India_s Religions
advertisement
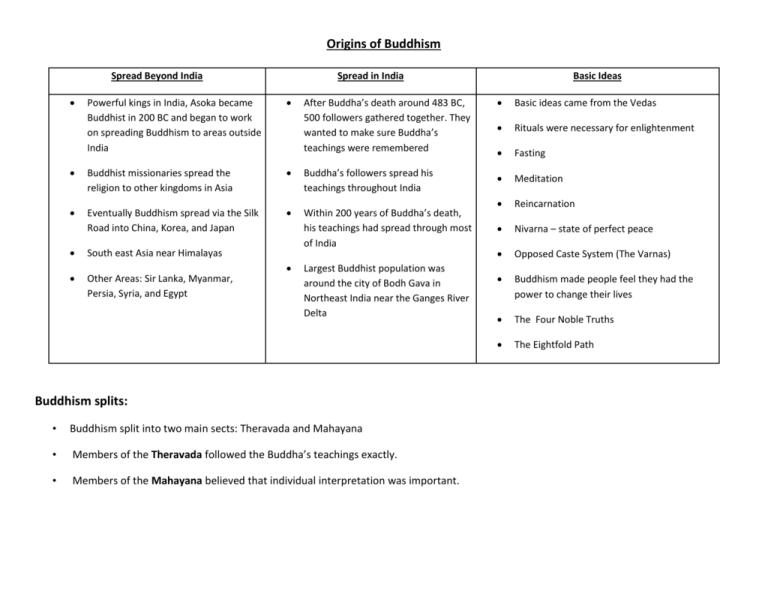
Origins of Buddhism Spread Beyond India Spread in India Powerful kings in India, Asoka became Buddhist in 200 BC and began to work on spreading Buddhism to areas outside India Buddhist missionaries spread the religion to other kingdoms in Asia Eventually Buddhism spread via the Silk Road into China, Korea, and Japan South east Asia near Himalayas Other Areas: Sir Lanka, Myanmar, Persia, Syria, and Egypt Basic Ideas After Buddha’s death around 483 BC, 500 followers gathered together. They wanted to make sure Buddha’s teachings were remembered Basic ideas came from the Vedas Rituals were necessary for enlightenment Fasting Buddha’s followers spread his teachings throughout India Meditation Within 200 years of Buddha’s death, his teachings had spread through most of India Reincarnation Nivarna – state of perfect peace Opposed Caste System (The Varnas) Buddhism made people feel they had the power to change their lives The Four Noble Truths The Eightfold Path Largest Buddhist population was around the city of Bodh Gava in Northeast India near the Ganges River Delta Buddhism splits: • Buddhism split into two main sects: Theravada and Mahayana • Members of the Theravada followed the Buddha’s teachings exactly. • Members of the Mahayana believed that individual interpretation was important. Origins of Hinduism Religion Brahmanism Polytheism Priest were called Brahmins Hinduism Hinduism believes in many gods, but they believe that all the gods are aspects of a single universal spirit called Brahman. Three aspects of Brahman are particularly important in Hinduism; Brahman, Siva, and Vishnu Origins Based on the Rigveda, oldest of the Vedas, written before 1000 BC Based also on a final group of Vedas text are Upanishads from 600 BC Developed out of Brahmanism and influences from other cultures Teachings Priest believed fire would carry a sacrifice to the gods Brahma A universal spirit named Brahman created the universe and everything in it. Everything in the world is just part of Brahman. Brahma Siva Vishnu Every soul is the architect of their own life Vedas Upanishads Ideas from Persia and other Central Asian Kingdoms Every person has a soul or Atman that will eventually join with Brahman. People’s souls are reincarnated many times before they can join Brahman. A person’s karma affects how he or she will be reincarnated Salvation is called moksha Dharma is a set of spiritual duties Karma is the effects that good and bad actions have on a person’s soul Ahimsa – practice of nonviolence towards all living things Polytheism Jainism/Jains Mahavira (Atheist) 559 BC Gods Jains React to Hinduism Origins of Jainism • 599 BC, established as an alternative to Hindu ritualism • Based on the teachings of Mahavira, who abandoned his life of luxury to become a monk Four Principles of Jainism • • • • Injure no life. Tell the truth. Do not steal. Own no property (practiced strict poverty) *By doing these things they could escape the cycle of rebirth and reach nirvana