Final Review Guide
advertisement

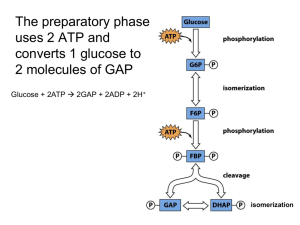
Final Review Guide: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. I. Carbohydrats Know the functional groups of carbohydrates, general formula Carbohydrate structure: Fisher projections, which Carbons are chiral and non-chiral Carbo naming: Tri-, tetr-, pent-, hexose # , Aldose/Ketoses/ difference between D/L and α/βstereoisomers Know the structure of the following monosaccharide structures linear as well as ringform: Glu, Gala, Fru, Ribose Know the structure and glycosidic bonds of the following disaccharides and their isomers: Maltose, Lactose, Sucrose Know similarities and differences of amylose, amylopectin, glycogen and cellulose Know where carbohydrates are digested and where the enzymes are located Where are carbs stored in the body? Know the products and names of oxidation/reduction/dehydration Rx of carbohydrates Know regulation of blood sugar, the two hormones,hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia What happens if the blood glucose is higher than the renal threshold? Know terms of diabetes symptoms: glycosuria, polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia II. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. LIPIDS Know the functional groups of a fatty acid, and which are hydrophobic/philic, what is aliphatic? What are the names, structures of a C12, C14, C16, C18 saturated fatty acid? Sort FA from 2. from lowest to highest boiling point, from lowest to highest solubility in water. Where are lipids digested, and stored in the body Draw a polyunsaturated C12:2 Omega-3 and Omega-6 FA in Kekule. Label the carboxyl carbon with #1 and the omega carbon end with a * Structure of Triglycerides: draw Glyceryl trihexanoate General Structure of Phospholipids General structure of a steroid nucleus Draw the saponification of Glyceryl trihexanoate with Potassium hydroxide Draw the complete hydrogenation of a polyunsaturated C12:2 Omega 3 FA Draw the partial hydrogenation of 13. forming a transfatty acid at a position of your choice Draw the hydrolysis of Glyeryl tripentanoate Draw the estrification of Glycerol and three Butanoic acids What does NSAID, recognize the structure of Aspirin Which enzymatic reaction does Aspirin inhibit? Define the words: analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, anti-coagulant Recognize cholesterol (use book, you do not need to memorized the details, but recognize it when you see it) outline the steroid nucleus in color, label the functional groups and identify whether they are polar or non-polar List the roles of cholesterol in the body Single bond (saturated), double cis, double trans (unsaturated): which one’s is/are found in nature, which is/are manmade? Double bonds from Q.18 rank from highest to lowest stabil? 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Where do phospholipids form a bilayer, where a monolayer? What does CAD stand for? CAD is the second leading cause of death in the US. How do you die of CAD? What is artheriosclerosis? What type of material is found in plaques? III. Proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Know the general structure of an Amino Acid and why it is called a zwitterions Know the main classes of proteins Know the meaning of the isoelectric point (IEP) , what happens at that pH Recognize the structural differences of nonpolar, polar, acidic, basic AA Understand a zwitterion Know the reaction forming peptide bonds and its general structure Recognize the peptide backbone, N-terminal and C-terminus of a peptide Know the general process of protein synthesis Know 1° and 2° , 3o and 4o protein structure and which structures govern those Explain denaturation what is an enzyme – what does it do, describe the active site and how a substrate fits know anabolic vs catabolic reactions explain the lock and key hypothesis Know what a prion is and how it causes proteopathic diseases IV. Metabolism 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. A. What is the net ATP, NADH, CO2 yield for metabolizing 1 mole of Glucose to Pyruvate? What is the net ATP yield for the aerobic metabolism of one mole glucose molecule to CO2? What is the net ATP yield for the anaerobic metabolism of one glucose molecule to lactic acid? A. What is the final electron acceptor of aerobic cellular respiration, know the reaction Is NAD the oxidized or reduced form of the coenzyme? Does NADH oxidize or reduce a substrate molecule? Draw a generalized coupled reaction using the words substrate, product, coenzyme at the appropriate locations 8. A. Write the thermochemical reaction of the combustion of glucose including enthalpy. What is the value for the enthalpy of glucose…know it! 9. Is the combustion of glucose endo or exothermic? 10. Recognize the main molecules of glycolysis when given names that reflect functional groups. 15. What is the coenzymes of a Kinase and Dehydrogenase Rx? 17. Where in the cell are the following metabolic pathways located: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, ETC, ATP synthase 18. How many compartments does a Mito have? C. If fully respiring, in which compartment can you find the lower pH? 19. Draw the full structure of an inorganic, fully dissociated phosphate ionPi 20. Sort the following functional groups from lowest to highest oxidized status: carboxylate, alkyl, aldehyde 21. Label parts of structures shown