Early Development of Invertebrates
advertisement

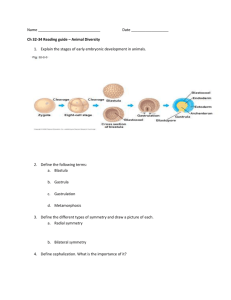
Early Development Selected Invertebrates Cleavage What characterizes this process? Cleavage How does the cell cycle of blastomeres compare with that of somatic cells? Cleavage What happens to the embryo during the mid-blastula transition? When does this occur? Cleavage What is karyokinesis and cytokinesis and how do they compare? Cleavage What influences the pattern of cleavage in a particular organism? Cleavage Cleavage Cleavage How are cell fates specified during cleavage? – cell-cell interactions – asymmetric distribution of morphogenic determinants Gastrulation What characterizes gastrulation in organisms? What kinds of movements occur? Axis Formation What are the three major body axes? Sea Urchin Development What does the cleavage pattern look like? Sea Urchin Development What characterizes the blastula stage? Sea Urchin Development At what stage are the fates of individual cells determined? Sea Urchin Development What role does βcatenin play in specification? Sea Urchin Development Sea Urchin Development When does axis specification occur? – animal-vegetal axis established before fertilization – anterior-posterior axis determined by a-v axis vegetal – determinants for posterior development – dorsal-ventral and left-right after fertilization d-v by first cleavage plane Sea Urchin Development How does gastrulation begin? Sea Urchin Development What appears to be responsible for the ingression of primary mesenchyme? Sea Urchin Development What appears to be responsible for the initial invagination that occurs during gastrulation? Sea Urchin Development What is the fate of these vegetal plate cells? Sea Urchin Development What happens during later stages of invagination? Sea Urchin Development Snail Development What kind of cleavage pattern characterizes these animals? Snail Development Orientation of cleavage plane determines right or left coiling snails Snail Development What appears to be responsible for the mosaic development seen in molluscs? Snail Development What is the polar lobe and why is it important? Snail Development Why does removal of the D blastomere or its first or second derivatives result in incomplete larvae? If D blastomeres don’t directly contribute cells to formation of many structures why are they so important to the formation of the same structures? Snail Development What other aspect of snail development does the polar lobe influence? – How do we know this to be true? Snail Development How does gastrulation take place in snails? Tunicate Development What makes these organisms rather unique? What type of cleavage pattern do they have? Tunicate Development In what way does the pigmentation in Styela partita provide developmental information? Tunicate Development What evidence is there of autonomous specification in tunicate blastomeres? – transplant experiments – RNA hybridization experiments – altering β-catenin levels in cells Tunicate Development What evidence is there for conditional specifiction? – BMP signal from endoderm induces anterior cell to become notocord works through activation of Brachury gene – FGF signal induces posterior cell to become mesenchyme Tunicate Development When are the embryonic axes established? – dorsal-ventral – prior to first cleavage – anterior-posterior – prior to first cleavage – left-right – first cleavage Tunicate Development What is gastrulation like in these organisms? Caenorhabditis elegans What does C. elegans look like? C. elegans What pattern of cleavage in seen in this nematode? C. elegans C. elegans What determines anterior-posterior axis? What is the importance of the Pgranules? C. elegans When is dorsal-ventral and left-right axes established? C. elegans In what way is autonomous specification demonstrated in this organism? – P1 develops without presence of AB cell In what way is conditional specification demonstrated? – AB cell requires cell-cell interactions – EMS requires signal from P2 C. elegans cell-cell signaling C. elegans Where in this organism is autonomous and conditional specification integrated? C. elegans When does gastrulation begin in this organism?