Gastrulation
advertisement

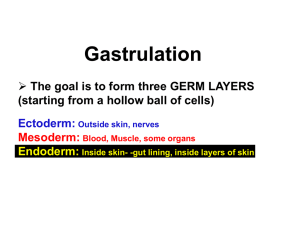
Gastrulation Gastrulation - The point in embryogenesis where the basic organization of the organism is established. A. Establishment of the three basic germ layers Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm B. Groups of cells that will give rise to specific organ systems and tissues are moved into the right position both externally and internally. C. Groups of cells that will influence each others differentiation are positioned so they can have an effect on each other. QUESTIONS? How are layers of tissue established? How do cells get to their proper positions for development? In part, this is accomplished by various types of Morphogenetic Movements. Morphogenetic Movements Epiboly Morphogenetic Movements Invagination, Evagination Morphogenetic Movements Involution Epiboly over a fold Involution Morphogenetic Movements Delamination Morphogenetic Movements Ingression Morphogenetic Movements Cell Migration Cell Migration Morphogenetic Movements “Intercalation: rows of cells move between one another, creating an array of cells that is longer (in one or more dimensions) but thinner.” “Convergent Extension: rows of cells intercalate, but the intercalation is highly directional.” - involved in formation of the primitive streak in avian and mammalian embryos. http://biology.kenyon.edu/courses/biol114/Chap14/Chapter_14.html Morphogenetic Movements Differential Growth .. .. .. .. time .... .. .. ... .. .. .. .. .. .. Starfish/Sea urchin gastrulation http://www.gastrulation.org/ http://www.uoguelph.ca/zoology/devobio/210labs/gastrulation1.html http://www.luc.edu/depts/biology/dev/urchgast.htm http://biology.kenyon.edu/courses/biol114/Chap14/Chapter_14.html ingression - primary and secondary mesenchyme invagination - initial formation of the archenteron convergent extension - lengthening of the archenteron Amphibian Gastrulation (Urodeles, e.g. salamanders) Urodele blastula Urodele 18 - 20 hr Urodele 18 - 20 hr Urodele 18 - 20 hr 28 hr 38 hr http://biology.kenyon.edu/courses/biol07/gastmovs.html 15 hr of time lapse, 48 min/sec http://www.gastrulation.org/ Shell Shell membrane Thin albumin Blastodisk Yolk Chalazae Air pocket http://www.zoomwhales.com/subjects/birds/label/chickenegg/ The morphogenetic movement that results in elongation of the primitive streak is convergent extension. z Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation Formation of the primitive streak Morphogenetic movement involved in the formation of the primitive streak is convergent extension. PRIMITIVE STREAK Actually, this is a human embryo. We have the same type of gastrulation as a chicken embryo, yet we do not have a large yolky egg. Why might this be? http://biology.kenyon.edu/courses/biol114/Chap14/Chapter_14A.html Establishing the Endoderm Extraembryonic endoderm Primary Hypoblast Secondary Hypoblast Embryonic endoderm Derived from cells that are originally in the epiblast that ingress through the primitive streak region and then migrate and insert into the hypoblast layer. Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation - primary and secondary hypoblast Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation Fate map as gastrulation is beginning Yolk Yolk Yolk Yolk Ingression during avian gastrulation Two regions of ingression: 1. Hensen’s Node 2. Primitive groove Timing (waves) of ingression: Later, Hensen’s node - initial waves 1st wave - foregut endoderm (mostly as primitive streak forms) 2nd wave - head mesoderm 3rd wave - chordamesoderm * Hensen’s node will contribute to somites as well *Some cells from Hensen’s node will remain in the epiblast and contribute to neural plate Ingression during avian gastrulation rimitive groove st wave - rest of embryonic endoderm (mostly as primitive streak forms) nd wave - mesoderm (embryonic & extraembryonic) Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation groove Embryonic ectoderm embryonic endoderm Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation - embryonic endoderm Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation Establishment of the primary germ layers Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation See animation on digital lab manual Chicken (Avian) Gastrulation