Historical Examples of Government Actions
advertisement
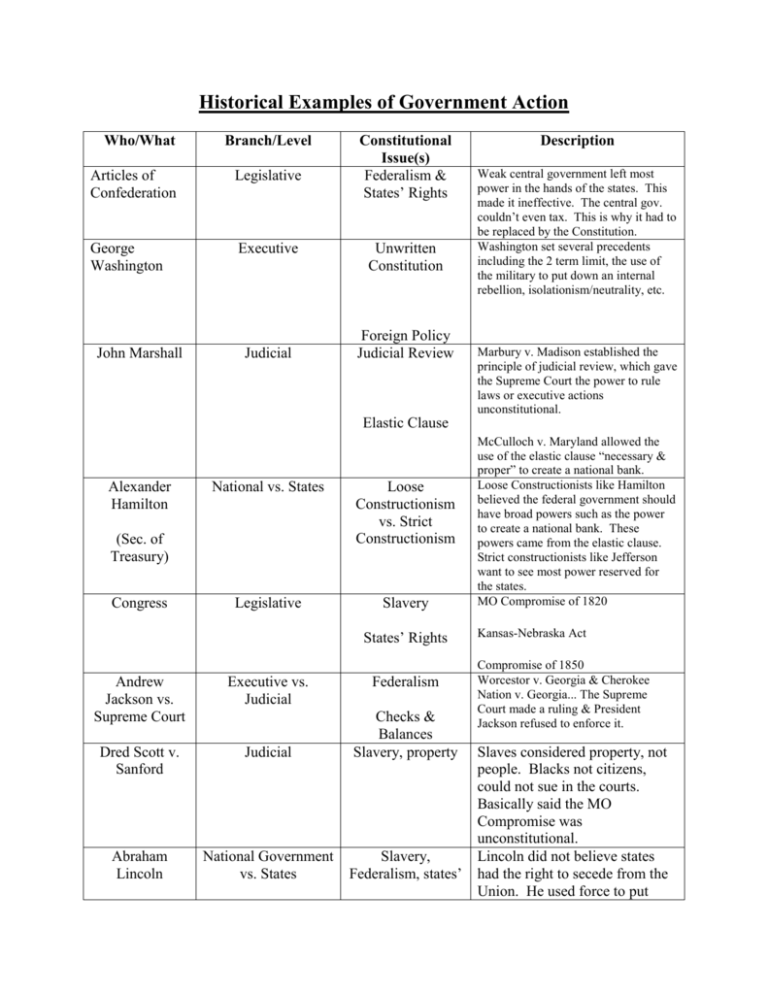
Historical Examples of Government Action Who/What Branch/Level Articles of Confederation Legislative George Washington Executive John Marshall Judicial Constitutional Issue(s) Federalism & States’ Rights Unwritten Constitution Foreign Policy Judicial Review Description Weak central government left most power in the hands of the states. This made it ineffective. The central gov. couldn’t even tax. This is why it had to be replaced by the Constitution. Washington set several precedents including the 2 term limit, the use of the military to put down an internal rebellion, isolationism/neutrality, etc. Marbury v. Madison established the principle of judicial review, which gave the Supreme Court the power to rule laws or executive actions unconstitutional. Elastic Clause Alexander Hamilton National vs. States Loose Constructionism vs. Strict Constructionism Legislative Slavery (Sec. of Treasury) Congress States’ Rights Andrew Jackson vs. Supreme Court Executive vs. Judicial Federalism Dred Scott v. Sanford Judicial Checks & Balances Slavery, property Abraham Lincoln National Government vs. States Slavery, Federalism, states’ McCulloch v. Maryland allowed the use of the elastic clause “necessary & proper” to create a national bank. Loose Constructionists like Hamilton believed the federal government should have broad powers such as the power to create a national bank. These powers came from the elastic clause. Strict constructionists like Jefferson want to see most power reserved for the states. MO Compromise of 1820 Kansas-Nebraska Act Compromise of 1850 Worcestor v. Georgia & Cherokee Nation v. Georgia... The Supreme Court made a ruling & President Jackson refused to enforce it. Slaves considered property, not people. Blacks not citizens, could not sue in the courts. Basically said the MO Compromise was unconstitutional. Lincoln did not believe states had the right to secede from the Union. He used force to put rights Radical Republicans vs. Andrew Johnson Legislative Branch vs. Executive Branch Checks & Balances Tilden v. Hayes Legislative and Executive Branches Selection of President in Ties Woodrow Wilson vs. Congress Executive vs. States Foreign Policy: isolationism FDR Executive Federalism down the rebellion of the southern states. Johnson’s vetoes: Reconstruction Acts: Federalism Impeachment: Compromise of 1877 Ratification of Treaty of Versailles Schecter Poultry Corp. v. U.S. National vs. States Wilson, FDR, Nixon, Checks on Judicial Court Packing: Branch Executive/Legislative Civil Liberties vs. Schenk v. U.S. &. Judicial National Security Korematsu v. U.S. NY Times v. U.S. Warren Court Judicial Rights of the Accused Gideon v. Wainwright Miranda v. Arizona Mapp v. Ohio Eisenhower, Kennedy & LBJ National vs. States 14th Amendment vs. states’ rights Enforcement of Brown v. BOED: Civil Rights Act of 1964: Voting Rights Act of 1965 Nixon Legislative vs. Executive Powers of President Nixon v. U.S. War Powers Act Ronald Reagan National & States Federalism Bill Clinton Legislative vs. Executive Powers of President George W. Bush Executive & Judicial Selection of President vs. Al Gore Federalism New Federalism... the federal gov. should be smaller and more power should be returned to the states. Impeachment Bush v. Gore








