Mexico presentation
advertisement

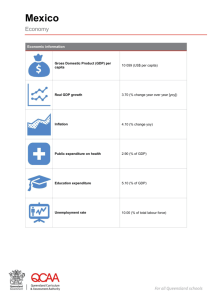
Mexico 1Lt S. Erin Elarton, USAF, MSC HCA 5312 Issues in International Health • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Agenda Areas of responsibility Peer nations Topography Climate Water and natural resources Natural disasters Comparisons Index of economic freedom Wellbeing index Transparency corruption index Human development index National demographics Population pyramid Aging Muslim population Poverty Immigrants and refugees Vaccinations • Health status • Morbidity & mortality statistics • HIV/AIDS • Tuberculosis • National health services • Structure of health care system • Healthcare providers • Costs/financing of health care • Pharmaceutical expenditures • Health care reform • External debt • Politics and elections • Telecommunications • Utilization of technology promoting health care • Size of military/armed forces History • Ancient Civilizations • 1521 Spain conquered Mexico – Brought diseases, caused pandemic • • • • • • 1821 Proclaimed Independence from Spain 1836 Texas Declared its Independence 1846-1848 Mexican-American War 1910 Mexican Revolution 1929 Mexican National Party (PNM) was created 2000 President Fox elected (PAN) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mexico Geography & Environment • Terrain – High, rugged mountains; low coastal plains; high plateaus; desert • Land use – arable land: 12% permanent crops: 1% permanent pastures: 39% forests and woodlands: 26% • Climate – Varies from tropical to desert • Natural resources – petroleum, silver, copper, gold, lead, zinc, natural gas, timber • Environmental issues – – – – Severe Air Pollution Raw sewage polluting rivers Deforestation Widespread erosion http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_Mexico http://www.countrywatch.com Water Resources • Population using improved drinking water sources (1999) – Total 86%, Rural 63% • Population using adequate sanitation – Total 73%, Rural 32% • Prolonged regional drought along US border – 1944 Treaty to share Rio Grande waters – US-Mexico Water Treaty Dispute http://www.prb.org/datafind/prjprbdata/wcprbdata.asp?DW=DR&SL http://www.texaswater.org/press/us_mexico_dispute.pdf Natural Disasters Disaster Earthquake Flood Volcano Wind storm Flood Wind storm Wind storm Earthquake Wind storm Extreme temp Date 19-Sep-85 1959 1949 27-Oct-59 Oct-99 1-Oct-76 28-Sep-55 28-Aug-73 12-Nov-61 Killed 8,776 2,000 1,000 960 636 600 500 500 436 Disaster Wind storm Flood Wind storm Wind storm Wind storm Wind storm Wind storm Flood Flood Date Affected 8-Oct-97 800,200 Oct-99 616,060 23-Sep-02 300,000 15-Jul-76 300,000 1-Oct-76 276,400 Aug-67 271,000 Dec-83 257,500 21-Sep-93 231,290 Aug-73 150,000 30-Apr-90 380 Earthquake 19-Sep-85 http://www.cred.be/emdat/profiles/natural/mexico.htm#top%20ten 130,204 Comparisons • • • • Human Development Index #55 Well-being Index #150 Transparency International Corruptions Perceptions Index #64 World Health Systems Rankings – – • Overall health system attainment #51 Overall health level #61 Migration #132 in world -2.84 – 8% of U.S. population is from Mexican origin http://www.who.int/whr2001/2001/archives/2000/en/statistics.htm http://www.iucn.org/info_and_news/press/wonrank.doc http://www.metropolis2003.at/en/WS9.1Sanchez.pdf http://www.transparency.org/pressreleases_archive/2003/dnld/cpi2003.pressrelease.en.doc http://www.undp.org/hdr2003/pdf/presskit/HDR03_PKE_HDI.pdf http://www.photius.com/wfb1999/rankings/migration_rate_0.html U.S. Department of State Consular Information • • • • • • Crime Drug penalties and prescription medications Prison conditions Kidnapping Public Transportation Insufficient safety standards http://www.travel.state.gov/mexico.html Pan American Health Organization • • • • • • • • Vector-borne diseases Vaccine-preventable diseases Intestinal infectious diseases Communicable chronic diseases Acute respiratory diseases Human Rabies STDs AIDS http://www.ops-oms.org/English/DD/AIS/cp_484.htm Politics • • • • • Representative and democratic republic 31 states and Federal District (Mexico City) 2,444 municipalities 2000 elections – new political party Bicameral National Congress (Congreso de la Union) – Senate and Chamber of Deputies – Women as percent of parliament 16% (US 14%) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mexico#Politics http://www.prb.org/datafind/prjprbdata/wcprbdata.asp?DW=DR&SL The Pew Research Center • Mexico’s view of U.S. slips – From 1999 to 2002, slipped from 68% to 64% • Personal concerns – Economic problems as top personal concern (65%) – Crime (17%) – Personal satisfaction rated similar to Western Europe • Satisfaction with State of the Country – 79% dissatisfied • Top 4 national problems – Crime, AIDS & disease, corrupt political leaders, terrorism http://people-press.org/reports/pdf/165.pdf Economy • World’s ninth largest economy • Index of Economic Freedom (2003) – Ranked #63 • Labor Force – 39.8M (2000) • Exports $1.58B (2002) – US 82.7%, Canada 5.4%, Japan 1.1% (2002) – Commodities: manufactured goods, oil and oil products, silver, fruits, vegetables, coffee, cotton http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mx.html http://cf.heritage.org/index2004test/country2.cfm?id=Mexico National Demographics Population Total Population Growth Rate (annual %) 0 – 14 Years (% of total) 15 – 64 Years (% of total) 65+ Years (% of total) Total Fertility Rate Adolescent Fertility Rate (births per 1,000 women age 15-19) Female Life Expectancy at Birth Male Life Expectancy at Birth Ethnicity: Mestizo 60.0% Mexico 104,907,991 1.43% 32.3% 63.1% 4.6% 2.53 64 75.49 69.26 United States 285,318,000 1.1% 20.9 66.7 12.4 2.07 48 80.05 74.37 Religions: Roman Catholic 89.0% Indigenous 30.0% Protestant 6.0% European descent 9.0% Other 5.0% Other 1.0% Muslim 0.26% http://devdata.worldbank.org/hnpstats/HnpAtaGlance.asp?sCtry=MEX,Mexico http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mx.html http://www.islamicpopulation.com/america_general.html Population Pyramid http://www.census.gov/cgi-bin/ipc/idbpyrs.pl?cty=MX&out=s&ymax=250 Common Diseases According to AFMIC & CDC • Diseases carried by insects – – – – – – Dengue Filariasis Leishmaniasis – cutaneous Malaria Onchocerciasis American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease) – West Nile Virus • Foodborne & waterborne diseases – Bacterial diarrhea – Hepatitis A – Typhoid / paratyphoid fever • Water-contact diseases – Leptospirosis • Direct or indirect personal contact – Hemorrhagic Conjunctivitis https://mic.afmic.detrick.army.mil/osis/search/sitesearch/filetest.php?query=mexico http://www.cdc.gov/travel/camerica.htm Socioeconomic Indicators SOCIOECONOMIC INDICATORS GNI PPP Per Capita Adult Female Literacy Rate (% age 15+) Adult Male Literacy Rate (% age 15+) GDP GDP real growth rate GDP per capita External Debt Inflation Population below poverty line Unemployment Rate YEAR MEXICO YEAR U.S 2001 2003 $8,240 90.50% 2001 1979 $34,280 97% 2003 94% 1979 97% 2002 2002 2002 2001 2002 2001 2001 $924B 0.70% $8,920 $191B 6.40% 40% 3% urban 2002 2002 2002 2001 2002 2001 2002 $10.5T 2.40% $36,300 $862B 1.60% 12.70% 6% http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mx.html http://www.nationmaster.com/country/mx http://www.prb.org/datafind/prjprbdata/wcprbdata.asp?DW=DR&SL Morbidity & Mortality HEALTH STATUS INDICATORS YEAR MEXICO YEAR U.S. Infant Mortality Rate (deaths per 1,000 live births) 2003 25 2003 6.9 Mortality Rate – under 5 per 1,000 live births 2001 29 2001 8 Malnutrition prevalence (% children under 5) 2001 7.5 1995 1.4 Adult Male Mortality Rate Adult Female Mortality Rate 2000 180 2000 141 2000 101 2000 83 Maternal Deaths per 100,000 live births 2002 65 2002 12 Low-birth weight Babies 1995 9.2 2001 7 TB incidence 2000 38.1 2001 5.4 People Living with 2001 150,000 2001 900,000 HIV/AIDS http://devdata.worldbank.org/hnpstats/HnpAtaGlance.asp?sCtry=MEX,Mexico http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mx.html http://www.prb.org/datafind/prjprbdata/wcprbdata.asp?DW=DR&SL Vaccinations 2002 Immunization Profilles Mexico U.S. BCG DTP1 DTP3 HepB3 99 92 91 91 97 94 88 Hib3 MCV Pol3 91 96 92 93 91 90 http://www.who.int/vaccines/globalsummary/immunization/CountryProfileResult.cfm Mexico’s Health System • Public Health Care – Secretariat of Health and Assistance – Institute of Social Security and Government Workers – Mexican Social Security Institute • Less than 10% of the Mexican population has private coverage https://mic.afmic.detrick.army.mil/osis/search/sitesearch/filetest.php?query=mexico http://open.imshealth.com/webshop2/IMSinclude/i_article_20040105.asp Healthcare Costs & Finance HEALTH CARE FINANCE YEAR MEXICO YEAR U.S. Total Health Expenditures (% of GDP) 2001 5 2001 13.9 Health Care Expenditures per capita ($US) Public health expenditures as % of total expenditures Private health expenditures as % of total expenditures Social Security Expenditures as % of health expenditures Physicians per 1,000 people Hospital Beds per 1,000 population 2000 $311 2000 $4,499 2001 44.3 2001 44.4 2001 55.7 2001 55.6 2001 66.5 2001 32.9 2000 1.8 2000 2.8 200 1.1 2000 4 http://www.who.int/country/mex/en/ http://devdata.worldbank.org/hnpstats/HnpAtaGlance.asp?sCtry=MEX,Mexico Health Care Aid • OECD – Aid from U.S. – 1990-92 US$60M – 1993-95 US$103.3M – 1996-98 US$241.7M • Inter-American Development Bank – Summary of IDB Financing ($US) • • • • 2002 Lending $1B 1961-2002 Lending $16B 2002 Disbursements $993B 1961-2002 Disbursements $13.2B http://www.iadb.org/exr/country/eng/mexico/index.cfm http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/22/31/25503059.pdf Telecommunications • Telephones: main lines in use: 12.32M (2000) • Mobile cellular: 2.3M (1998) • Radio broadcast stations: 1465 (2000) • Television broadcast stations: 236 (1997) • Internet Service Providers (ISPs): 51 (2000) • Internet users: 3.5M (2002) http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/mx.html Military Forces Armed Forces Personnel Strength World Ranking Army 130,000 #18 Air Force 8,000 #33 Navy 37,000 #15 Military Spending Military Expenditures per % GDP (FY99, Mexico & US) Military Expenditures Dollar Figure (FY99, Mexico & US) Mexico 1% United States 3.2% $4B $276.7 B http://www.nationmaster.com/country/mx/Military Military Health Care • Secretariats of National Defense and Navy operate separate health care services – Mexico City • The Central Military Hospital • Naval Medical Center – Physicians are well trained and well regarded by civilian authorities – Training of nursing and paramedical personnel is substandard compared to the U.S. • Blood supply is safe https://mic.afmic.detrick.army.mil/osis/search/sitesearch/filetest.php?query=mexico Implications for Military Planners • Viral or bacterial diarrhea could occur among personnel consuming local food, water, or ice • Water Resources • Disease Prevalence • Field conditions (including lack of hand washing and primitive sanitation) may facilitate person-to-person spread of epidemics