Mammals
advertisement

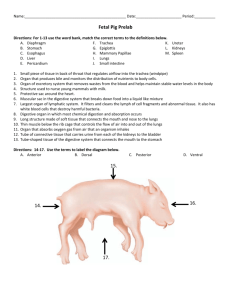
Mammals Classification • • • • Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrates Class: Mammalia • 20 different Orders • 4400 Species – Very diverse class – Live on every continent & in every ocean Key Mammalian Characteristics • 1. Endothermic: – Warm-blooded • Can live in any climate • Regulate internal temperature • VERY ACTIVE Key Mammalian Characteristics • 1. Endothermic: – Subcutaneous fat(under our skin) – Form insulation – Protection of internal organs Key Mammalian Characteristics • 1. Endothermic: – Sweat glands or panting, shedding – To cool down Key Mammalian Characteristics 2. Hair/Fur – Insulation – Camouflage – Protection Key Mammalian Characteristics 3. Completely divided 4 chambered heart – Has a complete septum • Very efficient heart b/c clean & dirty blood never mix Key Mammalian Characteristics 4. Milk production (mammary glands)modified sweat glands – Used by the female to feed young – Teats (provide milk from mammary glands) Key Mammalian Characteristics 4. Milk production Milk contains: • Protein • Vitamins • Fat • Calcium (sm. amt.) • Water Key Mammalian Characteristics 5.Single Jawbone – Lower jawbone is single 1 1 6. Specialized Teeth • Back teeth: chewing, grinding, crushing, slicing • Molars: grind food • Pre-molars: grind food 6. Specialized Teeth • Front Teeth: biting, cutting, seizing prey • Canines: grip & puncture prey • Incisors: to cut • 1st place physical digestion occurs Teeth and Skull Did you know that bone is 5X stronger than steel? Teeth and Skull History of Mammals • Evolved from mammal-like reptiles • Mammals & dinosaurs evolved @ same time (mice-size) • Once dinos went extinct – most successful at finding food – became larger Monotremes • Oviparity – Egg layers – lay 1-2 leathery eggs per year – feeds off yolk of egg – mammary glands • Live in New Guinea and Australia Marsupials • 280 species of marsupials – Ex. Opossum (live in US), kangaroo, koala • Viviparity – Give birth to live young – Develop in uterus(sm period of time) – Under-developed young crawl out of vagina into pouch where they feed off teats Placental • • 19 orders of placental animals Viviparity – Give birth to live younguterus, placenta, umbilical cord (provides nourishment to fetus from mother) – Gestation period (time it takes for full fetal development) – Cared for by parents – Fed w/ mammary glands until old enough to feed on own Gestation Periods Digestive System – Write Small **More Info in Unit Review** • To break down food into useable molecules= carried to cells via blood • 1) Mouth-teeth physical digestion • 2) Salivary glands – Produce saliva – Contains enzyme amylase • Chemical digestion of carbohydrates Digestive System • 3) Esophagus – Passageway for food from mouth to stomach – peristalsis: Wave-like motion that pushes food to stomach • 4) Cardiac Sphincter – End of esophagus, beginning of stomach – Ring of muscle – Keeps food moving in 1 direction – “heart burn” if food moves back into esophagus from sphincter Digestive System • 5) Stomach – Muscular sac which digests proteins – Physical digestion in form of churning – Chemical in form of HCl + pepsin to break down proteins – Special lining to protect from acid; can lead to ulcer – Chyme- undigested food+enzyme+acid Stomach Digestive System • • 6) Pyloric Sphincter – Ring of muscle which keeps food moving from stomach to sm. intestine 7) Small Intestine – ~20-21 ft. long – 3 sections – Duodenum: 10“ carries chyme to jejunum – Jejunum: 8’ carbs, proteins, lipids digestion; absorbed into blood – Ileum: 13’ takes undigested material to large intestine – Has villi Villi in Small Intestine -Villi increases surface area Digestive System • 8. Large Intestine – – – – larger diameter 3 ft. long to remove excess water too much water absorbed=constipation – too little water absorbed=diarrhea • 9. Rectum & Anus – holds solid waste until expelled (rectum) – exit (anus) Caecum/Appendix • Caecum-pig – “dead-end” – Helps digest plant material • Appendix-humans – No apparent function Rumen • Sheep, cows • Regurgitate-cud Digestive SystemAccessory Organs • Gall bladder – Stores bile: for the digestion of lipids • Pancreas– pancreatic amylasecarbs – lipase-lipids – pepsinogen- proteins – sends these enzymes to small intestine (don’t pass thru) Liver Gall Bladder Under Liver Stomach and Pancreas Pancreas To Digest… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Ingest Chew 10 to 30 times Swallow 4 to 8 seconds Churn 2 to 4 hours Absorb 3 to 5 hours Compact 10 hours to several days! Eliminate Respiratory System **more info in unit review** • To transports O2 and CO2 from atmosphere to the cells • Two types – External: air thru nose to lungs – Internal: gases w/ in blood are exchanged w/ cells Respiratory System • Nostrils/Nares- with hair to trap particles • Pharynx- food & air • Epiglottis small flap to separate food & air passage • Trachea- made of rings of cartilage so it doesn’t collapse “windpipe” Salivary Glands and Larynx Trachea Respiratory System • Bronchi-lead to lungs • Bronchioles- little tubes • Alveoli- little air sacs • Pleura – Secretes slippery fluid to reduce friction – Surrounds the lungs Respiratory System Respiratory System Respiratory System • What happens when you run & it’s cold outside? Avg. Pack of Cigarettes Circulatory System • • • • Heart is main organ – Veins-carry blood to heart – Arteries-carry blood away from heart Heart lies in center of chest/ thoracic cavity btw. lungs – Underneath sternum(breast bone) 4 chambers – 2 sides – Divided by a complete septum Spleen-destroys or recycles old red blood cells Liver and Spleen Circulatory System • Right – Pumps dirty blood (CO2) to lungs – pulmonary • Left – Pumps clean blood (O2) to body – systemic 60,000 miles of blood vessels STUDY blood pathway paragraph in notes!! Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Superior Vena Cava Pulmonary Artery (dO2 blood) to Lungs Pulmonary Vein (O2 blood) from Lungs Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Semilunar Valves (Pulmonary & Aortic) Inferior Vena Cava LABEL HEART Right Ventricle DIAGRAM Septum Left Ventricle (MOST MUSCULAR-PUMP) Bicuspid/Mitral Valve Left Atrium Aorta Male Posterior View Female Posterior view Nervous System • See Notesheet Unfolded Brain Surface Area=1m2 Average Brain Weighs= 3 lbs Excretory System • To filter out and eliminate metabolic wastes and help maintain homeostasis – Gets rid of excess H2O , salt, vitamins, toxins, minerals, and heat – Nitrogenous Waste: ammonia converted to urea in liver Excretory System • 2 kidneys-reddish bean shaped organ – Size of a clenched fist – Lie along in small of back Structure of a nephron • Each kidney is made up of one million+ nephrons (filtering unit) • Blood enters kidney via the renal artery • Blood is pushed through a nephron where excess H2O, salt, toxins, minerals, urea is filtered out. Structure of a nephron • Blood enters the bowman's capsule • Capsule filled w/ glomerulus( ball of blood vessels) • all substances are filtered out • Cleaned blood reenters cir. system Structure of a nephron • Impurities travel along the renal tube • Some items reenter blood; impurities empty into the renal pelvis 3 Main Parts of a Kidney • 3-parts – Cortex-outer portion of kidney – Medulla-inner region – Renal pelvishollowed out area where all waste gathers. Urine Formation • All nephrons empty into renal pelvis • Renal pelvis empties into the ureter(1/kidney) • Ureter leads to bladder and urine exits out the urethra Urine Formation • Average Adult: – ~1.5-2.3 Liters/day – Greatest amount of water loss • Must urinate 500mL to get rid of toxins **See Notes for Repro** Male or Female?!? Smallest Cell in Body Largest Cell in Body ½ Hour as a Single Cell Heart of the Embryo… Beats at 3 weeks!!!! All organs by 9 weeks… Eye Size= SAME!!! Skin weighs 9 lbs!!! Muscle Mass: -1/2 Men -1/4 Women 1 month to replace ALL skin cells Bone=matrix of hard minerals