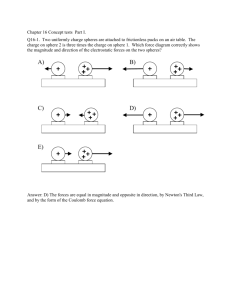
18.4 Charging by Contact and by Induction
advertisement

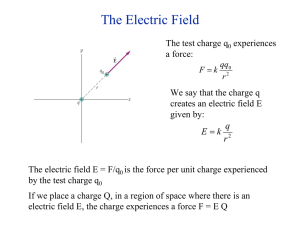
18.7 Electric Field Lines An isolated point, positive charge: 18.7 Electric Field Lines 18.7 Electric Field Lines 18.7 Electric Field Lines Electric field lines are always directed away from positive charges. Electric field of a negative point charge Electric field of a negative point charge The electric field lines are directed radially inward toward a negative point charge. Electric field between two parallel plates Electric field between two parallel plates Electric Dipole An electric dipole consists of two separated point charges that have the same magnitude but opposite signs. Electric Dipole An electric dipole consists of two separated point charges that have the same magnitude but opposite signs. Electric Dipole An electric dipole consists of two separated point charges that have the same magnitude but opposite signs. The dipole moment, p is the product of the magnitude of one of the charges and the distance between the charges. p=qL Electric Dipole An electric dipole consists of two separated point charges that have the same magnitude but opposite signs. The dipole moment, p is the product of the magnitude of one of the charges and the distance between the charges. p=qL Many molecules, such as H2O and HCl, have dipole moments. Electric field lines of a dipole Electric field lines of a dipole Electric field lines always begin on a positive charge and end on a negative charge. The number of lines leaving a positive charge or entering a negative charge is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. Electric field of two like point charges 18.8. The Electric Field Inside a Conductor: Shielding 18.8. The Electric Field Inside a Conductor: Shielding At electrostatic equilibrium: 1. Any excess charge resides on the surface. 2. The electric field is zero inside the conductor. Conductor in Electric Field Conductor in Electric Field Under electrostatic equilibrium: 1. The conductor shields the electric field. 2. The electric field just outside the surface a conductor is perpendicular to the surface. Conductor in Electric Field “Stray” electric fields are produced by various electrical appliances (e.g., hair driers, blenders, and vacuum cleaners), and these fields can interfere with the operation of sensitive electronic circuits, such as those in stereo amplifiers, televisions, and computers. To eliminate such interference, circuits are often enclosed within metal boxes that provide shielding from external fields. Conceptual Example 13 A charge +q is suspended at the center of a hollow, electrically neutral, spherical conductor, as Figure 18.31 illustrates. Show that this charge induces (a) a charge of –q on the interior surface and (b) a charge of +q on the exterior surface of the conductor. Conceptual Example 13 A charge +q is suspended at the center of a hollow, electrically neutral, spherical conductor, as Figure 18.31 illustrates. Show that this charge induces (a) a charge of –q on the interior surface and (b) a charge of +q on the exterior surface of the conductor. Copying Machine Laser Printer Inkjet Printer