Erikson - Streetsboro City Schools
advertisement

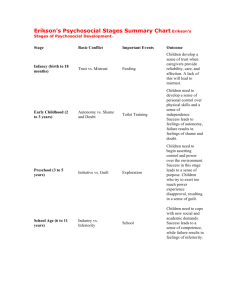
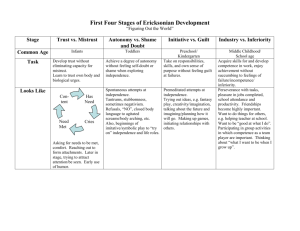
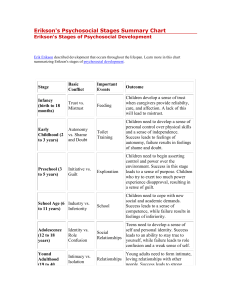
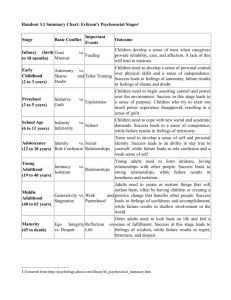
Erik Erikson Psychosocial Stages BY Lexi Altman and Chad Konik Erik Erikson ● Ego Psychologist ● Developed 8 stages of Psychosocial development. ● Stressed the emotional dynamics of social development. ● Born 1902 Frankfurt, Germany Erikson Early life ● Born to Danish parents ● Father left before he was born ● Mother remarried a German-Jewish pediatrician ● Mocked by non-Jews for his features and his faith Erikson’s Children Sue Erikson Kai T. (Daughter) Erikson (Son) Erikson Professional life ● ● ● ● Studied the work of Michelangelo in Rome No formal degree in Psychology Taught at Harvard and Yale Worked with Sioux and Yurok Native American groups Psychosocial Development ● The need for social approval is just as important as a child’s sexual and aggressive urges. ● Childhood experiences have a lasting impact. ● If a child isn’t used to having a parent stay in their life, that child could carry those abandonment issues with them and develop insecurities. ● Secure-positive and emotional bond; upset by mothers absence. ● Insecure- tendency to avoid reunion w/ parent or caregiver, Desire to be with parent or caregiver and some resistance to being reunited with mom. Erikson stages of psychosocial development ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Stage 1: Basic trust vs. Basic mistrust Stage 2: Autonomy vs. Shame Stage 3: Purpose initiative vs. Guilt Stage 4: Competence, Industry vs. Inferiority Stage 5: Fidelity, Identity vs. Role confusion Stage 6: Intimacy vs. Isolation Stage 7: Generativity vs. Stagnative Stage 8: Ego, Integrity vs. Despair Stage 1: Basic trust vs. Basic mistrust ● Infancy 0 to 1 1/2 ● Hope ● How you treat your infant. If you give it the stuff that they need like food, water, shelter then itll think the world is a good place ● if you don't give the infant the right stuff it'll grow up with a bad view upon the world. ● Childhood experiences have long lasting impacts ● Ainsworth-Emotional Attachment Trust V. Mistrust Stage 2: Autonomy Vs. Shame ● ● ● ● Ages: 1-3 years Discovering one's own abilities Asserting independence Children encouraged in their increase in independence become more confident ● Children criticized, overly controlled begin to feel inadequate and depend on others Autonomy V. Shame Trust V. Mistrust Stage 3: Initiative Vs. Guilt ● ● ● ● Ages: 3-6 years Rapid development years Asking questions If the parents treat the child's questioning as a nuisance, they feel guilt ● Too much guilt can result in the child being slow in interacting with others ● Some guilt is necessary to teach self-control Initiative V. Guilt Autonomy V. Shame Trust V. Mistrust Stage 4: Competence, industry vs. inferiority Initiative V. Guilt Autonomy V. Shame Trust V. Mistrust industry vs. inferiority ● School age (5-12) ● The child now feels like he needs to win approval ● If you make him feel approved then he’ll feel good about himself and get confidence ● If you make him feel not approved then he’ll doubt everything he does. Stage 5 Fidelity, identity vs. role confusion ● Age (12-18) ● Major stage where the child has to occupy the roles as adults ● They form their own Identity identity V. Role industry vs. ● They could become inferiority Initiative V. Guilt confused on their role Autonomy ● Identity formation vs. V. Shame Trust v. Identity confusion Mistrust Stage 6:Intimacy vs. Isolation Intimacy v isolation industry vs. inferiority Initiative V. Guilt Autonomy V. Shame Trust v. Mistrust Identity V. Role ● Struggle to form relationships ● Struggle to gain capacity for intimacy ● If not successful, can result in feeling socially isolated. Stage 7: Generativity Vs.Stagnation ● Ages:Middle adult ● Career, settle down in relationships, family, bigger Generativity V. Stagnation picture Intimacy V ● Give back to society by Isolation raising children, productive Identity V. Role at work, involved in industry vs. inferiority Initiative V. community Guilt ● Failure=Unproductive and Autonomy V. Shame stagnant Trust v. Mistrust Stage 8: Ego Integrity Vs. despair ● ● ● ● ● Ages: Older adult Senior citizens, slow productivity Contemplate accomplishments Success=Wisdom Wisdom-able to look back with a sense of closure and completeness ● Except death without fear Ego Integrity V. Despair industry vs. inferiority Initiative V. Guilt Autonomy V. Shame Trust v. Mistrust Generativity V. Stagnation Identity V. Role Erik Erikson Mary Ainsworth https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PxwWr6 T_O6s ● http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/Erikson. htmln ● http://www.erikson.edu/about/history/erikerikson ● http://www.muskingum.edu/~psych/psycw eb/history/erikson.htm