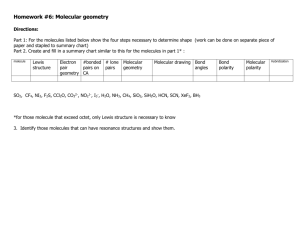
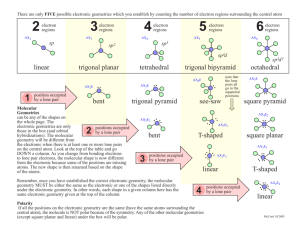
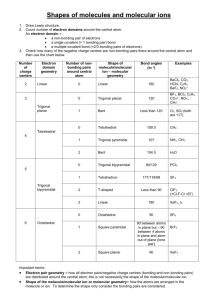
VSEPR Theory - MAEDA AP Chemistry
advertisement

Catalyst 1. 2. 3. Thalidomide Today’s Learning Targets • LT 2.6 – Using the concept of bond angles and electron repulsion, I can predict the electron and molecular geometry of a compound using the VSPER theory. • LT 2.7 – Using the molecular geometry of a compound, I can predict the polarity of a compound and the direction (if any) of a dipole moment. Exploration of Molecular Shapes • Take out the handout titled “Exploration of Molecular Shapes” • Complete with a group member • Make sure to consider Lecture 2.4 – VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory • Lewis structures are 2 dimensional drawings, but atoms bond to form 3 dimensional molecules. • Since electrons repel one another, molecules will bond so as to have the largest bond angle. ▫ If possible, they will be 180o apart. • This is the foundation of the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Shape Picture Bond Angle Linear 180o Trigonal Planar 120o Tetrahedral 109.5o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120o and 900 Octahedral 900 VSEPR Theory and Lewis Structures • When examining Lewis structures to determine shape, we consider electron domains around the central atom ▫ An electron domain is either a bond or lone pair found on the central atom. • The number of electron domains determines geometry of the electrons around the central atom. Molecular Shape Number of Electron Domains Linear 2 Trigonal Planar 3 Tetrahedral 4 Trigonal Bipyramidal 5 Octahedral 6 Class Example • Predict the electron domain geometry of CCl4 Table Talk • Predict the electron domain geometry of BCl3 Molecular Geometry • Whether an electron domain is in a bond or as a lone pair on the central atom will impact the final overall shape of the molecule. • When determining the final molecular shape, determine the number of domains as lone pairs and the number in bonds Class Example • Predict the electron domain geometry and the molecular geometry of NH3 Table Talk • Determine the electron domain geometry and the molecular geometry of H2O Table Talk • Determine the electron domain geometry and the molecular geometry of the following two molecules: ▫ SF4 ▫ IF6 Dipole Moments and VSEPR Theory • The dipole moment of a molecule changes when the molecular structure is considered. • For molecules of 2+ atoms, the dipole moment depends on: 1. The polarity of the bond 2. The geometry of the molecule Class Example • Determine the dipole moment of CO2 Class Example • Determine the dipole moment of H2O Table Talk • Determine the dipole moment of CCl4 Table Talk • Determine the dipole moment of CH3Cl Summarize Race to the Finish! • With your partner, you need to complete the grid you picked up on your way into class. • The molecules you need to answer for are around the room. • First group to finish with the correct answers gets 5 EC points for their next exam. Closing Time • Do questions from section 9.1 to 9.3 and read remainder of chapter 9 for Monday/Tuesday • AP Lab 4 Pre-lab due at start of class Monday/Tuesday