Lamendella_R_08_Major2_Powerpoint
advertisement

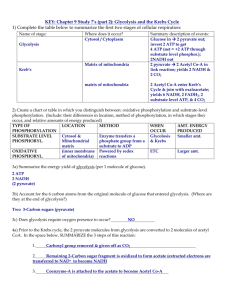
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Electron Transport System A review for the confused (like me!) Regina Lamendella AP Biology December 16, 2008 What is happening while you ingest donuts?? What is the purpose of glycolysis and cellular respiration? Doughnut = glucose = electrons = Electrons Overview Video • Write down the major “take home messages” from the video Glycolysis • 10-STEP reaction • (Rxns 1-5) Glucose is phosphorylated and cleaved to yield 2 molecules of triose glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. This process uses two ATPs. • (Rxns 6-10): The molecules of glyceraldehyde3-phosphate are converted to pyruvate, with concomitant generation of four ATPs and two NADH per glucose. • How many net ATPs? 1 ATP 1 ATP 2 NAD+ Glycolysis • Where are we within the cell? • What does ATP stand for? • What does NAD stand for? • How many carbons does pyruvate have? Adenosine Tri-Phosphate Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide H H Overall reaction for glycolysis Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 NADH + 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP Where do the pyruvate go next? Intermediary Reaction • Pyruvate (3-Carbon) Acetyl (2-Carbon)-CoA • 2 Pyruvate + 2 CoA + 2 NAD+ 2 Acetyl-CoA + 2 CO2 + 2 NADH Overall energy production so far… • Glycolysis: 2 ATP, 2 NADH • Intermediate reaction: 2 NADH Kreb’s Cycle • Roles of the Krebs cycle – Generate energy by oxidizing acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide and water – Supply biochemical intermediates for other pathways – Entry point of various degradative pathways for energy generation acetyl-CoA Squeezing the energy out of acetyl-CoA!!! Krebs Cycle • • • • • Where are we? What is ATP? What is NAD? What is FAD? How much energy is produced? FADFADH2 Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide H H Energy Production from Krebs Cycle Acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ + ADP + Pi → 3 NADH + ATP + 2 CO2 Wait we had two pyruvates to start… have to multiply above by 2!! 2 Acetyl-CoA + 6 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2Pi → 6 NADH + 2 ATP + 4 CO2 Energy Production So far… • Glycolysis: 2ATP, 2 NADH • Intermediate Step: 2 NADH • Kreb’s Cycle: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 • Where to next? Electron Transport System Video • Take notes and write down main points. Electron Transport System • • Electron transport chains are redox reactions that transfer electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor. The transfer of electrons is coupled to the translocation of protons across a membrane, producing a proton gradient. The proton gradient is used to produce useful work. NADH= 3 ATP FADH2= 2 ATP Total energy production after ETC • Glycolysis: 2ATP; 2 NADH= 6 ATP • Intermediate step: 2 NADH= 6 ATP • Krebs: 2 ATP; 6 NADH =18 ATP; 2 FADH2 = 4 ATP • 34 ATP from ETC • 2 ATP from Glycolysis • 2 ATP from Kreb’s directly • Total ATP production= 38 ATP