision is required now, others are experts. If we accept the authority of others, they must know better than us. Social Facilitation Definition: Stronger responses on simple or welllearned tasks in the presence of others Objectives: Predict impact of others on a person’s behavior. Social Loafing Define: The tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable. Objectives: Predict the impact of the presence of others on a person’s behavior. Deindividuation Definition: The loss of self-awareness and selfrestraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity. Deep: To Kill a Mockingbird Objective: Describe the structure and function of different kinds of group behavior Cognitive Dissonance Theory The theory that we act to reduce the discomfort we feel when two of our thoughts are inconsistent. Objective: Discuss attitude formation and change, including persuasion strategies and cognitive dissonance. Group Polarization Definition: Tendency for groups to take more extreme positions in the direction they were already inclined Example: A discussion occurs between people mildly in favor of gun control and mildly opposed to gun control. After the discussion, the people that were initially mildly in favor of gun control are now more strongly in favor of gun control. Groupthink Definition: phenomenon in which people strive for consensus within a group. In many cases, people will set aside their own personal beliefs or adopt the opinion of the rest of the group. •Tends to occur in isolated groups, especially in groups with no clear rules for decision making and where all of the people involved have similar backgrounds. Example: The Bay of Pigs Invasion- The invasion was planned by the Eisenhower administration but accepted by the Kennedy Administration without question when they took over. The administration ignored questions and accepted stereotypes about the Cubans. Objective: explain how individuals respond to expectation of others, including groupthink, conformity and obedience to authority. Prejudice Shallow: Negative , usually unjustified attitude toward people because they are members of a certain group Deep/Examples: For instance, people in the club don’t like Tyler because they don’t like his hair Stereotype Shallow: a fixed way of thinking about people you classify in a certain group Deep/Examples: All Asians are good in math Discrimination • Unjust treatment of certain types of people, backed by prejudicial views. • Example: People in da club be treatin’ Tyler like poo cause he’s white Outgroup People who are outside of one’s own ingroup, who are considered to be inferior; A group that is seen as different from one’s own Example: Jonathan doesn’t value the company of his tablemates because none of them are Fillipino. In group Bias Shallow meaning – The tendency of people to favor others of the same group. Deep meaning/Example – People of the same religion tend to relate better to eachother than people of different beliefs. In group Shallow meaning – A group a person identifies as being a member of. Deep meaning/Example – Josh played Football at liberty high school, and because of this he Identified as fitting in with the other football players. Norm Something that is seen as common, not unusual or standard within a group of people. A norm is something that isn't seen as out of the ordinary to someone in a specific group of people. For example, here in the United States, it’s normal to find a television in someone’s house. You wouldn’t walk into a united states citizen’s house and be shocked to find a TV. Culture “The customary beliefs, social forms, and material traits of a racial, religious, or social group; also : the characteristic features of everyday existence (as diversions or a way of life) shared by people in a place or time.” Culture is the lifestyle shared by a group of people, such as food, clothing, religious practice and social practices. For example, in the mainland of the United States, most people wear shoes, but in Hawaii, a lot of people rarely do. It’s an example of how the social practice of wearing shoes in public is practiced in some cultures, but not in others. This applies to so many other aspects of life. Objectives 2) Having an ingroup to relate to, and an outgroup to distance yourself from causes group behaviors like group polarization where members of a group gains 3) 5) 6) 7) Group 4: Social Influence Scapegoat Theory Definition: Is the theory that prejudice offers an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame. Example: Throughout history people of Jewish background have been blamed for many things like famine, drought and other misfortunate things. Objective 6 applies to the Scapegoat Theory because you are treating cultures differently based on one’s own prejudices to find someone to blame. Other Race Effect Definition: It is the tendency to recall faces of one’s own race more accurately than faces of other races. Example: If you are African American you can more accurately recall the face of your African American friend than the face of your Asian American friend. Objective 7 can apply to the Other-Race Effect because different race backgrounds effects the way you remember their face. Just-World Phenomenon Definiton: The tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get Examples: • Saying a girl was sexually abused as a result of revealing clothing or saying the wrong things • Saying domestic abuse was provoked by the spouse “Blaming the victim” Enables the reasoning that those who succeed must be good and those who suffer must be bad Objectives: • Describe processes that contribute to differential treatment of group members --People can see others as inferior using this theory • Describe the variables that contribute to altruism, aggression, and attraction Aggression Definition: A person who passes along a vicious rumor about you, the person who verbally assaults you, and the attacker who mugs you are aggressive. Neural Influences: Animal and human brains have neural systems that, when stimulated, either inhibit or produce aggressive behavior ~ Ex. A mild mannered woman had an electrode implanted in her brain’s limbic system (in the amygdala) by neurosurgeons seeking to diagnose the disorder. Since the brain had no sensory receptors, she was unable to feeling anything. But, something snapped in the brain and snarled at the doctor, “Take my blood pressure. Take it now,” she stood up and decided to strike the doctor. Aggression cont… Biochemical Influences: Hormones, alcohol, and other substances in the blood influence the neural systems that control aggression. ~ Ex. People who have been drinking commit 4 in 10 violent crimes and 3 in 4 acts of spousal abuse Social and Cultural Influences: Our reactions are more likely to be aggressive in situations where experience has taught us that aggression pays. ~ Children whose aggression successfully intimidates other children may become more aggressive ~ Ex. Social influences also appears in high wilence rates among cultures and families that experiences minimal father care. 9. Describe the variables that contribute to altruism, aggression, and attraction 7. Articulate the impact of social and cultural categories (e.g., gender, race, ethnicity) on self-concept and relations with others. Frusteration-Aggression Principle Definition: something that can occur when someone recognizes that they are being prevented from achieving a goal; their attitudes/behaviors go from frustrated to aggressive. Example: When the Seahawks start to fall behind in a game, the fans at the game become frustrated and then become aggressive, jumping up and down and yelling at the other team’s fans. Objectives: 4-Attitudes & how they change. Application-Feeling doubtful goes to frustration, frustration goes to aggression and anger. 5- Impact from the presence of others. Application-A person preventing another person from achieving a goal. 9- Variables that contribute to altruism, aggression, and attraction. Application- Being prevented or thinking that you’re prevented from achieving a goal causes aggression. Social exchange theory Shallow: The theory that our social behavior is an exchange process, the aim of which is to maximize benefits and minimize costs. Deep: When deciding to donate clothes to the local goodwill you will weigh the negatives (losing that fly shirt from 1986) against the positives (letting a new person experience your amazing sense of style). If the positives outweigh the negatives then you donate the clothes. Social exchange theory Shallow: The theory that our social behavior is an exchange process, the aim of which is to maximize benefits and minimize costs. Deep: When deciding to donate clothes to the local goodwill you will weigh the negatives (losing that fly shirt from 1986) against the positives (letting a new person experience your amazing sense of style). If the positives outweigh the negatives then you donate the clothes. Reciprocity norm Shallow: The expectation that people will help, not hurt, those who have helped them. Deep: If I helped you get out of a bar fight I would expect you not to try to cut me with your broken bottle. Social-Responsibility Norm Shallow Definition: An expectation that people will help those dependent upon them. Deep Strategy Definition: Helping an old lady cross the street even though you will not get anything in return. Conflict Shallow Definition: A perceived incompatibility of actions, goals, or ideas. Deep Strategy Definition: One parent has a different way of raising their child than the other parent. Social Trap Definition: A situation in which the conflicting parties, by each rationally pursuing self interest, become caught in mutually destructive behavior. 688 Example: A person chooses to buy himself a regular car, and save money because its not his personal car that contributes to the greenhouse gases. When in reality when enough people begin to think like that the collective result brings global climate change and other environmental damage. Mirror- Image Perceptions Definition: Mutual views often held by conflicting people, as when each side sees itself as ethical and peaceful and views the other side as evil and aggressive. Example: Mary thinks John is annoyed by her,so she ignores him and John responds by ignoring her as well justifying her original perception. Superordinate Goals Shallow: Shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation. Deep: We’re all in this together, the enemy of my enemy is my friend Example: Remember the Titans GRIT Shallow: Graduated and Reciprocated Initiatives in Tension-Reduction a strategy designed to decrease international tensions. Deep: United Nations conferences Overall objectives 3. Explain how individuals respond to expectations of others, including groupthink, conformity, and obedience to authority. 4. Discuss attitudes and how they change (e.g., central route to persuasion). 8. Anticipate the impact of behavior on a self-fulfilling prophecy.