Balance of Trade
advertisement

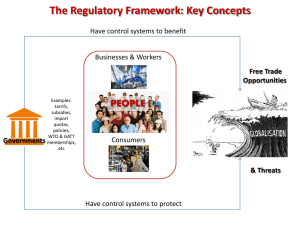
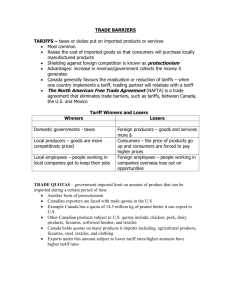
March 18/19, 2015 Warmups: Announcements: April 2, Due: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Macro bodies project Vocabulary journal Study Guide Unit 5 notebook Stop by the media center w/cards for Vineyard EQ What is the difference between balance of trade and balance of payments? Standard SSEIN2 IF the U.S. has imports worth $9 billion and its exports are worth $8 billion. The U.S. has a what? Define voluntary trade Define export Agenda: Notes Graded class activity. a) b) c) d) e) Define trade barriers as tariffs, quotas, embargoes, standards, and subsidies. Identify costs and benefits of trade barriers over time. List specific examples of trade barriers. List specific examples of trading blocks such as the EU, NAFTA, and ASEAN. Evaluate arguments for and against free trade. Free Traders: favor fewer or even no trade restrictions Protectionists: favor trade barriers that protect domestic industries Benefits of Barriers • provides revenue to importing country • Protects domestic producers of similar goods • Protects consumers from sub-standard quality • Helps businesses offset losses from international trade Costs of Barriers • Retaliation from other country • Higher prices for consumers • Inefficient use of resources • No supply or limited supply of goods Trading Blocs • A group of countries that come together to eliminate trade barriers in their region. • EU = European Union = 27 countries, Euro • NAFTA = North American Free Trade Agreement • ASEAN = Association of South East Asian Nations. Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, etc. • OPEC: Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries. Middle East and Venezuela Reasons for Barriers • Protecting infant industries • Protecting national security • Protecting domestic employment • Protecting workers in developing countries from unfair labor practices • Protecting the environment in developing countries. The Issue Free trade Promoting • Protection will be infant removed industries • Can’t predict which industries will grow • Retaliation from other countries Protecting Domestic Jobs From Developing Countries • Best not to interfere • Prices higher b/c protectionism • Free trade = new industries and jobs • Let them produce goods = become consumers Protectionism • Industries need to gain strength before competing globally • Need to grow and establish economies of scale • Protects workers from unemployment due to cheap labor in developing countries The Issue Free trade Protectionism National Defense • Disadvantages of a smaller supply • Potential for abuse • What happens during war? • Maintain industries critical to national security Environment • Too expensive for developing nations to follow • Richer the nation, more the citizens demand better environment • Used to support restrictions on trade with countries w/lax environmental standards Balance of payments dollars return to stimulate employment Restrictions help balance Types of Barriers • Trade Barrier = a law or action to restrict the flow of goods and services between two countries. • Tariff = a tax placed on goods when they are imported into a country. • Quota = a limit on the quantity of a good imported into a country. Types of Barriers • Embargo = – a complete ban on trade – Done for political purposes • Standards = requirements that a good must meet before it can enter the country as an import. • Subsidies = Government gives money to a business to offset loss. Examples • 2002 U. S. Tariffs on Steel: Bush issued tariffs on imported steel. • 2005 Quotas on China’s Textiles = new free trade rules from World Trade Organization U.S. and Europe lifted textile quotas in place for decades. • U.S. Embargo against Cuba, 1960-Present Examples • USDA Labeling Standards = U.S. Dept. of Ag requires all foods entering the U.S. to have proper nutritional and ingredient labeling. • U.S. Agricultural Subsidies = allows farmers to compete in world markets where prices are lower