APUSH
advertisement
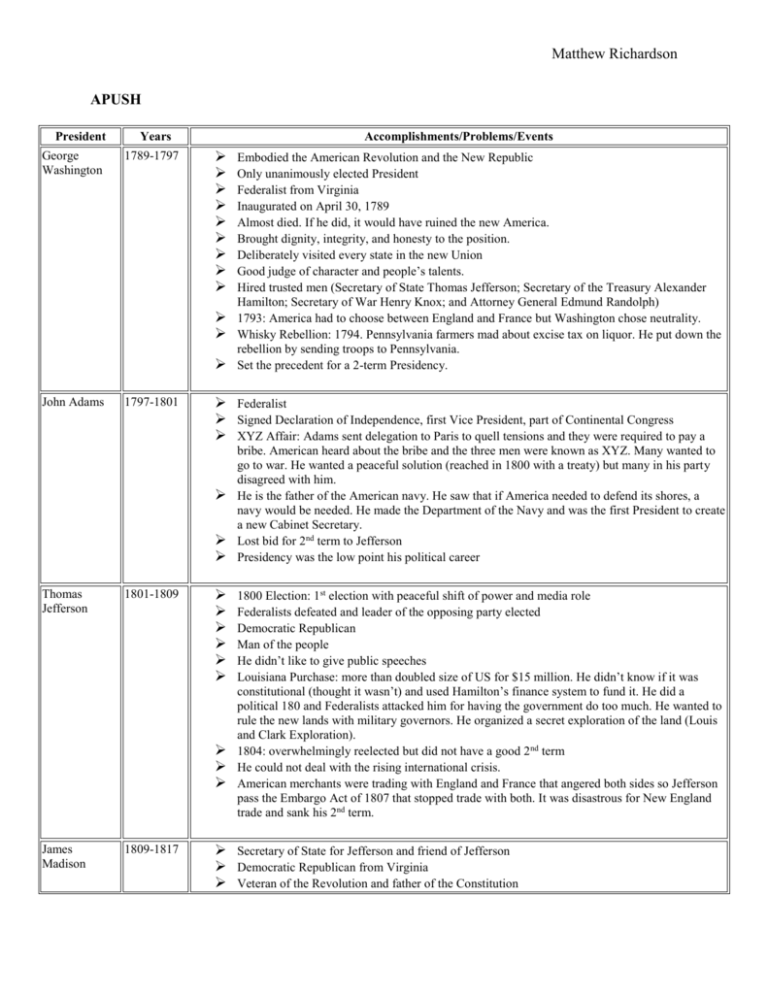
Matthew Richardson APUSH President George Washington Years 1789-1797 Accomplishments/Problems/Events John Adams 1797-1801 Federalist Signed Declaration of Independence, first Vice President, part of Continental Congress XYZ Affair: Adams sent delegation to Paris to quell tensions and they were required to pay a Thomas Jefferson 1801-1809 James Madison 1809-1817 Embodied the American Revolution and the New Republic Only unanimously elected President Federalist from Virginia Inaugurated on April 30, 1789 Almost died. If he did, it would have ruined the new America. Brought dignity, integrity, and honesty to the position. Deliberately visited every state in the new Union Good judge of character and people’s talents. Hired trusted men (Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson; Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton; Secretary of War Henry Knox; and Attorney General Edmund Randolph) 1793: America had to choose between England and France but Washington chose neutrality. Whisky Rebellion: 1794. Pennsylvania farmers mad about excise tax on liquor. He put down the rebellion by sending troops to Pennsylvania. Set the precedent for a 2-term Presidency. bribe. American heard about the bribe and the three men were known as XYZ. Many wanted to go to war. He wanted a peaceful solution (reached in 1800 with a treaty) but many in his party disagreed with him. He is the father of the American navy. He saw that if America needed to defend its shores, a navy would be needed. He made the Department of the Navy and was the first President to create a new Cabinet Secretary. Lost bid for 2nd term to Jefferson Presidency was the low point his political career 1800 Election: 1st election with peaceful shift of power and media role Federalists defeated and leader of the opposing party elected Democratic Republican Man of the people He didn’t like to give public speeches Louisiana Purchase: more than doubled size of US for $15 million. He didn’t know if it was constitutional (thought it wasn’t) and used Hamilton’s finance system to fund it. He did a political 180 and Federalists attacked him for having the government do too much. He wanted to rule the new lands with military governors. He organized a secret exploration of the land (Louis and Clark Exploration). 1804: overwhelmingly reelected but did not have a good 2 nd term He could not deal with the rising international crisis. American merchants were trading with England and France that angered both sides so Jefferson pass the Embargo Act of 1807 that stopped trade with both. It was disastrous for New England trade and sank his 2nd term. Secretary of State for Jefferson and friend of Jefferson Democratic Republican from Virginia Veteran of the Revolution and father of the Constitution Matthew Richardson Wife was Dolly Madison and brought the First Lady to the position Had lavish parties with oyster ice cream, Dolly’s favorite War of 1812 defined his Presidency. It was sparked by British seizing of American ships. Diplomatic efforts went nowhere. He was the 1st President to ask Congress for war declaration. The British military was much stronger than the American one. Sent Monroe to negotiate peace with England (Treaty of Ghent) that ended 1812 War Battle of New Orleans: (Andrew Jackson was a general) was after treaty 1812 War brought American Presidency to international affairs James Monroe 1817-1825 1816: harmonious election. Party politics seemingly vanished Democratic Republican from Virginia Last of the Revolutionary generation to hold office and last of Virginia dynasty Hands off executive that hired great people to cabinet and delegated authority Missouri petitioned to statehood but would it be free or slave? Would veto anything that prevented states from self-determination Missouri Compromise of 1820: Missouri enters as slave state and Maine enters as free state. American Colonization Society: wanted to ship slaves back to Liberia Monroe Doctrine (1823): American continents are not to be invaded by foreign powers. Written by John Quincy Adams (Secretary of State) John Quincy Adams Secretary of State for Monroe Jackson, Crawford, Clay, and Calhoun also wanted the job 1st election where states counted popular vote Jackson won popular vote but did not get majority of popular vote and it was between Jackson and Adams with Clay as Speaker of House. Corrupt Bargain: Adams won election and Clay was Secretary of State political demons and put his dad’s Presidency in a better light. He wanted to prove Adams was right. He wanted to show that he could do a good job despite the corrupt bargain. He didn’t play the patronage game (fire people against him and hire people for him). Later elected to the House. He was outspoken in the fight against slavery. LEGACY 1825-1829 Andrew Jackson Martin Van Buren 1829-1837 1837-1841 Election of 1828: dirtiest campaign in history. Adams said that he was a gambler. Adams attacked Jackson and Rachel (married Jackson before a divorce was final). Jackson said that Adams lived with his wife before marriage and provided a virgin for a Russian tsar. The election was about character Old Hickory, hero of New Orleans and conqueror of Florida Democrat from Tennessee Hero of the Common Man After the Eaton affair, he no longer trusted his cabinet members and fired and hired many. Bank War: began in 1832 when Congress renewed the Bank Charter early. Clay wanted the Bank re-chartered and Jackson hated Clay so he didn’t support the bank. Clay was running for reelection and was supported by the bank President so they tried to force Jackson to sign an act or Jackson would lose his reelection bid but Jackson did not agree. Jackson vetoed the bank bill. Jackson’s hand-picked heir Democrat from New York Father of Democrat Party Acted like an aristocrat Matthew Richardson Inherited financial ruins of Jackson’s Bank War Panic of 1837, 1939 (worse than 1837) caused by collapse in cotton prices Did not want to address annexation of Texas out of fear to ignite slavery discussion William H. Harrison 1841 (died) John Tyler 1841-1845 Thought there was too much power in federal government but expanded it Whig from Virginia Webster told him that cabinet would make all decision by consensus and Tyler said that they James Polk 1845-1849 Chosen by new Whig Party because he resembled Jackson Supported rechartering of Bank of US 1st election with open public rallies, songs, and slogans Tippecanoe and Tyler Too War Hero (Battle of Tippecanoe) Symbolized by log cabin Economy decided the election but his old age worried people Whig from Ohio would work with him or resign. The Whigs were worried that the Whig legislation that Harrison promised would not be passed. Tyler did not share Whig view Tyler vetoed 2 laws rechartering the bank. The Whigs kicked Tyler out of their party. Webster-Ashburton Treaty: settled northern border between US and Canada Annexation of Texas (passed through joint resolution) Not trusted by Democrats so he did not run for reelection Dark horse candidate but embraced because he wanted to continue Jackson’s work Democrat He was one of the most accessible Presidents. He was the 1st servant of the people and the “hardest-working President”. He had gas lights installed in the White House so he could work overnight and he was the 1st to work deeply in the budget and wanted budget requests sent to him first. Manifest destiny was his Presidential mandate 4 Goals: settle Oregon battle between Britain and the US, bring California into US, independent treasury to fix credit mess of Jackson, lower tariffs on imports into country. He threatened war with UK to settle Oregon battle. (54 40 or fight) and fought with Mexico to settle Texas, California, and SW. Zachary Taylor 1849-1850 (died) Milliard Fillmore 1850-1853 Whig from New York Unremarkable Both the North and South wanted to settle the West with their own ideals. Whig from Louisiana War hero (appealed to North) and Louisiana landholder and slaveholder (appealed to South) “Old Rough and Ready” Would go along with whatever Congress proposed Southern extremists threatened succession if Congress did not agree with them Compromise of 1850 Taylor threatened to veto Compromise of 1850 Became an ardent unionist Matthew Richardson “Accidental President” Fired all of the cabinet Signed Compromise of 1850 Supported slavery because he thought without it the Southern economy would collapse and thought it was protected by the Constitution Franklin Pierce 1853-1857 Northern Democrat with strong ties to South People thought he would bring balance and peace to the US Offensive to no one but left office reviled by all Participated in the large drinking culture of the time but was mainly sober during his Presidency Vice President King died Kansas-Nebraska Act designed to repeal Missouri Compromise of 1820 and let Kansas and Nebraska (both north of line) to decide for themselves if they wanted slavery or not James Buchanan 1857-1861 Democrat from Pennsylvania America’s only Bachelor President 1st Homosexual President with Pierce’s VP King Pro-Southern Brought nation to Civil War Near treasonous (supported Southern Constitution) Abraham Lincoln 1861-1865 (died) Created the Republican Party against the expansion of slavery spurred by Kansas-Nebraska Acts South lost its ally in the White House 8 states were Border States and 6 were the Deep South. 7 Southern states elected Jefferson Davis Andrew Johnson 1865-1869 their President. American icon (Lincoln logs, etc) Republican from Illinois Wanted to restore union like it was before they succeeded Drew people to him, especially young people Compelled to seek the truth, Honest Abe Northern troops needed supplies and Lincoln told Davis if the South attacked their supply boats they would be responsible for starting the war. They fired on Fort Sumter and 4 states joined the South. The Civil War began. Presidency defined by the Civil War. Nullified Emancipation Proclamation He later wanted to abolish slavery in the South to hurt their economy and end it in America. He then delivered the Emancipation Proclamation. Lee’s rebel army was marching to Pennsylvania and the Battle of Gettysburg occurred. The Gettysburg address rallied support for the Union. Visited soldiers to encourage them in their fights Laid out roadmap for peace and reconstruction in the states (malice for none, etc) in 2 nd inauguration Lee surrendered to Grant so war was almost over but Lincoln was not vindictive Shot on Good Friday by John Wilkes Booth Democrat-Union from Tennessee Southerner and a Democrat. Once owned a few slaves but remained with Union despite being from the South. He was chosen to broaden the ticket’s appeal. Matthew Richardson Ulysses 1869-1877 Simpson Grant Rutherford B. Hayes 1877-1881 Wanted to preserve the Federal Union “Last Jacksonian” Voice of Common White Man Most racist President Thaddeus Stevens and Charles Sumner wanted the South to be punished Congress extended the Freedman’s Bureau started by Lincoln but Johnson vetoed it Congress and Johnson were at odds; Johnson vetoed many Congressional acts (29 vetoes to 12 of Jackson) Civil Rights Bill of 1866: could be passed without Johnson. It was a federal law in the United States that made everyone born in the U.S full citizens. It was aimed at the Freedmen (freed slaves) and was a major policy during Reconstruction. Tenure of Congress Act: passed despite Johnson’s veto. It denied the President the power to remove from office anyone who had been appointed by a past President without the advice and consent of the United States Senate, unless the Senate approved the removal during the next full session of Congress. Congress prepared to impeach him, mostly motivated by political reasons. He avoided impeachment by 1 vote and continued the rest of his term quietly. Popular in the North Republican from Ohio Elected without majority of white vote (Blacks in South voted for him; 12% of total vote) Got a $20 speeding ticket for driving a horse drawn carriage too fast “Let us have peace” KKK began to act against Blacks so Grant launched a “war on terror” by sending troops to round up Klan’s men 1872: most peaceful year since the Civil war due to Grant’s leadership Grant became synonymous for corruption (Credit Moblier, Whisky Ring, etc) Despite scandals, his popularity won him reelection in 1872 Southern states began to be recaptured by the Democrats 1873: economic depression in the North Southern governments are beginning to be overthrown by terrorist groups but Grant did nothing. His presidency marked the end of Reconstruction. He had problems with Indians: Custer annihilated at Battle of Little Big Horn. He is remembered more for his magnificent failures than his well-intentioned efforts. Republican Ohio governor Would appoint people based on merit not spoil system He thought he lost the election to Tilden. Hayes lost the popular vote and several results from states were in dispute. Specially appointed committee voted on party lines to give 3 states in dispute to Hayes. The Great Compromise won him the election but he had to do certain things (unknown). It is suspected that he had to end Reconstruction by withdrawing the last federal troops from the South. He also attempted to reestablish honest government after the corrupt Grant administration. “Lemonade Lucy”: his wife banned liquor from the White House. He ordered the removal of troops from state houses. He felt betrayed by former Confederate leaders. The window closed on Reconstruction and doomed Blacks a lower class for 100 years. The New York Custom House was run by a corrupt man. The leader of the house was often rich because the person controlled much trade and thus going money from the tariffs (no income tax). Matthew Richardson James A. Garfield 1881 (died) Wanted civil rights for Black Americans and worked on education reform He was the 1st president to go the West and would not run for reelection. Vetoed efforts to restrict Chinese immigration Reflected political stalemate and patronage problems of the Gilded Age Republican from Ohio He tried to make everybody happy but made nobody happy. He was expected to address civil service reform. Killed by an insane man named Charles Guiteau barely a month into his presidency. No major accomplishments. Overwhelmed in first weeks in office by Republicans seeking ~100,000 federal jobs. Garfield’s choice of Halfbreeds (led by James G. Blaine) for most offices provoked a bitter contest with Senator Roscoe Conkling and his Stawarts. Republicans who were not Halfbreeds or Stalwarts were Mugwumps. A “Halfbreed” Reflected political stalemate and patronage problems of the Gilded Age Chester Arthur 1881-1885 Republican from New York Although he was a “Stalwart”, he tried to distance himself from them. He supported a bill reforming the civil service and approved the development of a modern American navy. He began to question the high protective tariff and thus was denied re-nomination by the Grover Cleveland 1885-1889 Benjamin Harrison 1889-1893 Republican Party in 1884. Lived a Gilded Age life and did not want to work hard He had to break from his party and his old friend Conkling Signed the Pendleton Act which broke the back of corrupt political machines. Upgraded the US Navy Much executive power had been ceded to Congress (in the era from Johnson to Arthur) Reflected political stalemate and patronage problems of the Gilded Age Presidential power was largely shadowed by Carnegie, Rockefeller, and JP Morgan Democrat and New York governor Devoted his life to cleaning up corrupt government Republicans pointed out that Cleveland had an illegitimate child. He took full responsibility and Americans forgave him. Cleveland won over Blaine He saw his job as to stop bad things from happening so he vetoed many acts that he saw as unwarranted drains on federal money. He did not think he could enact change. “People should support government but government should not support people.” Objected pensions for Civil War veterans. He did not want to financially support the people in an era where they needed it. Lost veteran vote in 1888 election Republican-backed high tariff determined the 1888 election. Democrats campaigned for Cleveland and a lower tariff. Republicans campaigned for Benjamin Harrison and a high tariff. Republicans agreed that a lower tariff would wreck business prosperity. They used this fear to raise campaign funds from big business and to rally workers in the North, whose jobs depended on the success of the US industry. The Republicans also attacked Cleveland’s vetoes of pension Matthew Richardson Grover Cleveland 1893-1897 Election of 1892: James Weaver was a Populist candidate and was relatively successful (22 William McKinley 1897-1901 (died) Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 bills to bring out the veteran vote. Cleveland received more popular votes but ended up losing because Harrison swept the North. Republican from Indiana Civil War veteran Lost the support of those around him because he was indifferent about things Alienated political bosses in the Republican party Nearly bankrupted the National Treasury 1st Billion Dollar Congress through McKinley Tariff of 1890, increases in monthly pensions to Civil War veterans, widows, and children, Sherman Antitrust Act, Sherman Silver Purchase Act of 1890, and a bill protecting the voting rights of African Americans (passed in House but defeated in Senate). electoral votes). The Populist ticket lost badly in the South and failed to attract urban workers in the North. The fear of Populists uniting poor blacks and whites drove conservative Southern Democrats to use every technique to disfranchise African Americans. Between Harrison and Cleveland, the unpopularity of the high-tax McKinley Tariff cost Harrison part of the election and Cleveland won. Democrat from New York Returned to Presidency Panic of 1893: great industrial bubble of 19 th century burst. Cleveland championed the gold standard but otherwise had a hands-off policy toward the economy. It was a result of over speculation and dozens of railroads went into bankruptcy as a result of overbuilding. Unemployment and farm foreclosures rose. As the depression worsened and unemployment rose, conservatives feared class war between capital and labor. They were alarmed by Coxey’s Army – a march to Washington in 1894 by thousands of unemployed people led by Populist Jacob Coxey of Ohio. The army demanded that the federal government spend $500 million in pubic works programs to create jobs. Coxey and other protesters were arrested for trespassing and the dejected army left for home. Coin’s Financial School by William Harvey in 1894 taught Americans that their troubles were caused by a conspiracy of rich bankers and that prosperity would return only if the government coined silver in unlimited quantities. Last of laid-back 19th century presidents Could not deal with changing tides Last Civil War veteran to be President Republican from Ohio 1st President to modernly manage the media Cubans suffering under Spanish regime and rebels were put into concentration camps Foreign nations were taking land and there was a fear that if the US did not take land, they would be overshadowed. They began to expand American military power in the Caribbean and Pacific. Americans also needed natural resources. Sent a warship to Cuba to protect American interests USS Maine exploded and American outcry made him go to war with Spain. Roosevelt resigned his executive position and organized the volunteer Rough Riders. It was an easy victory over Spain and the US became an imperial power. Roosevelt was Assistant Secretary of the Navy and wanted war with Spain Republican from New York He went after America’s greatest evil: too much power in the hands of business. He sued JP Matthew Richardson William Howard Taft 1909-1913 Morgan’s Northern Securities Corporation and Morgan’s monopoly was crushed. Thus, he was known as a trustbuster but really was a trust regulator. He feared that if he couldn’t get corporate America to let steam out of the pot, it would blow up. Many were poor. America had poor infrastructure and sanitation and working conditions for people (particularly coal miners) were miserable. Coal miners went on strike and without coal, the country would freeze. He threatened to nationalize the coal industry and got employees and employers to compromise on a way that favored labor. His resolution paved the way to better working conditions. He thought that the President needed to watch out for the American people. Square Deal: social and economic reforms. It had 3 C’s: control of the corporations, consumer protection, and conservation of natural resources. He thought Americans had a duty to civilize the rest of the world and that we were a world leader. Increased immigration worsened already poor working conditions. Working class and immigrant working conditions worsened. Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle exposed poor working conditions. He passed the Meat Inspection Act and the Pure Food and Drug Act. He wanted to promote conservation because he feared that if the frontier disappeared, so would the American identity. He created better labor conditions and business regulation. He chose Taft to be his successor since he said he would not run again for reelection. Republican from Ohio He was overall reluctant to be President but his wife pushed him. He was a lawyer and wanted to be a Supreme Court judge. He delegated responsibility and let his Cabinet members do as they please. He thought the President should merely uphold the Constitution. Roosevelt and Taft battled for the Republican nomination but they chose Taft for his Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 Warren G. 1921-1923 conservative politics. Roosevelt joined the Progressive Bull Moose. The division in the Republican Party let the Democratic Wilson win. Taft came in 3 rd. He later became Chief Justice of the US, a job he did well and liked. He regulated more trusts than Roosevelt and saw the 20 th century imperial Presidency that would abuse the position that might emerge. Election of 1912: between Taft, Wilson, and Roosevelt. Democrat from New Jersey (Governor before Presidency) New Freedom Create federal reserve to manage national currency Most Americans wanted nothing to do with WWI so he pledged neutrality but events such as the Lusitania, etc dragged the US into the war. 1st Democratic incumbent to win reelection since Jackson “The world must be made safe for democracy” Central to his idea of peace was the League of Nations that would be able to end war and connect countries. He obsessed over it. He let Pershing control America’s military. He wanted to keep the American army separate to show that the American motives were different than that of Europe. Congress passed the Sedition and Espionage Acts of 1918 made it a crime to criticize the government. Americans were tired of war abroad and Progressive reforms domestically. They wanted a Matthew Richardson Harding (died) Calvin Coolidge 1923-1929 Herbert Hoover Franklin Delano Roosevelt 1929-1933 1933-1945 (died) conservative President. Republican from Ohio Former Newspaper man He tried to surround himself with the best people for his Cabinet. His most important achievement was Budget and Accounting Act of 1921 gave the executive branch greater control over federal spending. It required the President for the first time in history to submit a federal budget to Congress. He arranged a conference in Washington with Britain, Japan, France, and Italy to set a limit on arms. Washington Naval Conference was the only serious arms limitation in the 1920s and 30s. He was the first sitting President to go to Alaska. After his death, scandals were revealed. Albert Fall (Secretary of Interior) illegally leased oil lands in America to oil businesses for a financial kickback (Teapot Dome). He was also accused of cheating on his wife. Although he was good with Congress and the budget, the scandals tainted his Presidency. Republican from Massachusetts Mean-spirited and not social Previously a lawyer and governor Believed in limited government and delegated power to his Cabinet He was elected to a full term of his own He kept a tight reign on the federal budget and killed pensions for postal workers and WWI soldiers and lowered taxes. Small government, booming business Business = American life Presided over era of prosperity but could not foresee the Great Depression Andrew Miller – Secretary of the Treasury did not understand the financial situation and Coolidge trusted him. Did not run for 2nd term and Hoover won Hoover = presidential failure Organized relief effort after WWI to save starving people in Belgium Food administrator under Wilson Secretary of Commerce for Harding and Coolidge Elected because he was a large public figure in the years before Republican from California First president born West of Mississippi River Managed like a CEO. Successful millionaire before Presidency Invented Hooverball Big business Republican who didn’t relate to common man “Only trouble with capitalism is capitalists” Hooverhotel, Hooverville, Hoover flag began in summer of 1932 Bonus Army: WWI veterans marched on Washington demanding pensions from the war early and he sent troops to control them. FDR offered hope for tomorrow but under Hoover it looked like nothing was getting better. Crippled by polio at 39 Political flexibility and charisma helped him the Presidency New Deal: series of initiatives that tried to stabilize American life in all parts of America Democrat from New York Matthew Richardson Eleanor Roosevelt: partner in New Deal. She helped him with his polio and toured the country Harry S. Truman 1945-1953 Democrat from Missouri He was informed of the Manhattan Project after he became President and had to decide whether they were going to drop the atomic bomb. 1 million-500000 casualties if Japan was invaded Potsdam Conference: unconditional surrender of Japan or destruction August 15, 1945: Japanese surrendered “The buck stops here” US vs USSR: Acheson and Marshall helped him make decisions Containment Policy = Truman Doctrine: asserted US right to help nations fend off Communist aggression Marshall Plan: US spent $12-14 billion to reconstruct Europe. SUCCESS NATO Role model of Democracy Jan 1948: executive order ended segregation in military Republican from Kansas He was reluctant to let the country go in the wrong direction so he ran for President. Mastermind of D-Day Rather play golf than govern His hero was George Washington Dwight D. Eisenhower 1953-1961 for him and connected him to the country. She supported social welfare and was the conscience of the New Deal. “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself” Hundred Days Congress Letter Legislation Social Security Act of 1935: unemployment, old-age, survivors, disability, and retirement He showed the American people that he was doing something and cared “Happy days are here again” He was losing his appeal but WWII helped his Presidency pick up speed again. 1937: he began to see war and began to convince isolationists that it might be necessary to intervene in the future Summer of 1940: France fell to Nazis November 1940: broke George Washington’s precedent and was elected to 3 rd term 1940-41: aided Allies but proclaimed neutrality Pearl Harbor (December 7, 1941) started his role as a war President. He picked great generals for WWII. He ordered the internment of Japanese on February 19, 1942 to please anti-Japanese chaos. They believed the Japanese couldn’t be trusted. He was criticized for his failure to respond to the plight of European Jews that were in concentration camps. Although he knew about the camps, he didn’t act on it much. He thought the most important thing to do was win the war and that if they won it would help the Jews, etc. D-Day (June 6, 1944): attack on the beaches of Normandy to get a hold on mainland Europe 1944: ran for a 4th term 5 months after D-Day Yalta: meeting of Allies to discuss shape of New World Order. FDR and Churchill convinced Stalin to agree to the UN. 1945: he died Matthew Richardson John F. Kennedy 1961-1963 (died) Lyndon Baines 1963-1969 Johnson Richard Nixon 1969-1974 (resigned) “I Like Ike” Ended Korean War with armistice still used today Wanted to pursue peace by downsizing military Spent less on defense and used the money for to improve infrastructure and quality of life World’s largest public works bill: Federal Highway Act 1954: Brown v. Board of Education banned segregation in schools Chief Justice Earl Warren passed it. Eisenhower distanced himself from the decision because he thought it wasn’t time for desegregation and thought it wasn’t his place. S Vietnam would be democratic. Supported creation of the Bank of Vietnam, etc Democrat from Massachusetts “1000 Days” in office Role model for American men Health problems and sex scandals made him lose popularity Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis Advertised capitalism in the Cold War “Open Door” policy Was his own Chief of Staff Wanted people to come directly to come to him with bad news Bay of Pigs: group of Cuban exiles would go to overthrow Castro’s regime. It was a disaster but he took complete responsibility and America liked him. Peace Corps created “War on Poverty” Challenged America to reach for unimaginable (go to moon, etc) Cuban Missile Crisis: Oct 16, 1962. CIA told Kennedy that aerial photographs placed/were placing bases for nuclear missiles in Cuba capable of delivering nuclear attack anywhere in the US. CLOSE TO THERMONUCLEAR WAR Democrat from Texas Wanted to fulfill Kennedy’s legacy Wanted to be greatest President in history Rose from poverty and was larger than life. He was cunning and aware of people and their actions. He could analyze people. In-your-face management style Johnson treatment: overwhelmed people to get what he wanted. Get in your face, bribe, shout, etc to get your own way. 6’ 2” scared people Great Society Wanted to raise the discriminated and the underprivileged to new heights Voting rights Act of 1965 Civil Rights of 1964 and 1968 Medicaid, Medicare Federal funding for education 1968 ran on platform with secret plan to end war but he wanted to keep the war going. He didn’t want the Democrats to win anything that would prevent him from passing legislation. Republican from California Congressman, US Senator, and Vice President Presidency was vehicle for punishing enemies and promoting friends. Matthew Richardson He had a desperate need to prove himself. Obsessed with power and had to be in control at all times Bypassed Secretary of State and Secretary of Defense so that Kissinger (National Security Gerald Ford 1974-1977 Adviser and Secretary of State in Nixon’s 2nd term) and Nixon could control foreign policy. Publicly endorsed plan to end the war but privately escalated war by bombing Cambodia and invading Laos When the news came out about Cambodia and Laos, he ordered widespread wiretapping to trace the leak. Nixon and Kissinger came up with the Triangular Diplomacy to end Vietnam War. They wanted to disengage from Vietnam while playing USSR and China against each other. Key to peace was good relations with China (Vietnam’s ally). They formed a diplomatic relationship with Chinese (Nixon recognized the Communist government in 1979) and then reached an agreement with Hanoi. Nixon used his relationship with China to put pressure on the USSR to reach a treaty limiting antiballistic missiles (would have expanded arms race). The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I) secured this agreement. “Peace with honor” in Vietnam Could exert leverage with USSR Played both sides of the fence (China and USSR) Visit to China in 1972 Strategic arms limitation treaty Breakthroughs with communist world led to reelection Ceasefire with Vietnam in 1973 Promised S Vietnam President that US would bomb N if the N president did not follow ceasefire Watergate: Nixon’s associates broke into the offices of the Democratic national headquarters in the Watergate complex in DC. The break-in and attempted bugging were only a part of illegal activities and “dirty tricks” conducted by the Nixon administration and the Committee to ReElect the President (CREEP). Previously, Nixon wiretapped government employees to stop news leaks. Presidential aides created a group (the “plumbers”) to stop leaks and discredit opponents. The “plumbers” burglarized Daniel Ellsberg’s office (he leaked the Pentagon Papers) to discredit Ellsberg. The White House also created an “enemies list” of prominent Americans who opposed Nixon and/or the Vietnam War. People on the list were investigated by government agencies (IRS, etc). Watergate, etc reflected the Nixon administration’s attitude to do anything to promote national security. Republican from Michigan Walked into White House full of turmoil America felt betrayed of Washington Congress wanted to regain power they felt was stolen from them Consensus building history Ford was needed after Nixon Frustrated with inability to preside over business of the nation Spent more than ½ of his time dealing with Watergate aftermath and then cut it off to deal with internal improvements (inflation, etc) Gave Nixon pardon to prevent Watergate from consuming his term N Vietnam broke peace accord and Ford requested help to help S Vietnamese but Congress refused. Congress did not know that Nixon had promised aid. This prompted S Vietnamese to try to escape using drastic measures. Saigon fell to the Communists. Did not have support of the nation Wanted his legacy to be “leave the country better than the way I found it” Matthew Richardson Wanted to forget about Vietnam and Watergate so turned to Carter. Jimmy Carter 1977-1981 Peanut farmer and 1-term governor Promised never to tell a lie Inspired confidence and optimism in the country (needed after Watergate and various Ronald Reagan 1981-1989 assassinations) Was selling the fact that he was not a Washington outsider Homespun image Democrat from Georgia Wanted to be a different kind of President Walked inaugural route Family was a part of his campaign Micromanager Deeply religious and Southern Baptist Protestant work ethic Added posts for energy and education to Cabinet President who made human rights central to foreign policy 1978: Camp David Accords between Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin. The two leaders first met in Jerusalem and Carter then invited both to meet at Camp David, Maryland. After 13 days, the three negotiated the Camp David Accords (September 1978) that provided a framework for a peace settlement between Egypt and Israel. Egypt later became the first Arab nation to recognize Israel and Israel withdrew its troops from the Sinai territory taken from Egypt in the Six-Day War of 1967. Carter tried to bring peace between Israel and Egypt and address problems of the Palestinians. The treaty was opposed by the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) and most of the Arab world, but it proved the 1 st step to a negotiated peace in the Middle East. The signing of the Camp David accords were the high marks of his Presidency. Conservative rhetoric Republican from California Previously an actor “Teflon President” Nancy Reagan Disengaged manager “Great Communicator” Challenger Disaster: Challenger shuttle exploded while leaving Iran Contra Affair: Since 1980, Iran and Iraq had been feuding. Reagan aides proposed (Americans didn’t know) that the US government sell antitank and antiaircraft missiles to Iran for its help in freeing the Americans held hostage by a radical Arab group. In 1986, another aide proposed that the profits of the arms deal with Iran should fund the contras in Nicaragua. Reagan denied the knowledge of the illegal diversion of funds (illegal because it violated the Boland Amendment and the congressional budget authority). This led to images of an uninformed, hands-off president who was easily manipulated by advisers. He avoided criminal charges but partially accepted responsibility. Core Beliefs: government is the problem not the solution to our problem Wanted to shrink government Supply-side economics: tax cuts reduced government spending, would increase investment by private sector, and lead to increased production, jobs, and prosperity. Supply-side economics reminded some of the “trickle-down” economics of the 1920s in which the wealthy prospered and some of their increased spending helped the middle class and the poor. This contrasts with Keynesian economics favored by Democrats with relied on government spending to boost Matthew Richardson George Herbert Walker Bush 1989-1993 Republican from Texas VP for Reagan Won the election with bold campaign of READ MY LIPS NO NEW TAXES Decisive 1st sitting VP to win since Van Buren Formerly 2 term Congressman from Texas, head of CIA Yale graduate Preppy image allowed him to be characterized as a wimp by opponents WWII hero Wanted to show he was more engaged than Reagan Wanted to govern country based off of consensus End of Cold War and Gulf War against Hussein defined his Presidency Needed Gorbachev’s help Did not celebrate fall of Berlin Wall to fizzle out relations with Gorbachev. He did not want the Cold War to end with a BANG. Most difficult test of Presidency: Hussein of Iraq invaded Kuwait (naked aggression) Would go to war to protect Persian energy reserves for West (1991) so he went to war Got support of the UN, European nations, and Middle Eastern countries Cared about support of other countries Iraqi army surrendered from Kuwait and Bush could have send troops into Baghdad to topple Hussein from power but he didn’t. He let Hussein stay in power since he said he only wanted to get him out of Kuwait. After the war, his approval rating shot up and he was expected to be reelected. HOWEVER, Reagan’s deficit made him raise taxes and cost him the election. Legacy of political moderation Inadequate salesman of his policies but good overall strategist, etc Charismatic Democrat from Arkansas 1st Rock ‘n Roll President (played saxophone) Ran youthful campaign (went on MTV and told America what type of underwear he wore, etc) Natural politician Seductive and charming Famous for his handshake Rhodes scholar Empathetic “I feel your pain” William Clinton 1993-2001 consumer income and demand. Deregulation led to more money in the hands of investors and higher income Americans Build military Lower taxes Led to huge deficits Overwhelmingly reelected and trumpeted return of prosperity Overlooked AIDS, homelessness, and women’s rights Did not want to use government for social engineering His leadership won the Cold War for America Strong rhetoric was his political cover so he could take soft stance on Soviet counterpart (Gorbachev). The 2 had summit meetings. The two became fast friends but Reagan’s aids were worried that Gorbachev would overpower Reagan Matthew Richardson George W. Bush 2001-2009 Chaotic management style Wanted to listen to different opinions and viewpoints Valued Hilary Clinton’s opinion 1st First Lady to have an office in the West Wing Republican party gained control of both Houses There was a surplus of revenues. Republicans wanted tax revenue cuts (elimination of estate taxes and taxes on 2-income families). Clinton wanted to use the projected surplus to support Social Security, expand Medicare, and reduce national debt. Newt Gingrich (Republican Speaker of the House) led attack on federal programs and spending. Clinton and moderates agreed with the goal of a balanced budget but Clinton wanted a “leaner not meaner” budget. This confrontation resulted in 2 shutdowns of the federal government in late 1995, which many American blamed on an overzealous Congress. Clinton refused to compromise on Medicare, Social Security, and the national debt. Republican from Texas 2000: Al Gore v George W Bush. Gore won popular vote but neither won electoral vote. Florida needed to be decided on to know the winner. Whoever won Florida won the position. A 5-4 partisan Supreme Court decision halted the recounts and gave the position to Bush. Bush tried to avenge his father. Only Presidential son to win office along with John Q. Adams More conservative than Bush Sr. America is the good force Took policy steps to ensure that good would triumph over evil National sheriff, “protecting the homeland” One of the most decisive Presidents in history Delegates to advisors Inarticulate speaking Lack of curiosity for details Ran a tight ship. Was early for everything. Wanted brief things, salute Commander in Chief 9/11 made it so he couldn’t have a leisurely Presidency Launched military campaign to rid Afghanistan of Taliban. Was supported by Americans Department of Homeland Security 2002 State of the Union address widened enemies to N Korea and Iraq (AXIS OF EVIL). This allowed him to invade Iraq. He cited preemptive unilateral war as a reason to invade Iraq though it was not favored internationally 2004: reelected to 2nd term








