Trust busting and
advertisement

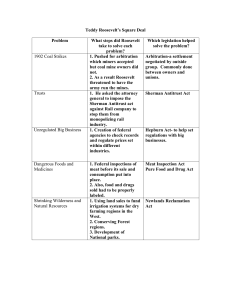
SLOGAN Protecting the Small QUOTES “We wish to control big business so as to secure among other things good wages for the wage workers and reasonable prices for the consumers.”(Theodor Roosevelt) “If necessary the nation has got to posses the right of supervision and control as regards the great corporations which are its creatures, particularly as regards the great business combinations which derive a portion of their importance from the existence of some monopolistic tendency.”(Theodor Roosevelt) TRUST BUSTING government activities seeking to dissolve corporate trusts and monopolies SHERMAN ANTITRUST ACT • In 1890 the Government took a stand against monopolies in fear that would crush free competition. • Sherman Antitrust Act passed to stop companies from interfering with free trade. • Almost impossible to enforce • Act didn’t define words like trust, prosecuting companies was not easy. • If companies felt any pressure from the government, they would just throw out their trust and reorganize into individual corporations • Supreme Court refused the act, and threw out seven of the eight causes • Government gave up on the enforcement of the Sherman Antitrust Act • Businesses continued to consolidate NORTHERN SECURITIES • In the twentieth century American were growing into great interregional systems • Separate railroad companies co-operated with each other • Two greats of the American railroad and finance were involved in railroad consolidation • J.P. Morgan • Wall Streets most powerful investment banker at the time • Highest interests were his holdings in the Northern Pacific Railroad • James J. Hill • St. Paul based “empire builder” • Owned the Northern railroad • His railroad crossed the same states as the Northern Pacific lines • Morgan and Hill saw an advantage in controlling the Burlington railroad • Created new corporation, The Northern Securities • Did not think about the power TR would bring to the presidency • Roosevelt prosecuted the Northern Securities company • 1904, Supreme Court shut it down RR REGULATION • 1887 congress passed the Interstate Commerce Act • Established a 5 member board called the Interstate Board of Commission • Railroad companies held monopolies in the area they served • Railroad companies set their own prices for shipment • Offered lower rates to customers with larger loads • In the 1860’s the Granger movement took place, which went against railroad monopolies for their high prices • Granger Movement- begun by farmers who called for government regulation of railroads and other industries whose prices and practices were monopolistic and unfair. • Granger movement failed and original interstate Commerce Act guidelines remaind ELKINS ACT • Senator B. Elkins presented the senate with the Elkins Act in early 1902 • In 1903 the Elkins Act was put into place to stop the practice of rebates • Rebates- A deduction from an amount to be paid or a return of part of an amount given in payment. • Gave federal courts power to end rate discrimination • The Elkins Act also upheld rates published by the Interstate Commerce Act HEPBURN ACT • Passed in 1906 the Hepburn act gave the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) the authority to make the railroad rates • The Hepburn Act was written by William Peters Hepburn • The ICC’s original purpose was to regulate railroads to ensure fair rates and regulate other aspects of common carriers FEDERAL TRADE ACT • Passed In 1914, the Federal Trade Act established the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) • FTC- a federal agency, established in 1914, that administers antitrust and consumer protection legislation in pursuit of free and fair competition in the marketplace. • The Federal Trade Act was one of Wilsons biggest acts against trusts • This act was issued “cease & desist” orders on large corporations to curb unfair trade practices • Also gave more flexibility to the U.S. Congress for judicial matters • Passed in the senate by a 43-5 vote on September 8th, 1914 and passed the house on the 10th • The Federal Trade Act’s principal mission was the promotion of consumer protection and the elimination and prevention of anti-competitive business practices CLAYTON ANTITRUST ACT • Passed in 1914 to clarify and supplement the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 • Drafted by Henry De Lamar Clayton • The Clayton Antitrust Act prohibited exclusive sales contracts, local price cutting, rebates, and intercorporate stock holdings COAL STRIKE • Took place in 1902, was also known as the Anthracite Coal Strike • United Mine Workers of America in the Anthracite coal fields of eastern Pennsylvania • Miners were demanding higher wages, shorter work days, and recognition of their union(UMWA) • Strike threatened to shut down winter fuel supply to all major cities • President Roosevelt set up a fact-finding commission that suspended the strike PRESIDENTS • Theodor Roosevelt • William Taft • Woodrow Willson